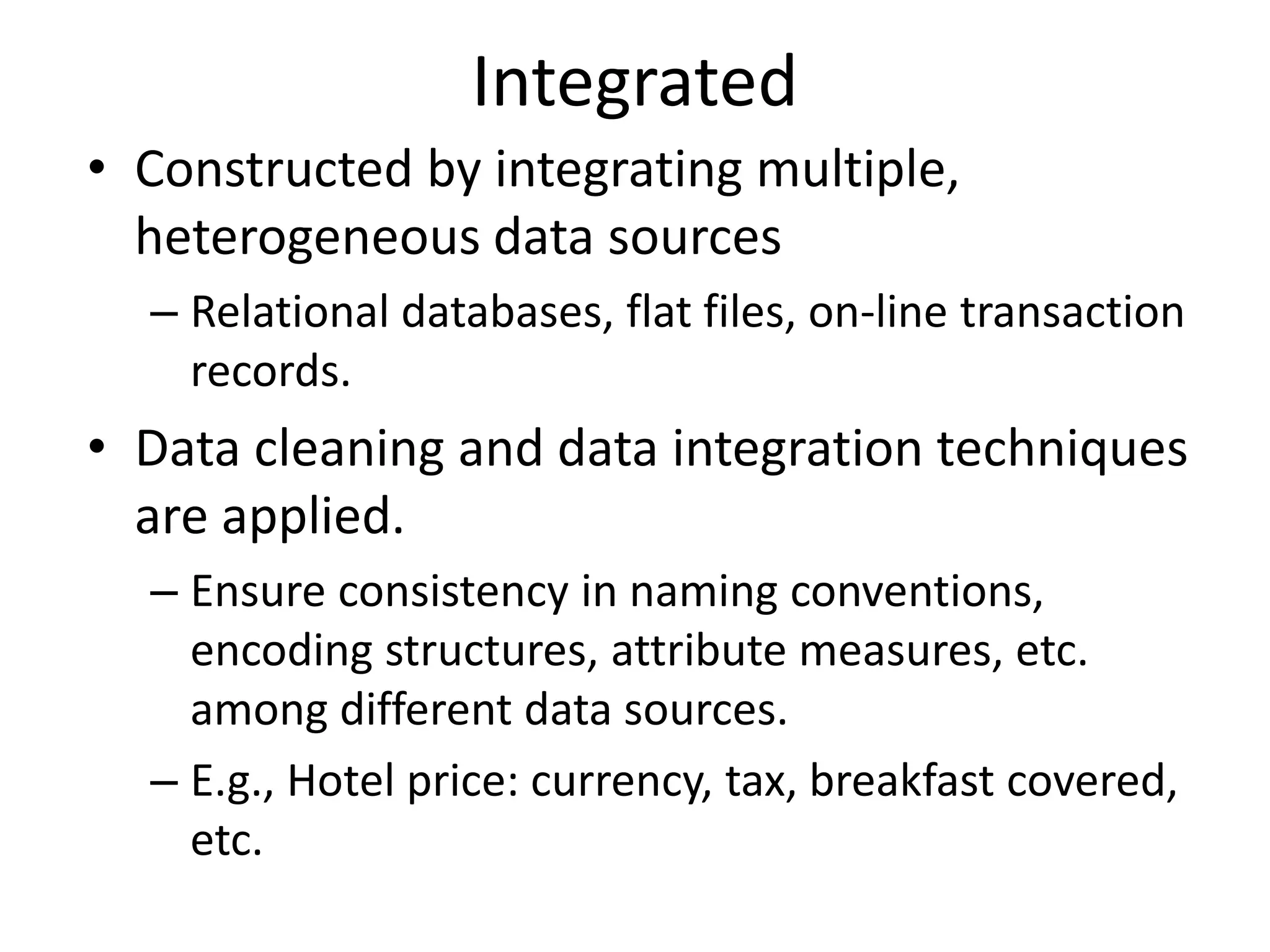
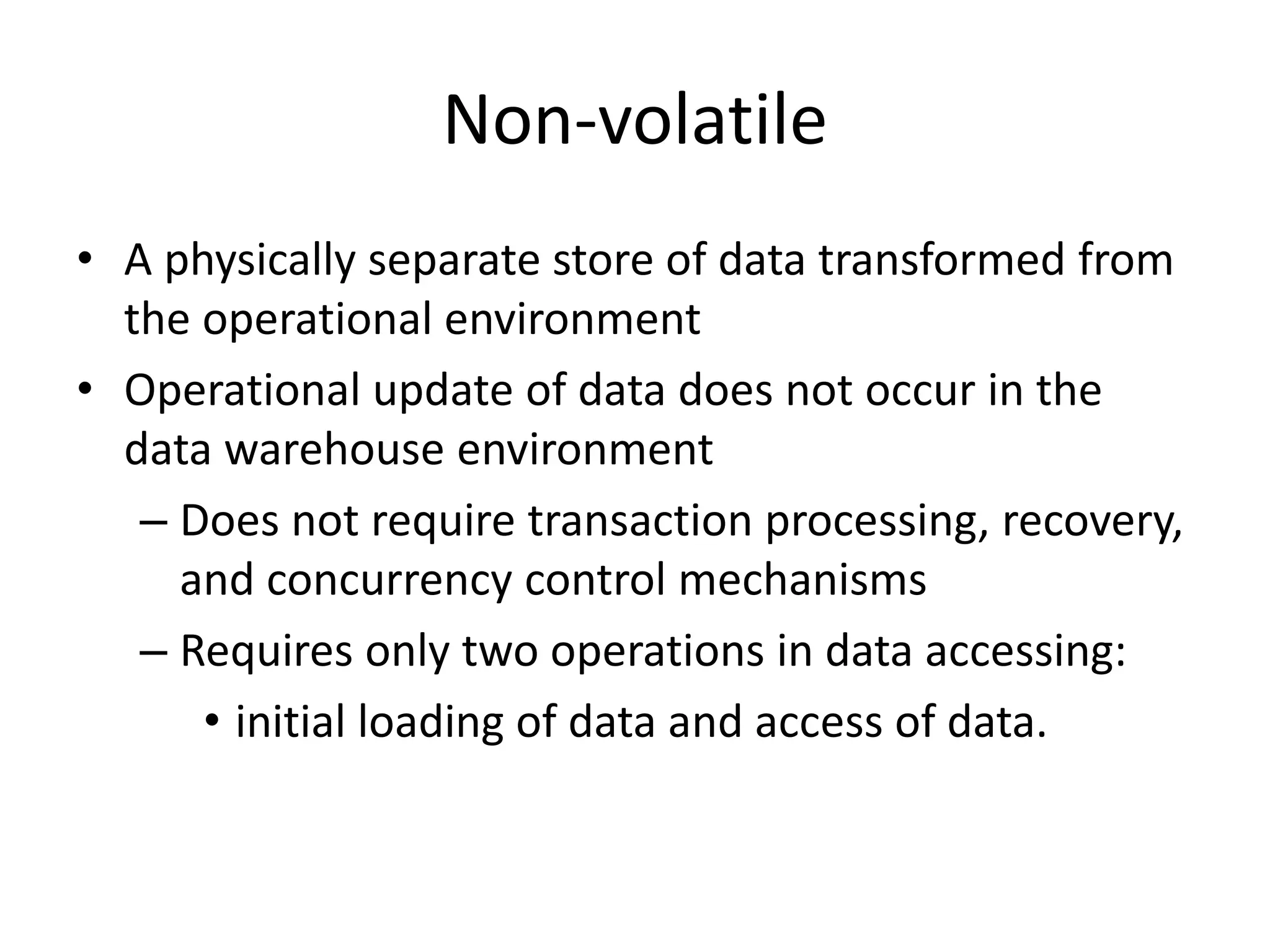
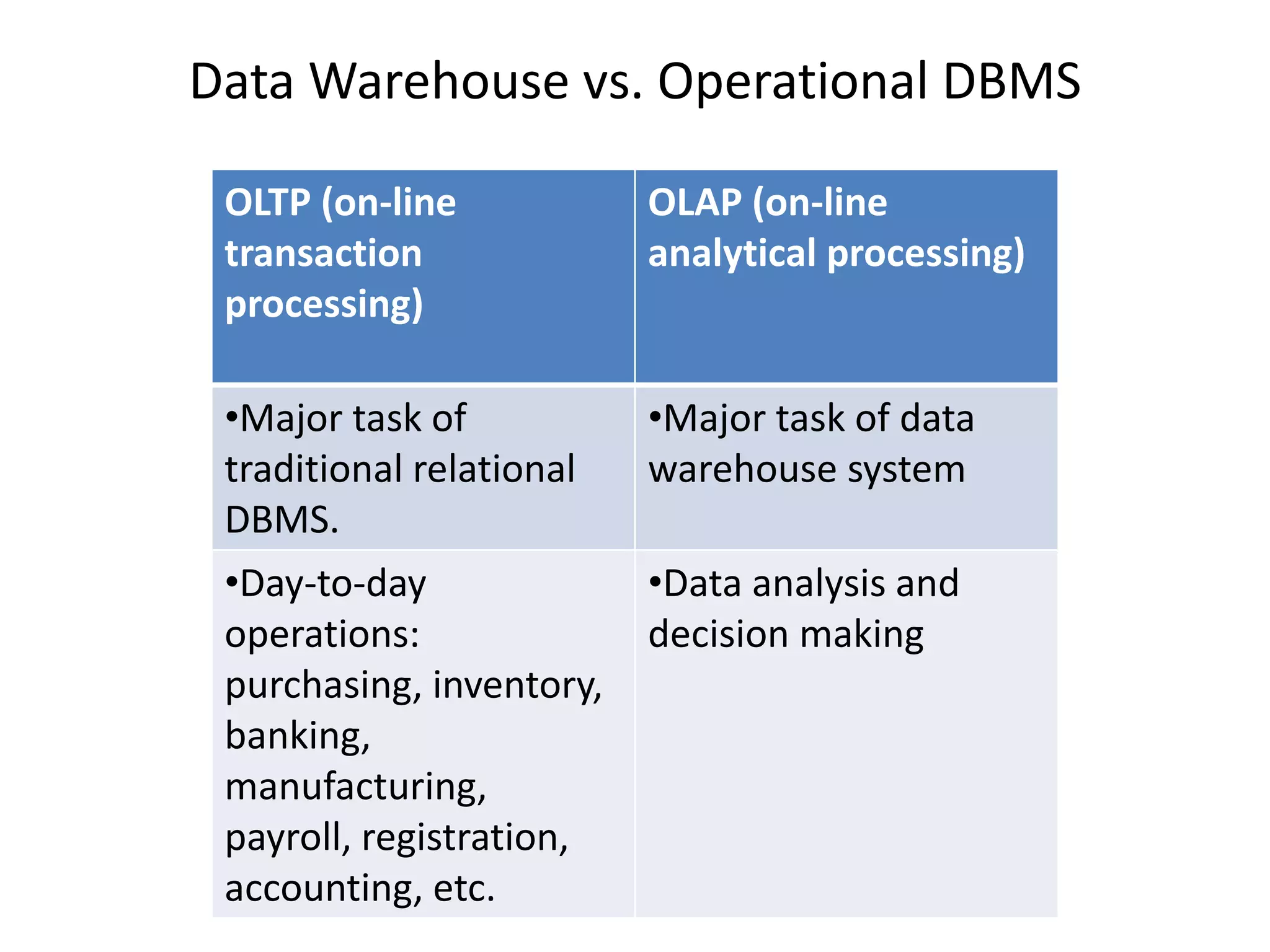
This document provides an introduction to data warehouses. It defines a data warehouse as a subject-oriented, integrated, time-variant and non-volatile collection of data to support management decision making. The key features of a data warehouse are that it is subject-oriented, integrated, time variant and non-volatile. It also distinguishes between operational databases used for transaction processing and data warehouses used for analytical processing and decision making.