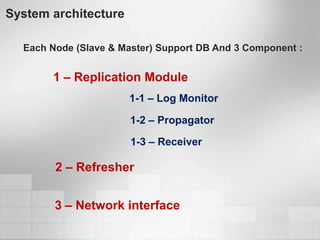
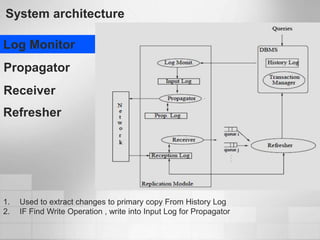
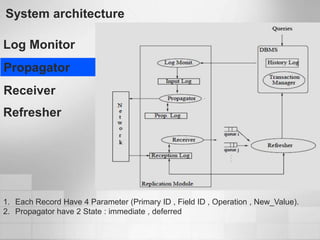
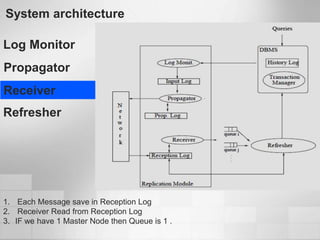
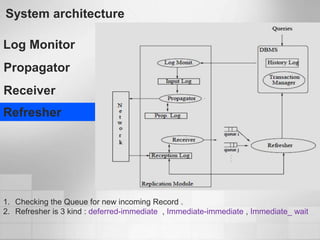
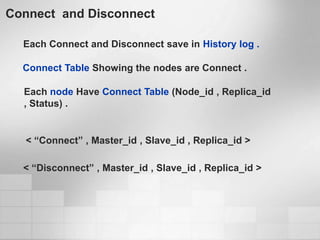
1. Software metrics are used to quantify attributes of software objects by mapping symbols to those objects. There are different types of metrics that can be calculated.
2. Important metrics include McCabe's cyclomatic complexity metric, which measures the number of linearly independent paths through a program, and Halstead's software science metrics which measure properties like program volume and difficulty.
3. Product metrics measure attributes of the software independent of how it was produced, like lines of code. Process metrics measure attributes relating to the development process.