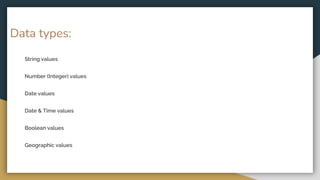
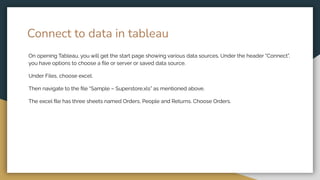
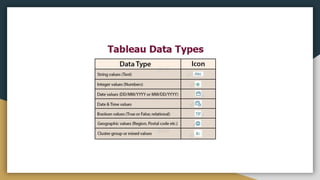
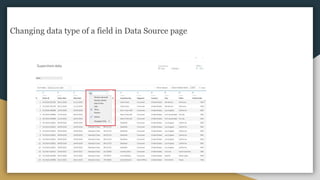
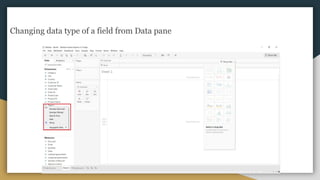
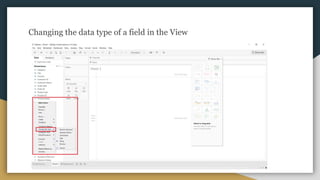
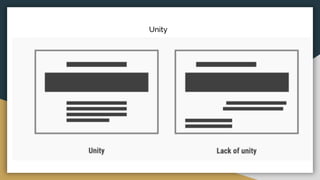
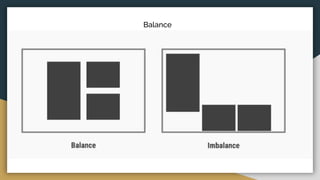
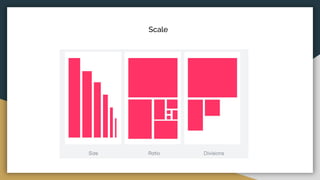
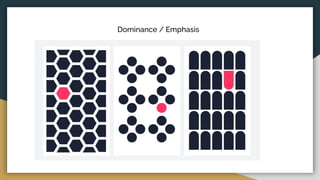
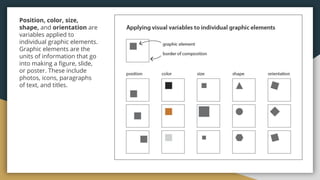
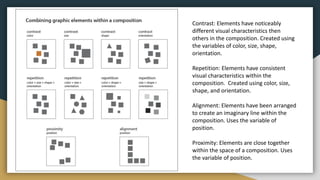
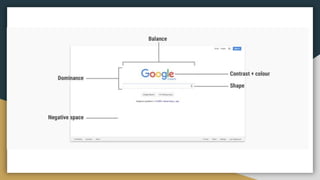
The document discusses various data types including string values, number values, date values, boolean values, and geographic values. It then provides information on connecting to data in Tableau and selecting the "Orders" sheet from the "Sample - Superstore.xls" excel file. The next section provides an objective and instructions for an assignment involving sales data analysis and deriving meaningful insights. Basic visual design principles such as hierarchy, balance, contrast, scale, and dominance/emphasis are then defined in 2-3 sentences each.