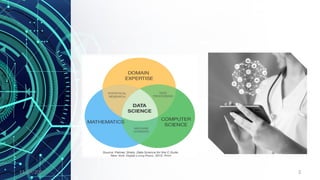
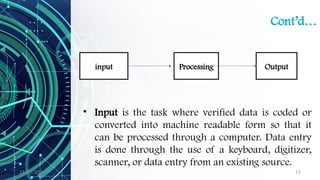
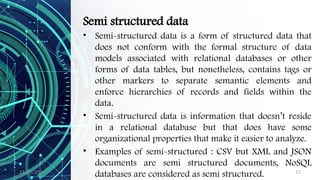
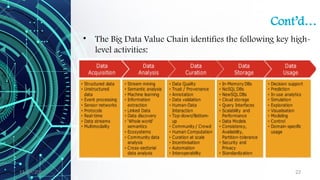
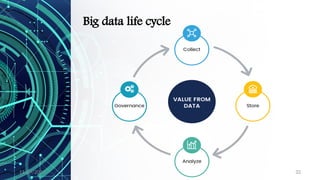
The document provides an overview of data science, including its definition, the distinction between data and information, and the data processing life cycle. It outlines the roles and skills of data scientists, the various types of data (structured, semi-structured, and unstructured), and introduces concepts related to big data and the Hadoop ecosystem. Additionally, it highlights the importance of understanding data types and metadata in the context of data analytics.