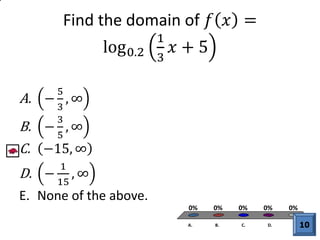
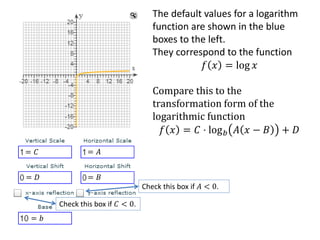
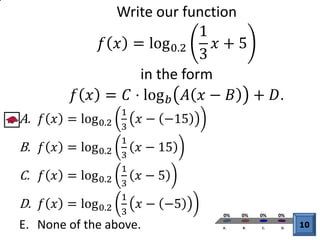
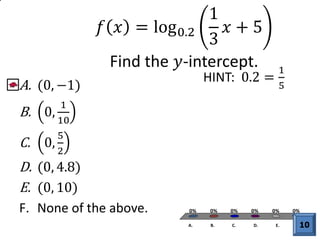
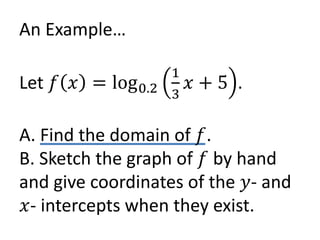
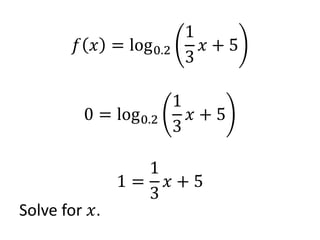The document discusses logarithmic functions, particularly focusing on their inverse relationship with exponential functions. It includes examples of finding the domain of a logarithmic function, sketching its graph, and identifying intercepts. Various methods and questions are presented related to transforming and analyzing logarithmic functions.


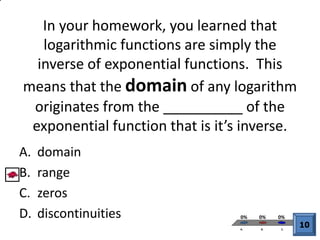

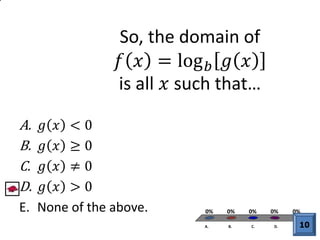
![We know that when
푓 푥 = log푏 [푔 푥 ] ,
the domain is all 푥
such that 푔 푥 > 0.
Back to our problem…
푓 푥 = log0.2
1
3
푥 + 5
1
3
푥 + 5 > 0
Solve for 푥 to find the
domain of 푓.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-140928225830-phpapp02/85/3-3-Logarithmic-Functions-7-320.jpg)