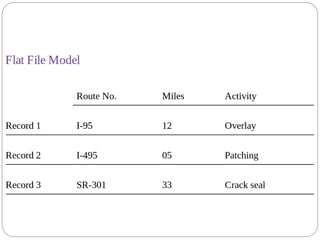
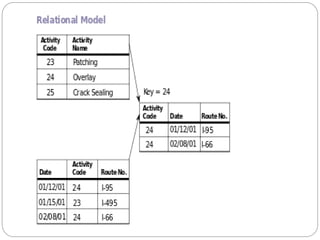
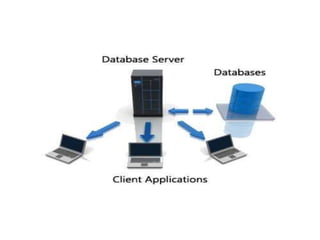
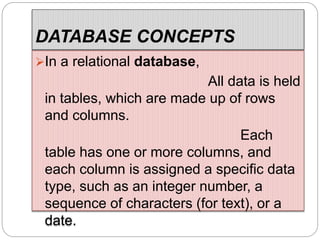
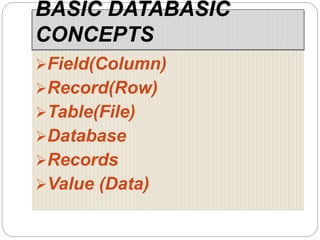
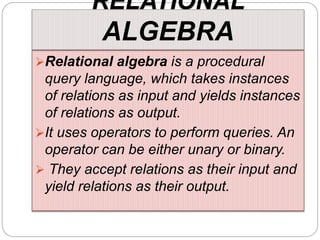
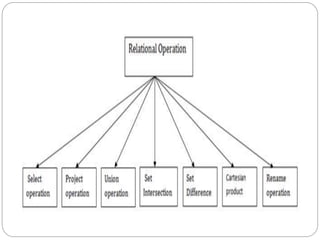
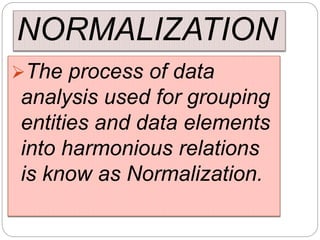
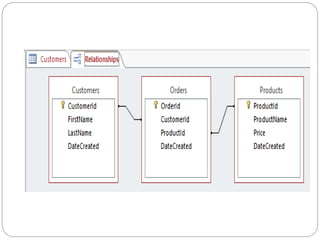
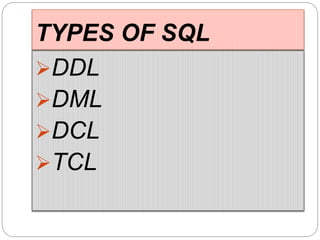
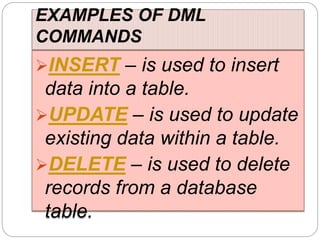
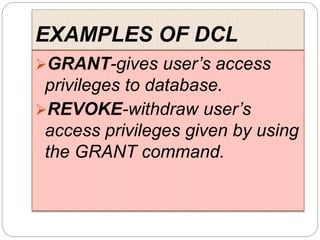
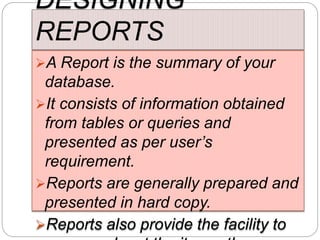
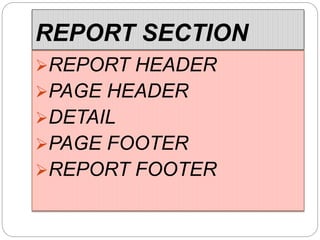
This document provides an overview of databases. It defines a database as an organized collection of data and discusses the main types: flat file, relational, and RDBMS. Key concepts covered include fields, records, tables, relationships, normalization, relational algebra, and SQL. SQL commands like SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE are presented. The document also discusses database servers, concepts like primary and foreign keys, and designing reports with headers, footers and details.