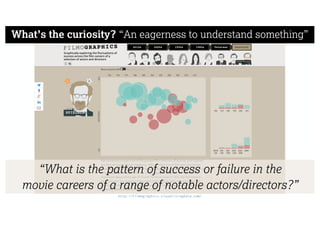
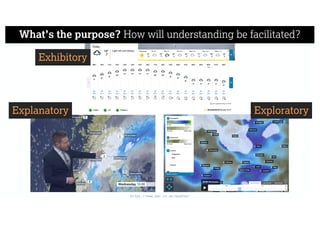
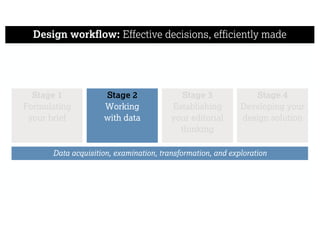
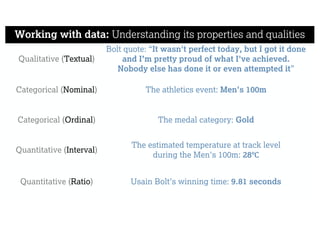
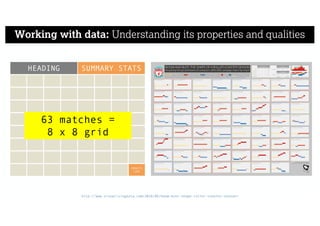
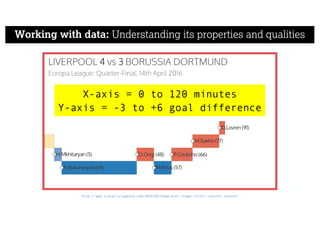
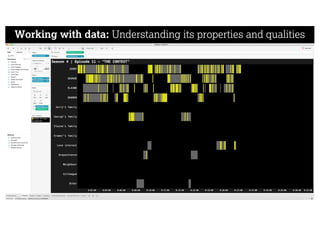
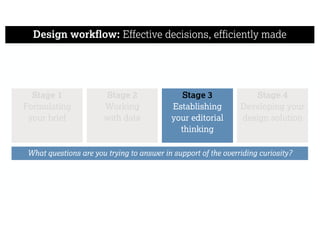
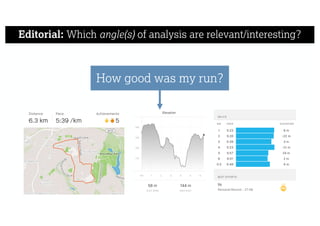
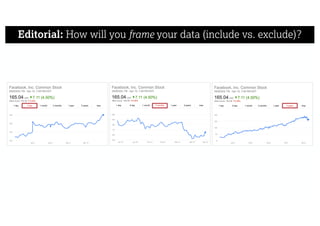
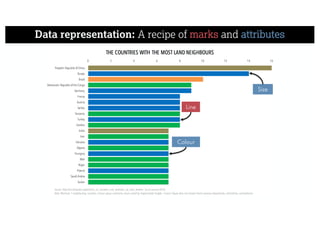
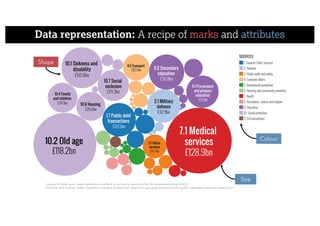
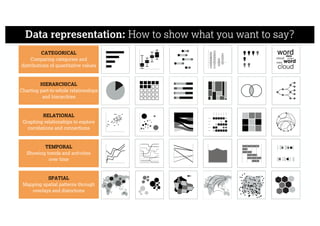
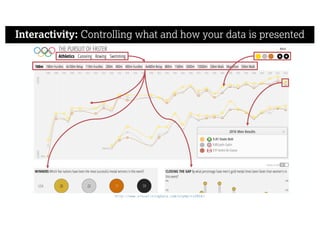
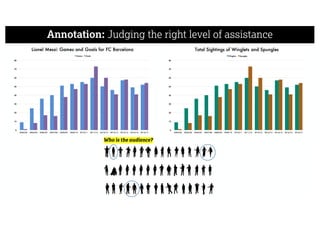
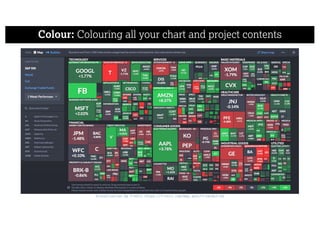
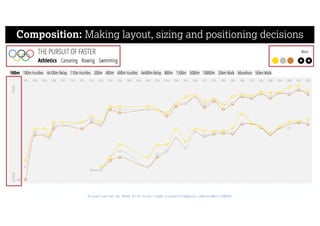
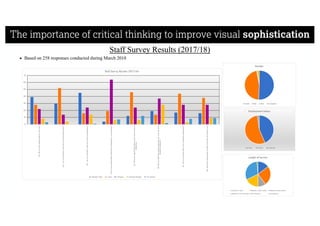
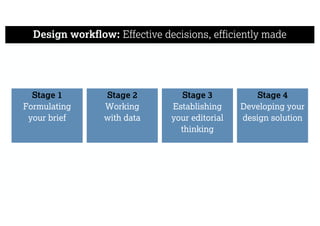
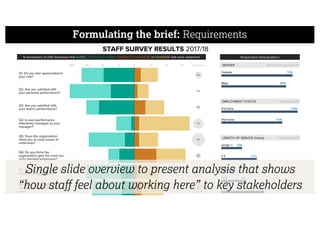
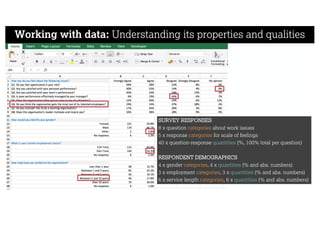
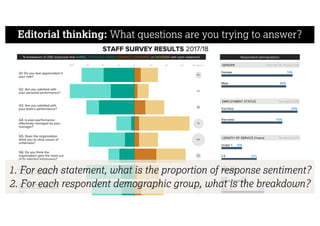
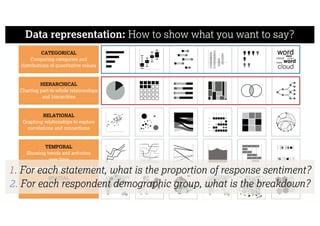
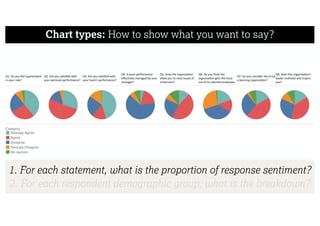
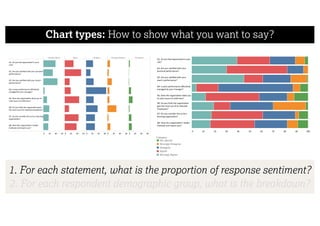
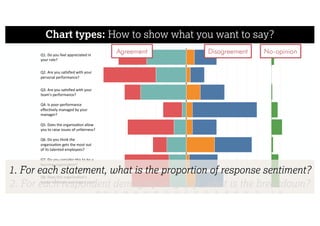
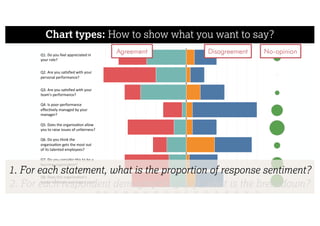
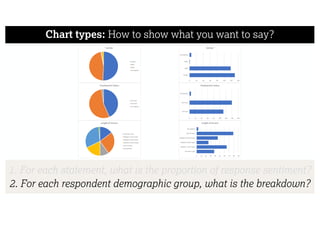
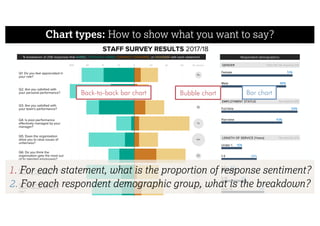
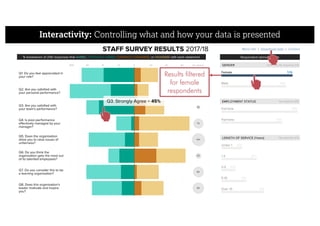
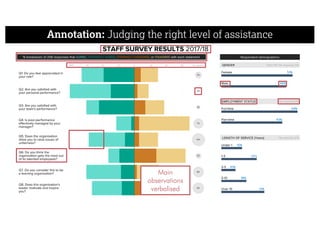
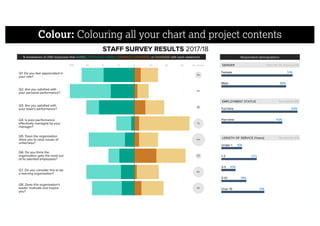
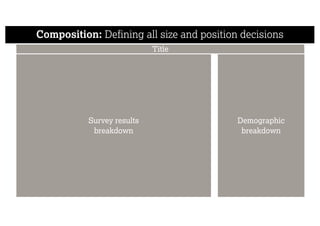
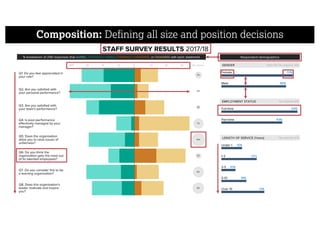
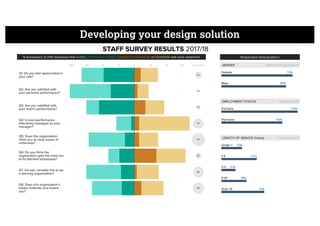
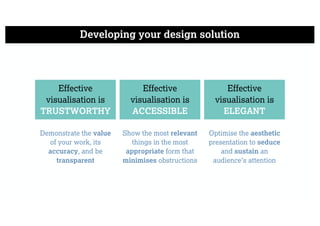
This document describes a framework for effective data visualization design. It discusses establishing an editorial perspective by determining which questions the visualization should answer. It also covers working with data, such as understanding its properties and qualities. The document outlines various design considerations like data representation, interactivity, annotation, color, and composition. An example demonstrates applying the framework to develop a single slide summarizing staff sentiment survey results. Key stages of the framework include formulating the brief, working with data, editorial thinking, and developing the design solution.