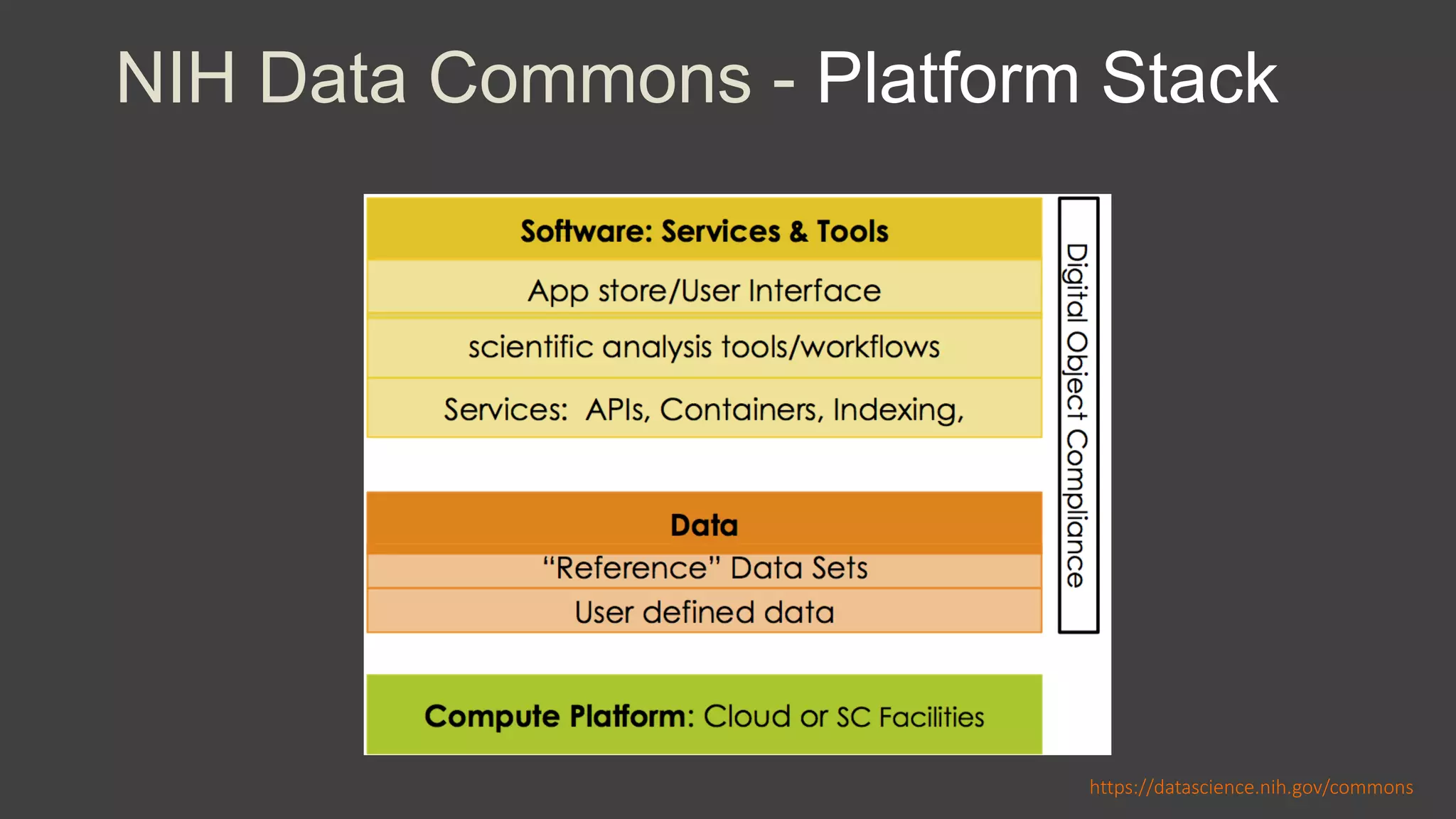
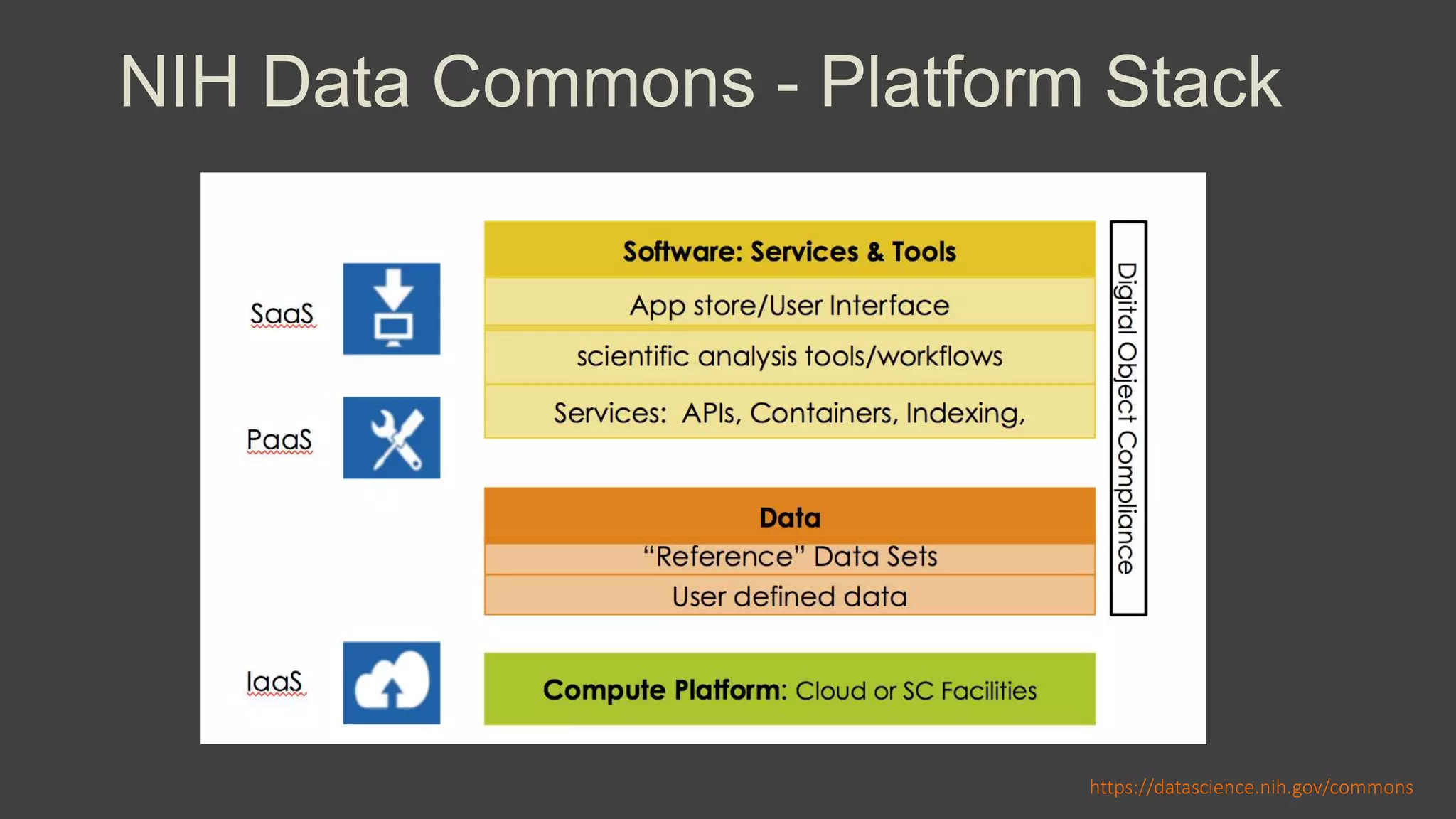
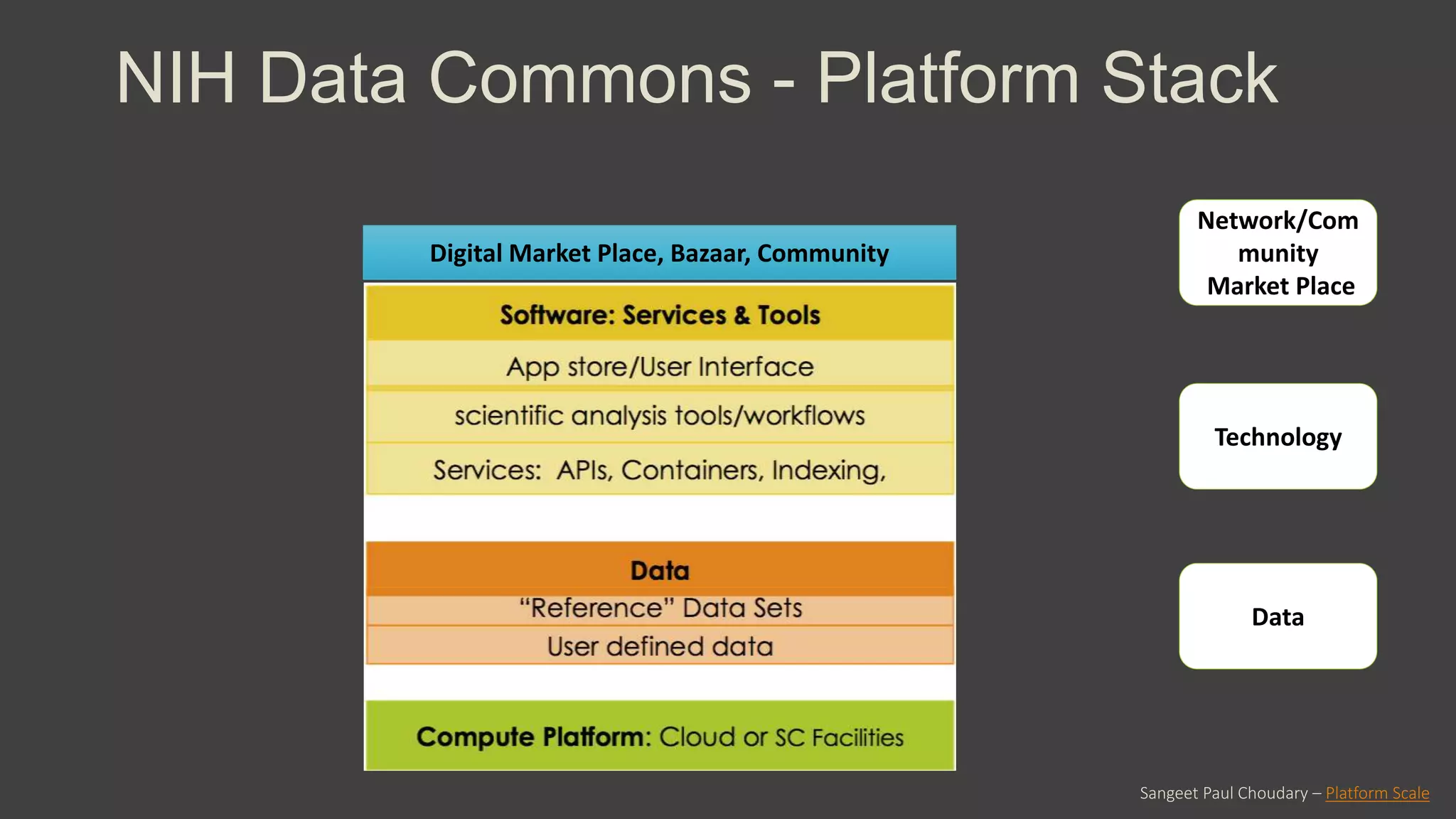
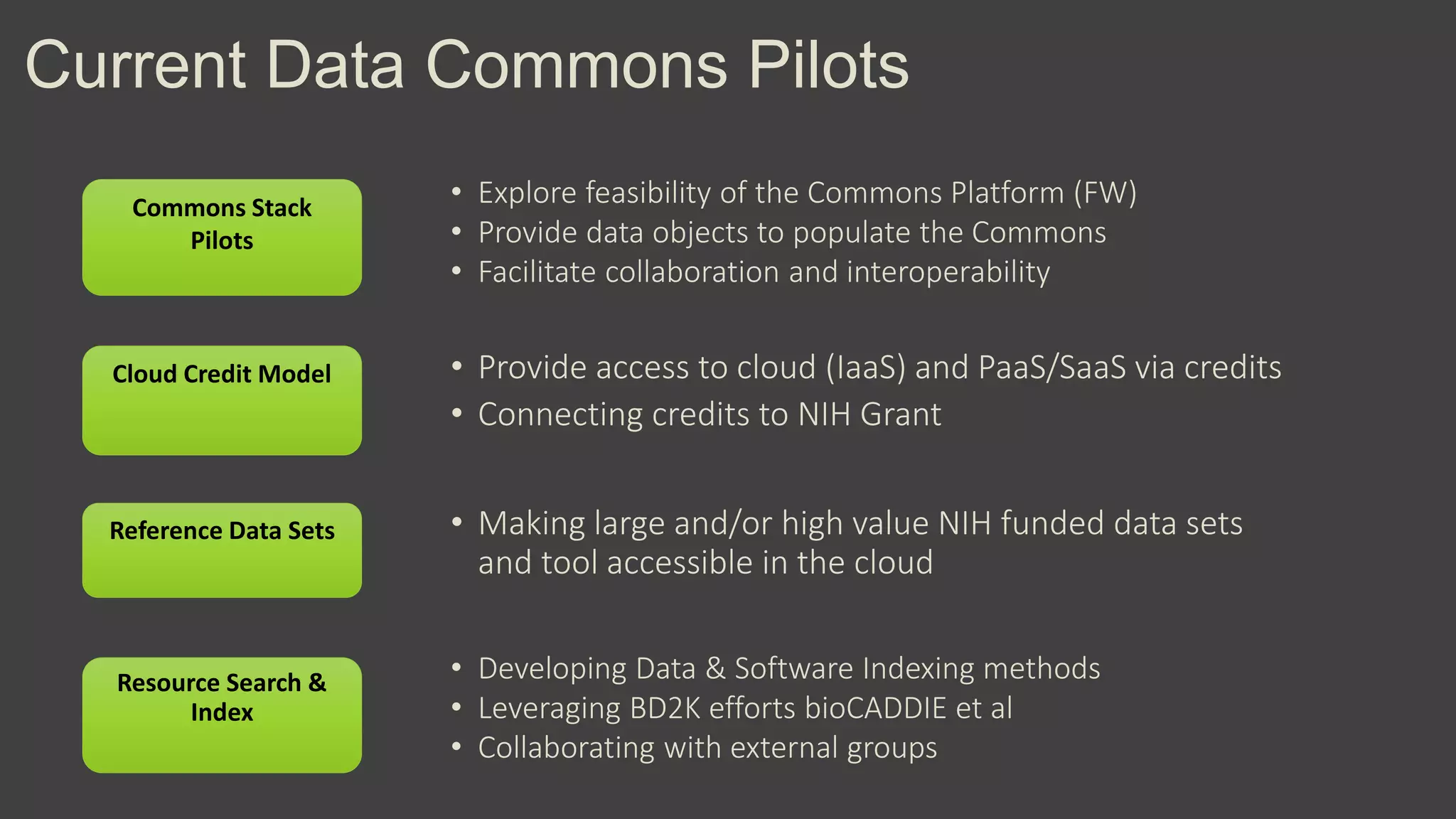
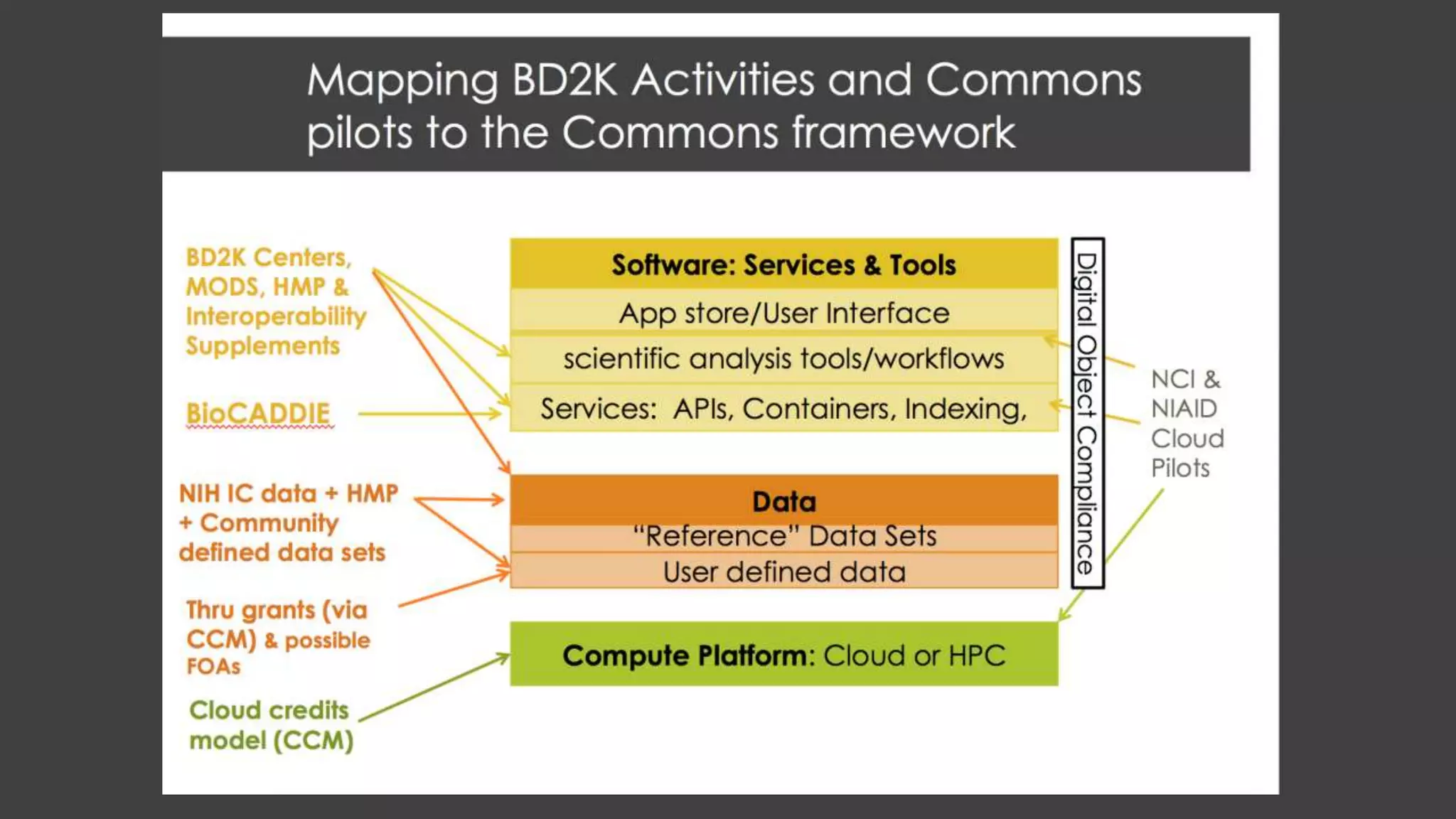
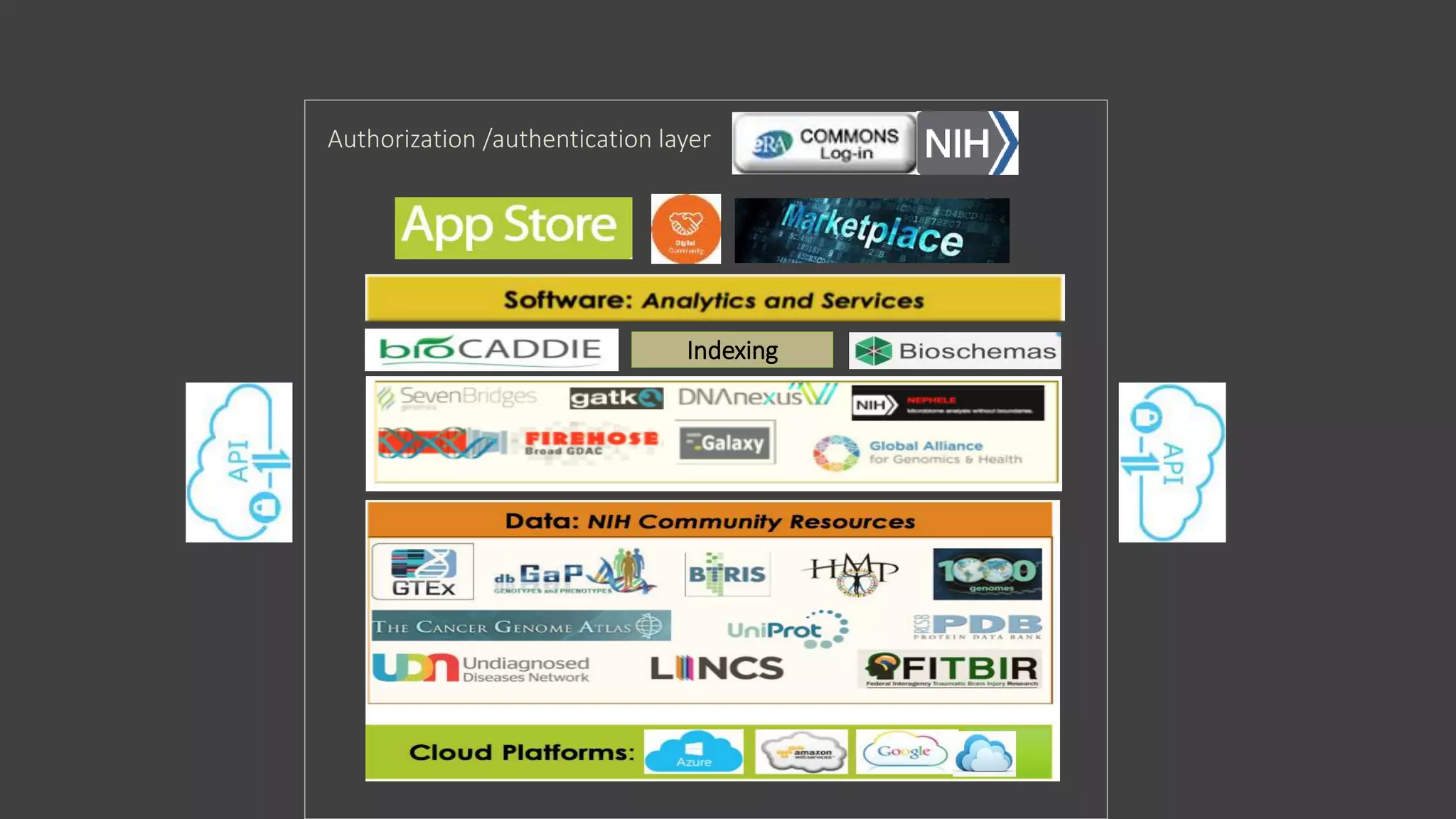
The NIH Data Commons is a platform designed to create a digital ecosystem for sharing and utilizing FAIR (Findable, Accessible, Interoperable, Reproducible) data. It allows seamless transactions of digital assets like research data and tools while fostering collaboration among researchers. The initiative includes pilot programs to enhance data accessibility and interoperability through cloud technology and innovative data management strategies.