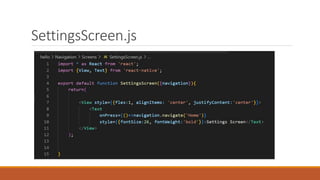
This document provides an overview and examples of core components, styling, and navigation in React Native. It discusses core components like <View>, <Text>, <Image>, <ScrollView>, and <TextInput>. It also covers styling components using StyleSheet and different navigation patterns like tab, stack, and drawer navigation. Practical examples are provided to demonstrate setting up a basic tab navigator and integrating search functionality into an app.