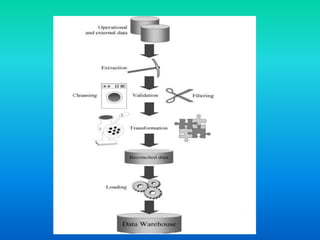
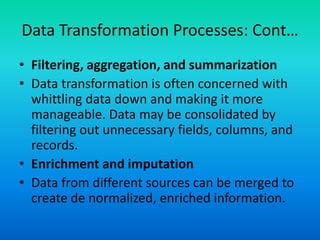
Data transformation involves changing the format, structure, or values of data to make it better organized and easier for both humans and computers to use. It includes constructive, destructive, aesthetic, and structural changes. The main transformation processes are conversion and normalization to make data uniform, matching to associate equivalent fields, and selection to reduce fields and records. Specific processes include extraction and parsing to shape data format and structure, translation and mapping, filtering and aggregation, enrichment and imputation, indexing and ordering, anonymization and encryption, and modeling, typecasting, formatting and renaming. Data transformation facilitates compatibility between applications and systems and prepares data to populate a reconciled data layer.