Data models
•Download as PPTX, PDF•
3 likes•504 views
The document discusses different types of data models including logical, physical, and record-based models. It describes key concepts of data models like entities, attributes, relationships and different relationship types. Specific models covered are hierarchical, network, and relational with details on their structure, advantages and disadvantages.
Report
Share
Report
Share
More Related Content
What's hot (20)
Similar to Data models
Similar to Data models (20)
Student POST Database processing models showcase the logical s.docx

Student POST Database processing models showcase the logical s.docx
Database System Concepts AND architecture [Autosaved].pptx![Database System Concepts AND architecture [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Database System Concepts AND architecture [Autosaved].pptx](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Database System Concepts AND architecture [Autosaved].pptx
chapter 2-DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND architecture [Autosaved].pdf![chapter 2-DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND architecture [Autosaved].pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![chapter 2-DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND architecture [Autosaved].pdf](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
chapter 2-DATABASE SYSTEM CONCEPTS AND architecture [Autosaved].pdf
Recently uploaded
https://app.box.com/s/4hfk1xwgxnova7f4dm37birdzflj806wGIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
https://app.box.com/s/tkvuef7ygq0mecwlj72eucr4g9d3ljcs50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...

50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...Nguyen Thanh Tu Collection
Recently uploaded (20)
Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf

Sectors of the Indian Economy - Class 10 Study Notes pdf
Adversarial Attention Modeling for Multi-dimensional Emotion Regression.pdf

Adversarial Attention Modeling for Multi-dimensional Emotion Regression.pdf
GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...

GIÁO ÁN DẠY THÊM (KẾ HOẠCH BÀI BUỔI 2) - TIẾNG ANH 8 GLOBAL SUCCESS (2 CỘT) N...
Basic Civil Engineering Notes of Chapter-6, Topic- Ecosystem, Biodiversity G...

Basic Civil Engineering Notes of Chapter-6, Topic- Ecosystem, Biodiversity G...
Jose-Rizal-and-Philippine-Nationalism-National-Symbol-2.pptx

Jose-Rizal-and-Philippine-Nationalism-National-Symbol-2.pptx
Home assignment II on Spectroscopy 2024 Answers.pdf

Home assignment II on Spectroscopy 2024 Answers.pdf
INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf

INU_CAPSTONEDESIGN_비밀번호486_업로드용 발표자료.pdf
50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...

50 ĐỀ LUYỆN THI IOE LỚP 9 - NĂM HỌC 2022-2023 (CÓ LINK HÌNH, FILE AUDIO VÀ ĐÁ...
Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx

Instructions for Submissions thorugh G- Classroom.pptx
Industrial Training Report- AKTU Industrial Training Report

Industrial Training Report- AKTU Industrial Training Report
Basic Civil Engg Notes_Chapter-6_Environment Pollution & Engineering

Basic Civil Engg Notes_Chapter-6_Environment Pollution & Engineering
Data models
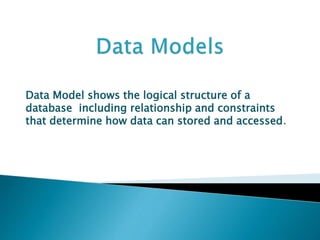
- 1. Data Model shows the logical structure of a database including relationship and constraints that determine how data can stored and accessed.
- 2. Structural part:-consisting of set of rules according to which databases can be constructed. Manipulative Part:- define the types of operations that are allowed on the data. Integrity Rules:- which ensure that data is accurate.
- 3. Entity:-Anything about which data are to be collected and stored. Attribute:- A characteristic of an entity. Relationship:-An association among entities. One to one(1:1) relationship One to many(1:M) relationship Many to one(M:1) relationship Many to many(M:M) relationship
- 4. Object Based Data Models Physical Data Models Record Based Logical Data Models
- 5. It uses concepts such as Entities, attributes and relationship. Types of object based models: Entity Relationship Object Oriented Semantics Functional
- 6. It describe how data is stored in the computer, representing information such as record structures, record ordering and access paths. Less no. of models are there.
- 7. It is used to specify the overall logical structure of the database and to provide a higher level description of the implementation. Structured database in fixed formats.
- 8. Hierarchical Model Network Model Relational Model
- 9. HIERARCHICAL DIAGRAM: Hierarchical model is one of the oldest database in which data is organized into tree like structure. This model uses a one to many (1:M) relationship for data elements. Hierarchical database were popular in early database design, in the era of mainframe computers.
- 10. Simplicity Data security Data Integrity Efficiency Complexity Not Flexible Dependence Extra Space
- 11. NETWORK MODEL In 1965 C.W.BACHMAN developed the first network data model to present complex data relationships more effectively than hierarchical model. In network model the multiple parent-child relationships are used.
- 12. Conceptual Simplicity Capability Data Integrity Ease to access data Data Independence Complexity Confusion Lack of structural Independence
- 13. RELATIONAL MODEL The most popular data model in DBMS is the relational data model . In this model ,data is organized in the terms of rows(tuple) and columns(attributes) in a table known as RELATION. The principal of relational model were first outlined by Dr.E.F.Codd.
- 14. Conceptual Simplicity Structural Independence Design Implementation Security Hardware Overheads Expensive Storage