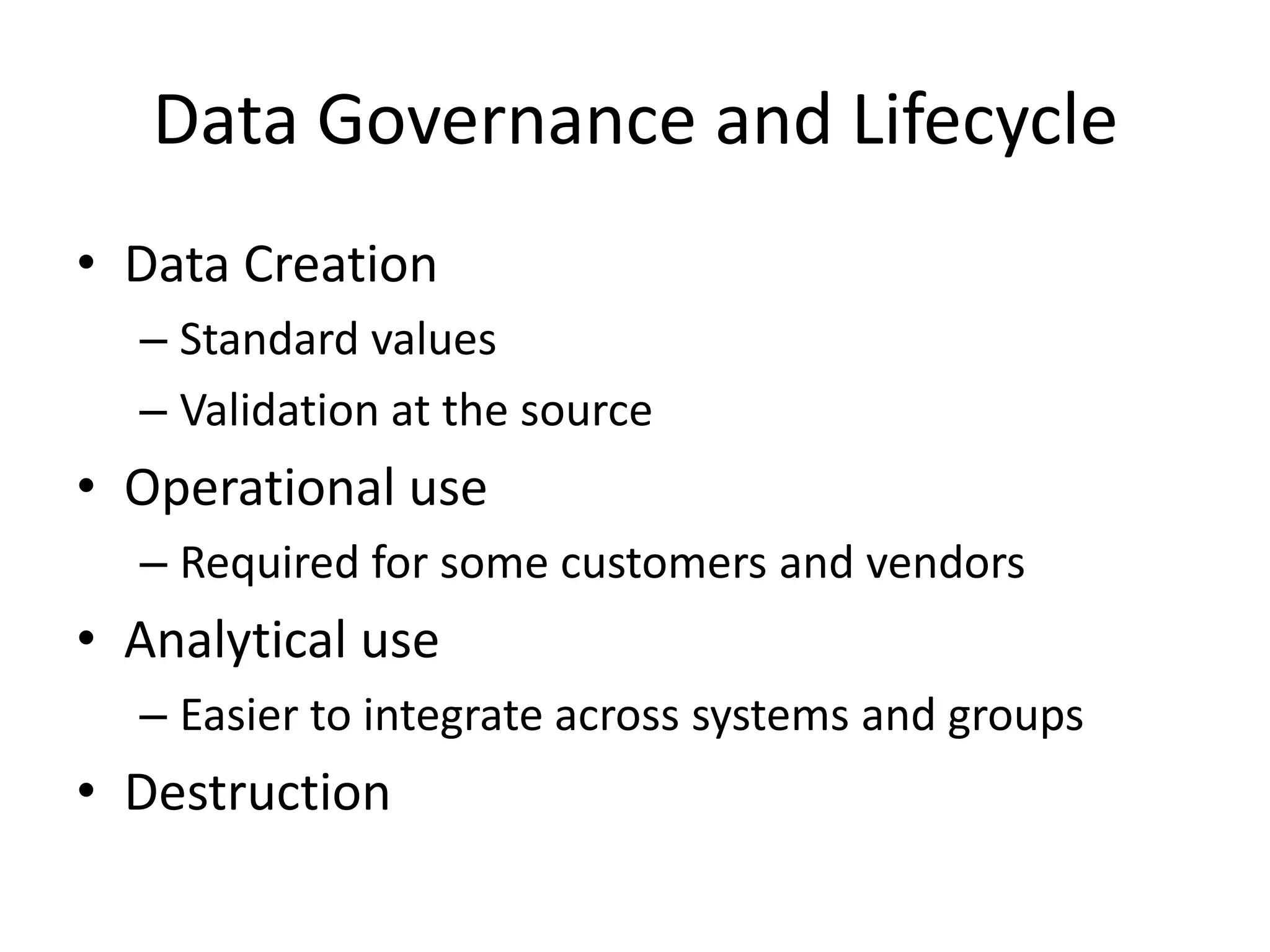
This document discusses the importance of data governance and quality for business intelligence systems. It notes that 70-80% of BI projects fail due to issues like poor quality data. The life cycle of data is outlined as creation, operational use, analytical use, and destruction. Both business and IT have responsibilities for data as a corporate resource. The document advocates establishing data governance practices like data stewardship, a data dictionary, and master data management to standardize, cleanse, and manage data across the organization. Strong management promotion and treating governance as a cultural change rather than just a program are also recommended.