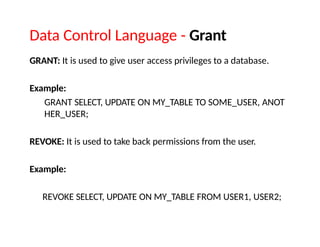
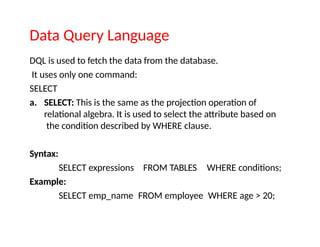
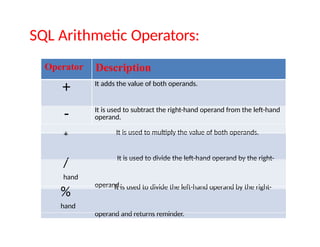
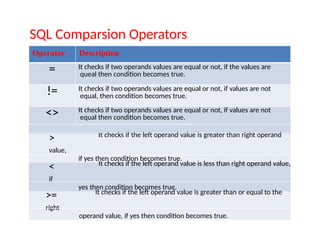
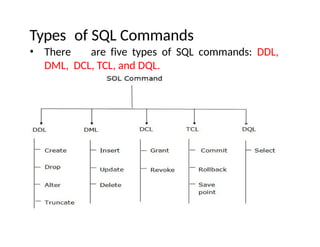
SQL stands for Structured Query Language, used for managing and manipulating data within relational database systems. It includes various commands categorized into DDL, DML, DCL, TCL, and DQL for tasks such as defining structures, updating records, and controlling access. Additionally, SQL provides operators for arithmetic, comparison, and logical operations to facilitate complex queries.



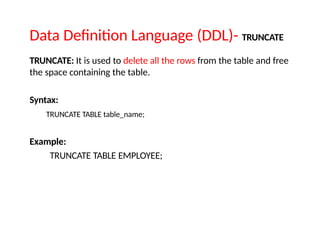
![Data Definition Language (DDL)- CREATE
CREATE It is used to create a new table in the database.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE TABLE_NAME (COLUMN_NAME DATATYPES[,....]);
Example:
CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE(Name VARCHAR2(20), Email VARCHA
R2(100), DOB DATE);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-241205141816-e470c357/85/SQLBasic-to-advance-for-the-beggineers-pptx-8-320.jpg)


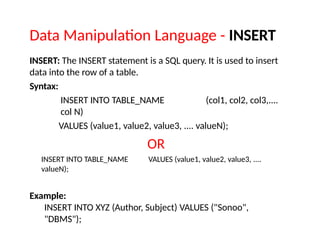
![Data Manipulation Language - UPDATE
Update: This command is used to update or modify the value of a
column in the table.
Syntax:
UPDATE table_name SET [column_name1= value1,...column_n
ameN = valueN] [WHERE CONDITION]
Example:
UPDATE students
SET User_Name = 'Sonoo'
WHERE Student_Id = '3'](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sql-241205141816-e470c357/85/SQLBasic-to-advance-for-the-beggineers-pptx-14-320.jpg)