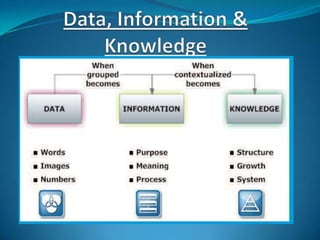
This document provides an overview of data mining and knowledge discovery in databases (KDD). It defines data mining as the process of extracting interesting and useful patterns from large databases. KDD is described as identifying valid and understandable patterns in data. The document outlines the differences between data, information, and knowledge, and discusses how data mining can be used to turn data into knowledge. It also summarizes some common applications of data mining such as in retail, finance, science, and recommender systems. Finally, it briefly discusses the roles of data warehouses and data cleaning in the data mining process.