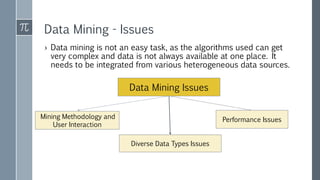
Data mining involves semi-automatically analyzing large databases to discover rules and patterns from data. There are two main categories of data mining tasks: descriptive tasks like finding frequent patterns, associations, and clusters in data; and classification and prediction tasks like using decision trees or neural networks to classify data. Data mining is applied across many domains including financial analysis, retail, telecommunications, biology, and intrusion detection.