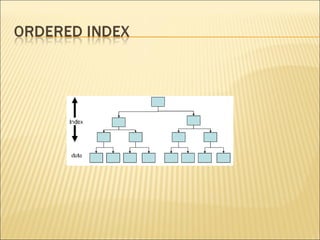
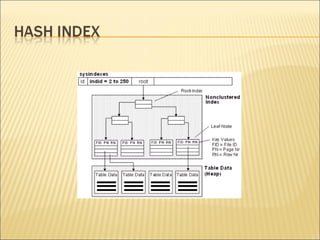
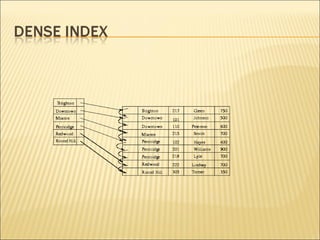
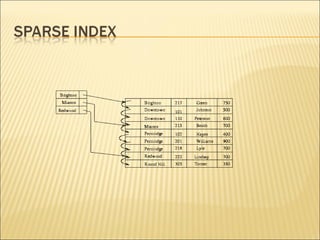
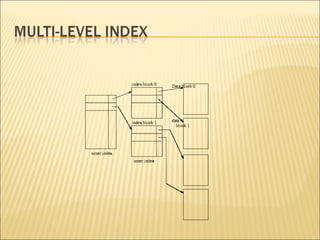
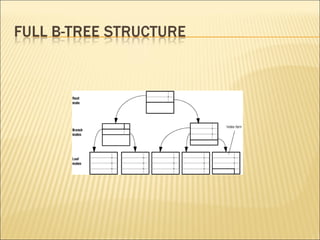
The document discusses data indexing, which is a data structure added to files to provide faster data access. Indexing reduces the number of blocks a database management system must check when performing operations like reading, modifying, updating, and deleting data. An index contains a search key and pointer, where the search key is used to look up records and the pointer contains the address of stored data. Common indexing techniques include ordered/primary indexes that access sorted data and hash indexes that uniformly distribute data across buckets. When choosing an indexing technique, factors like access type, time, space overhead are considered. B-trees are commonly used indexing data structures that can grow and shrink dynamically with root, branch and leaf nodes.