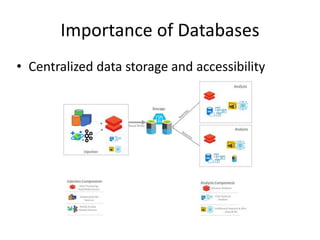
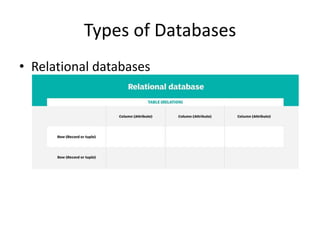
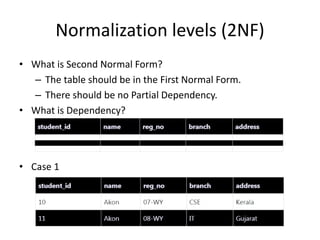
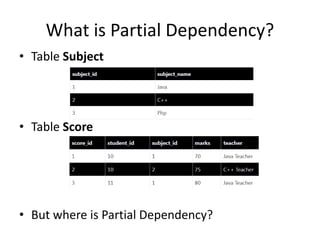
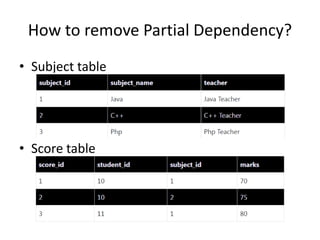
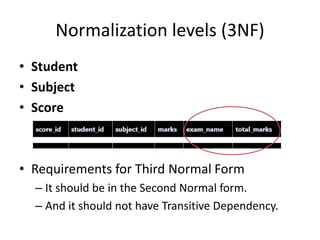
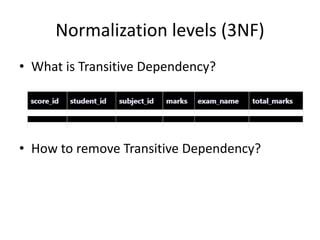
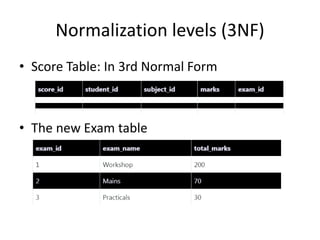
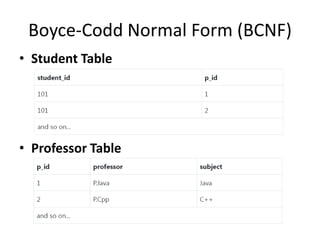
This document provides an overview and agenda for a presentation on database management. It covers topics such as the definition and importance of databases, different types of databases including relational and NoSQL, components of a database system, database design principles like normalization, data querying and manipulation using SQL, database security, administration and maintenance. The document also discusses normalization forms including 1NF, 2NF, 3NF and BCNF and provides examples.