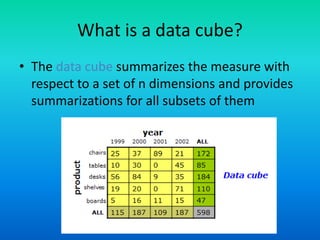
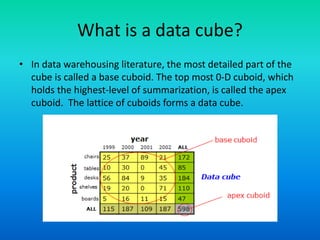
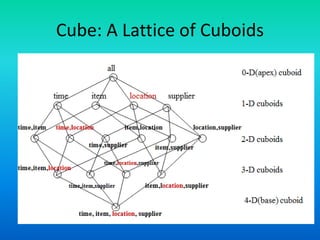
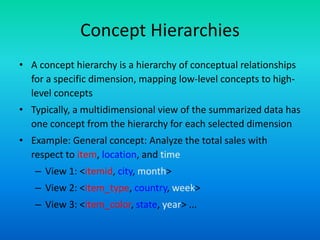
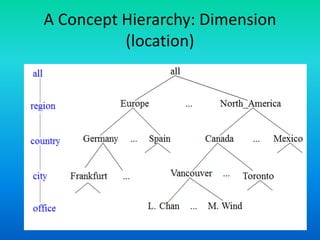
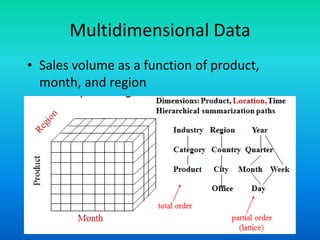
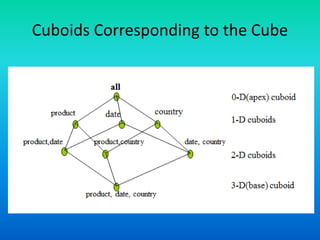
The document discusses data warehouses utilizing a multidimensional data model comprising data cubes that represent facts and dimensions, such as sales data analyzed from various perspectives. It explains the concept of data cubes, the different types of aggregate functions (distributive, algebraic, holistic), and introduces concept hierarchies that define relationships between low-level and high-level concepts for multidimensional analysis. The example provided illustrates how sales can be analyzed based on product, time, and location across different views.