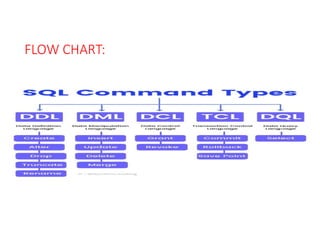
Structured Query Language (SQL) is used to define, manipulate, and retrieve data from a relational database. The main SQL commands are: Data Definition Language (DDL) to define schemas; Data Manipulation Language (DML) to add, modify and delete data; Data Control Language (DCL) to grant and revoke user privileges; Transaction Control Language (TCL) to commit and rollback transactions; and Data Query Language (DQL) to fetch data with SELECT statements. Common DDL commands are CREATE, ALTER, and DROP to create, modify, and remove tables. DML includes INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE to add, modify and remove rows.