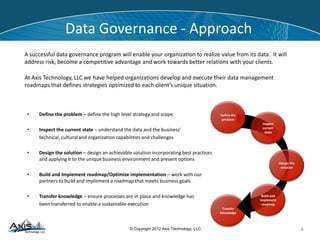
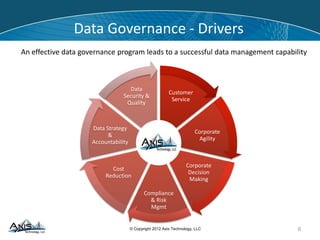
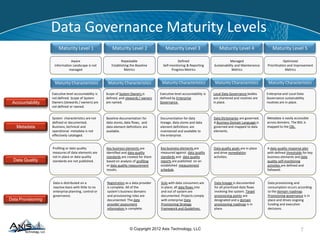
Successful data governance requires a strategy that aligns regulatory drivers with business needs, addressing organizational, technological, and cultural changes. Key challenges include the complexity of data management and the need for effective policies to maintain data accuracy and security, particularly in industries like finance and insurance. An effective data governance program can drive business growth by reducing costs, improving compliance, and enhancing client service through better data management.