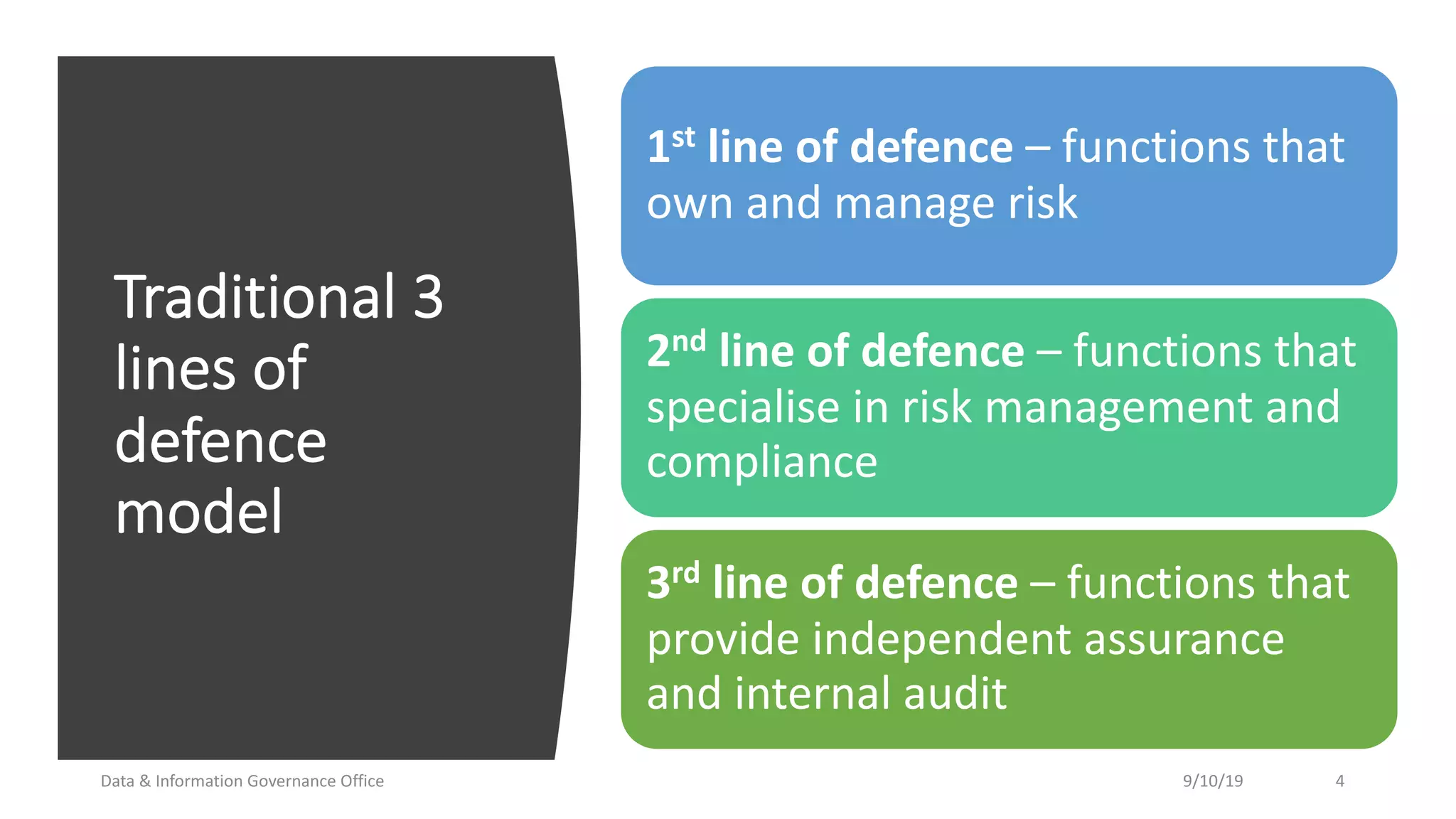
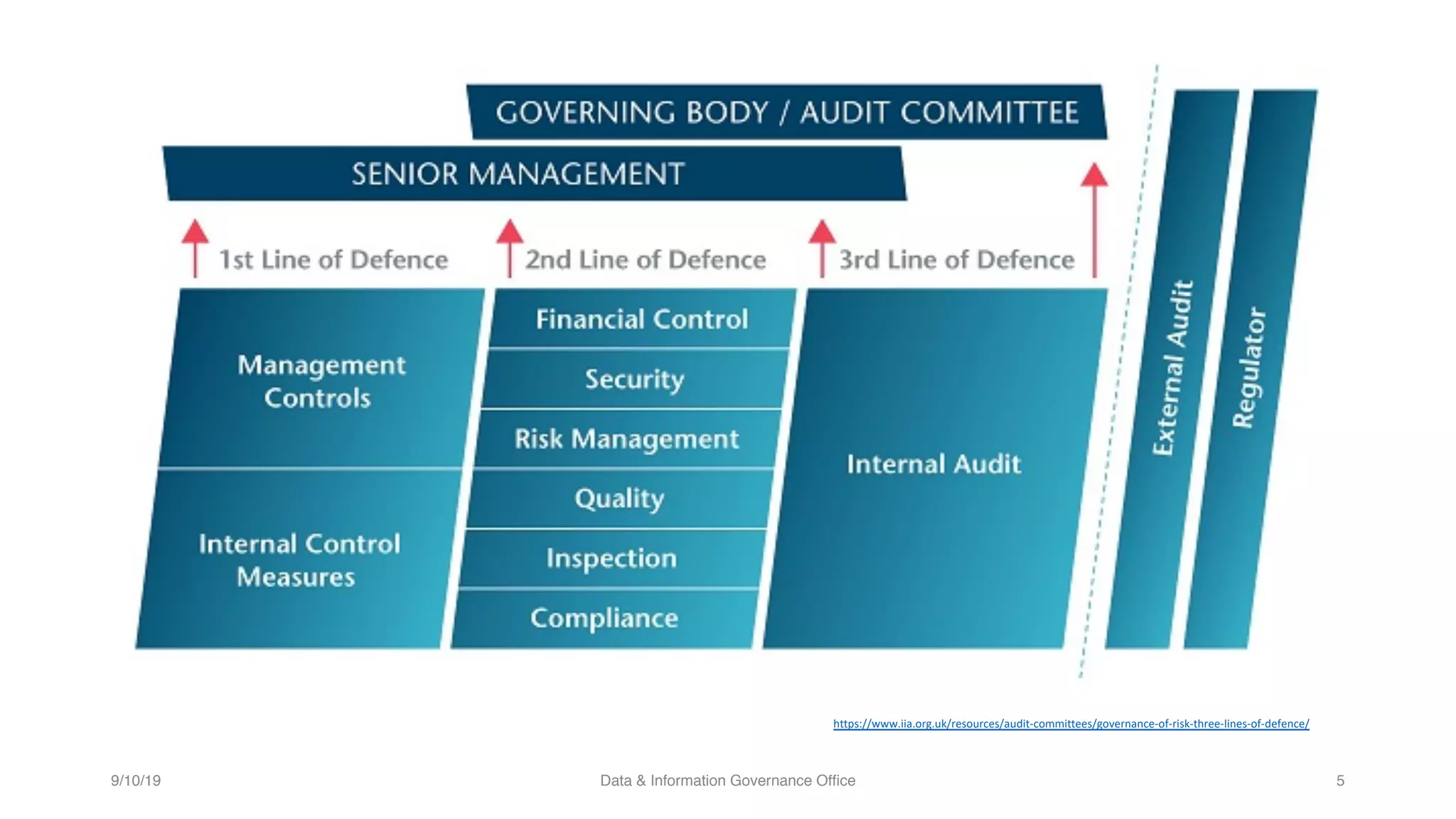
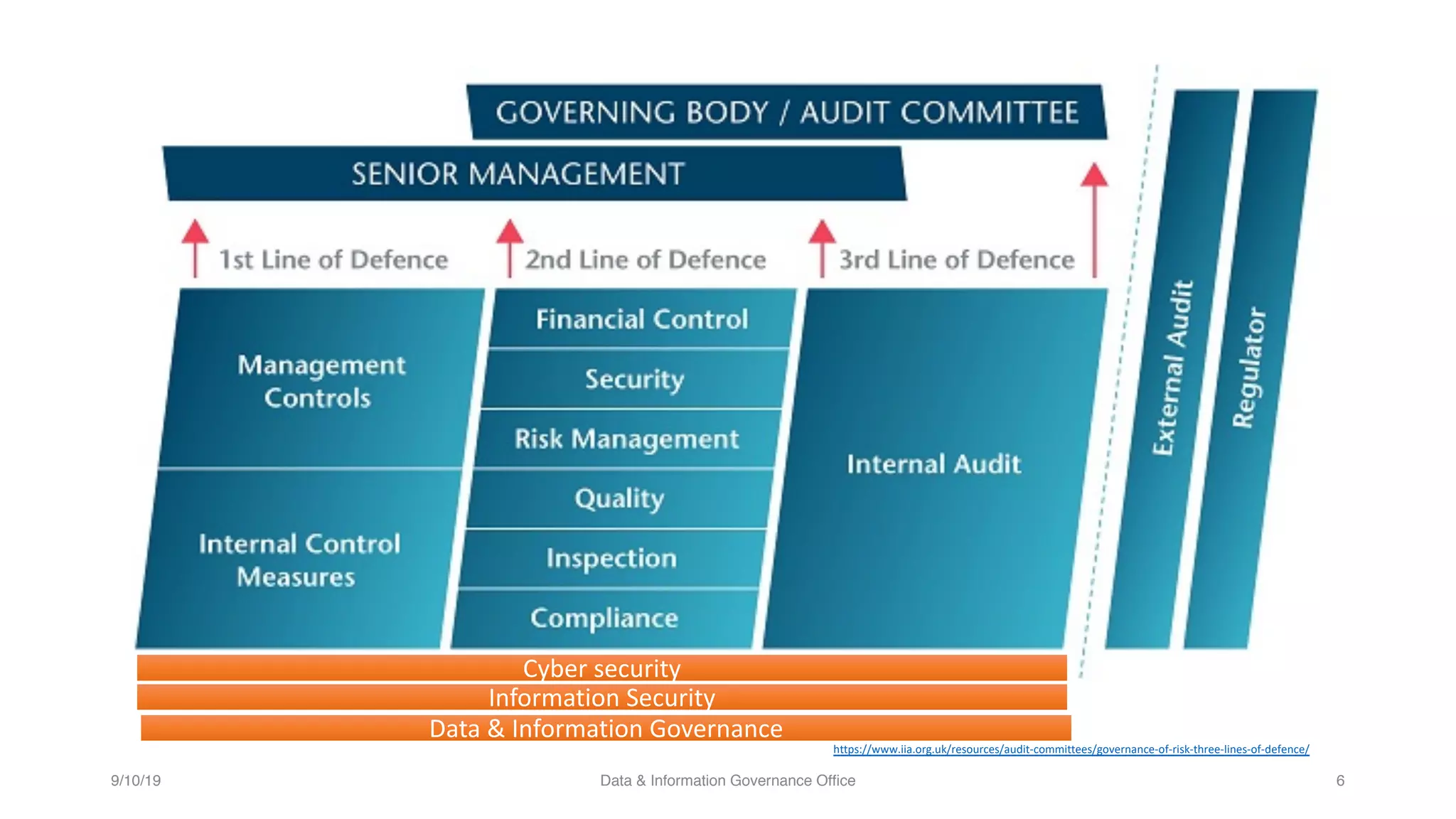
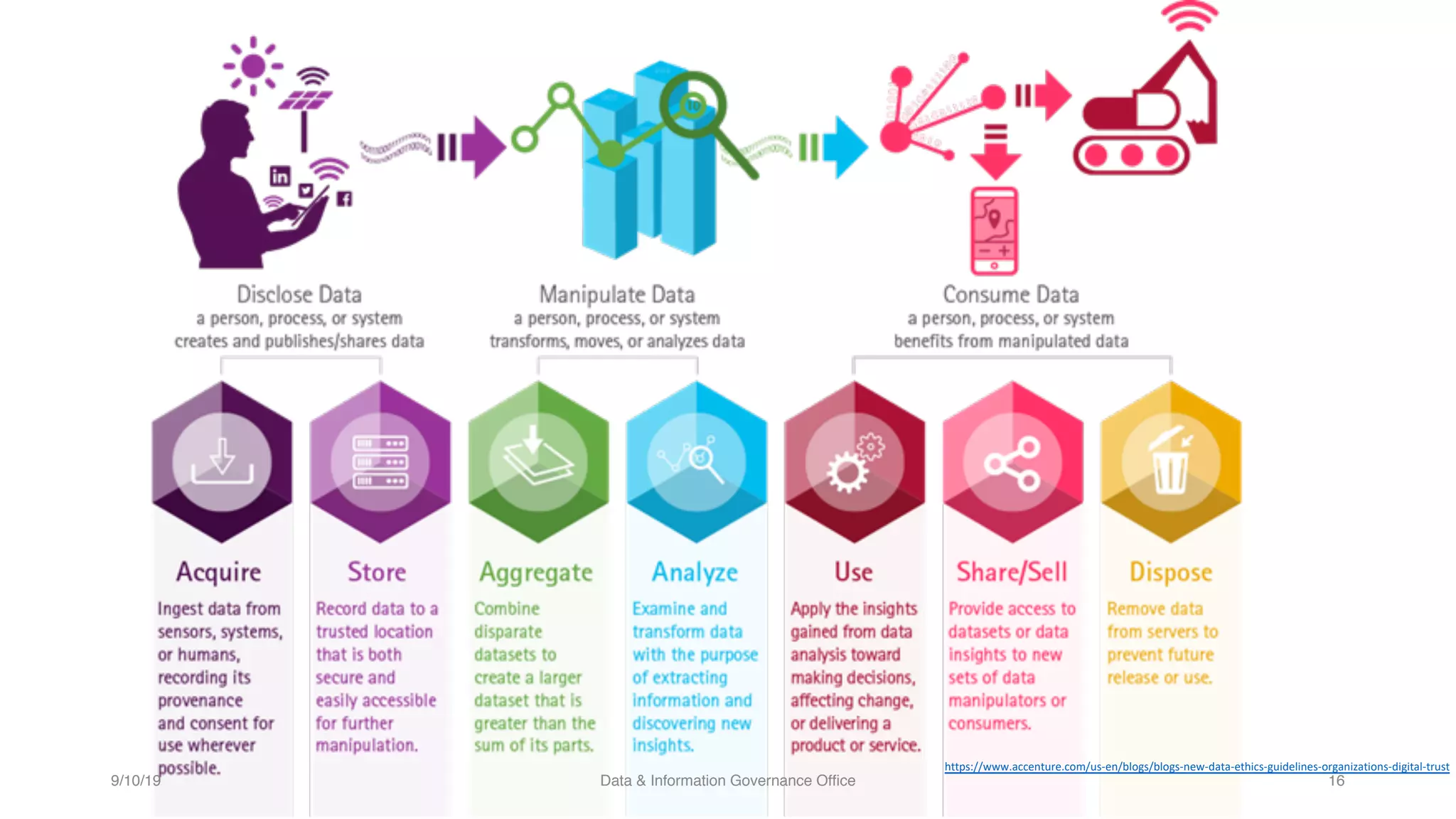
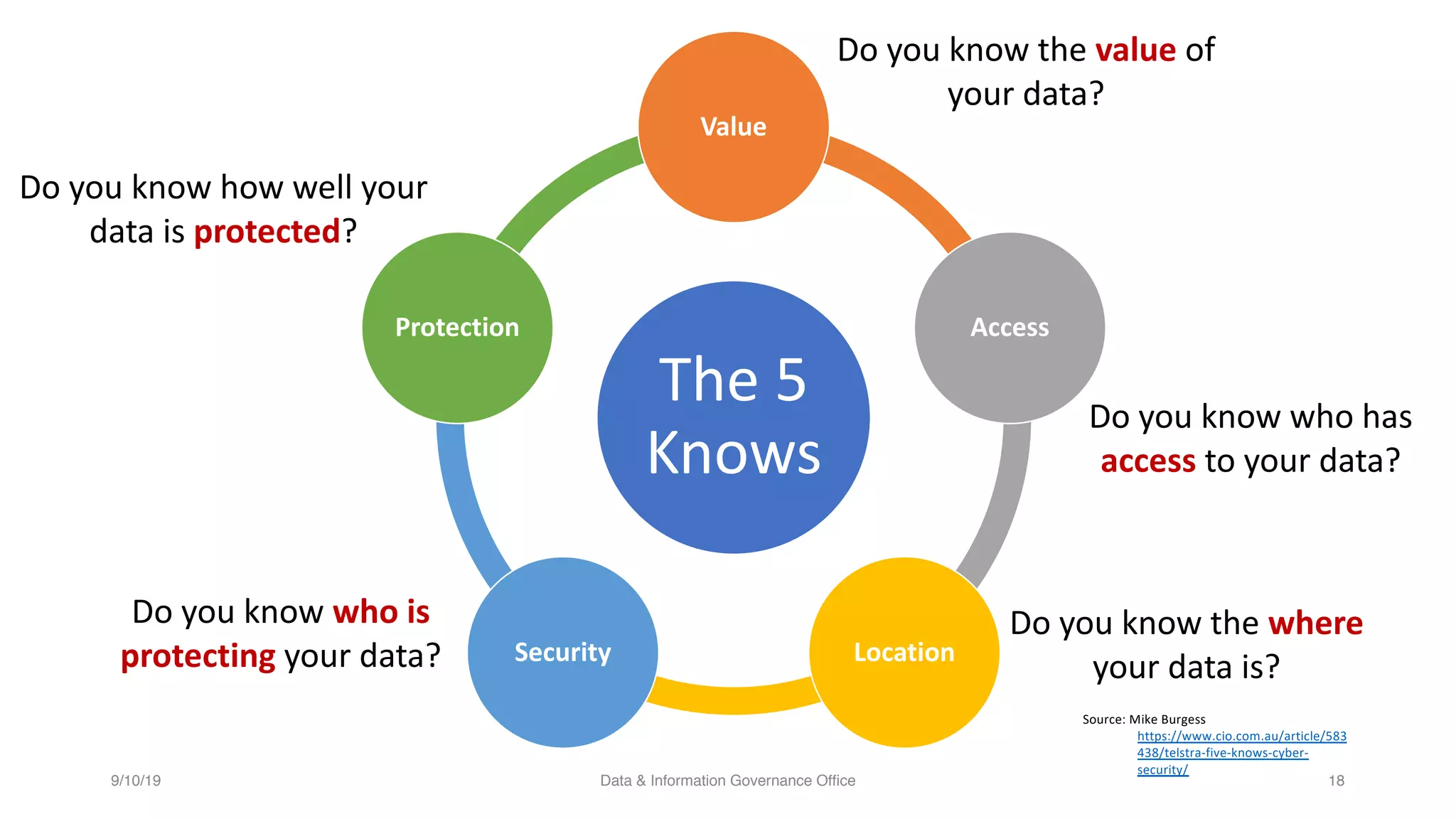
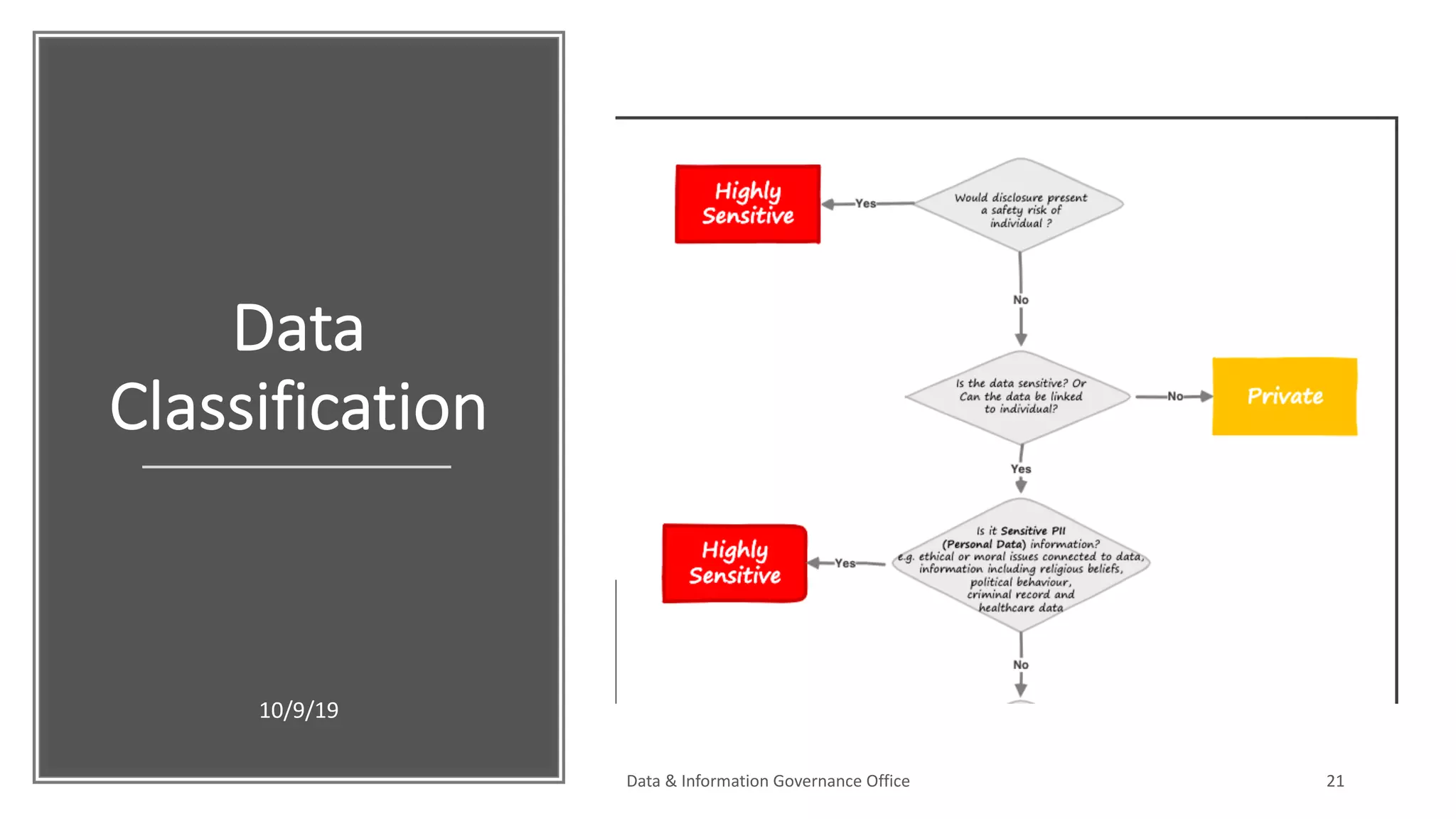
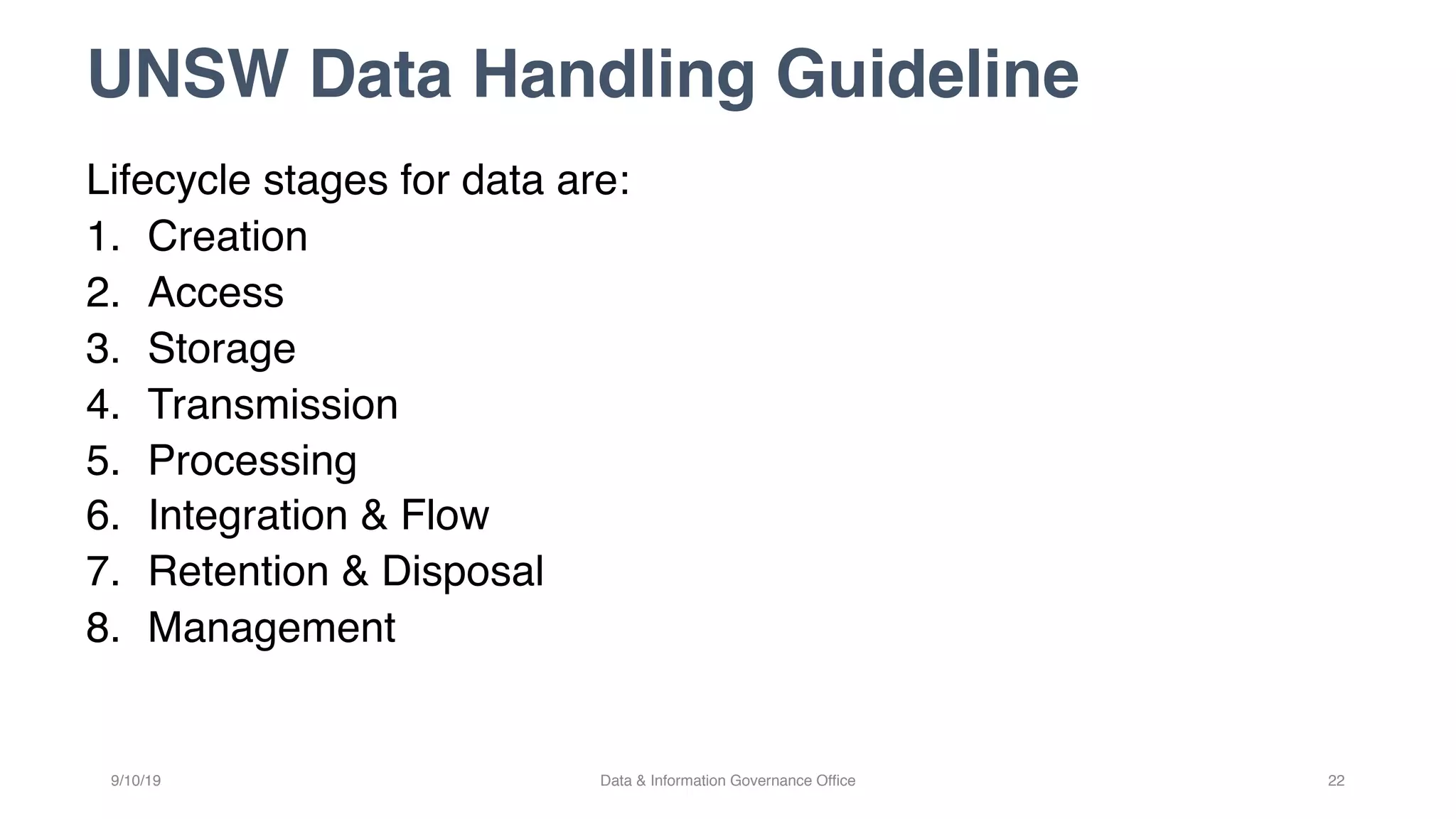
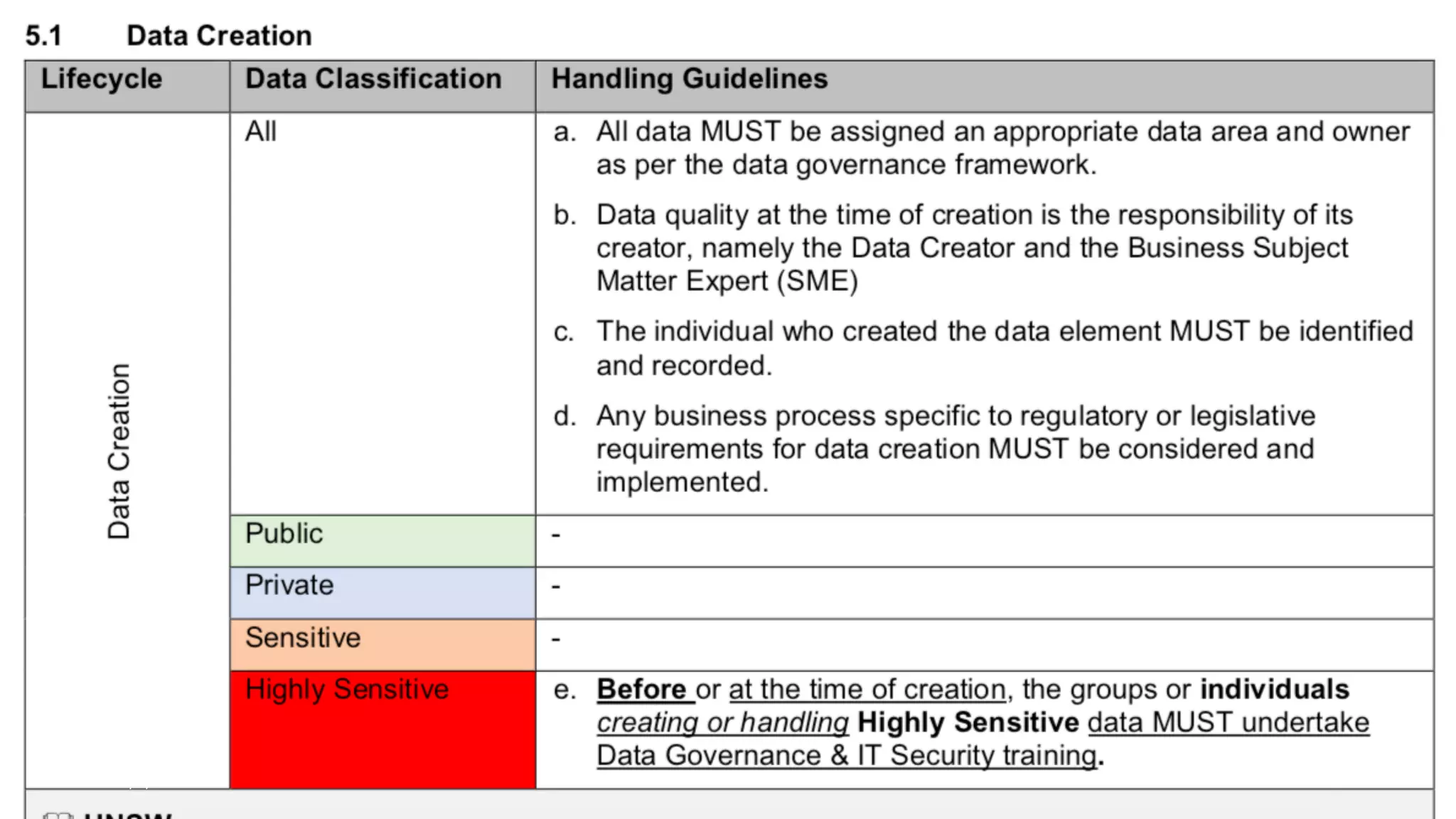
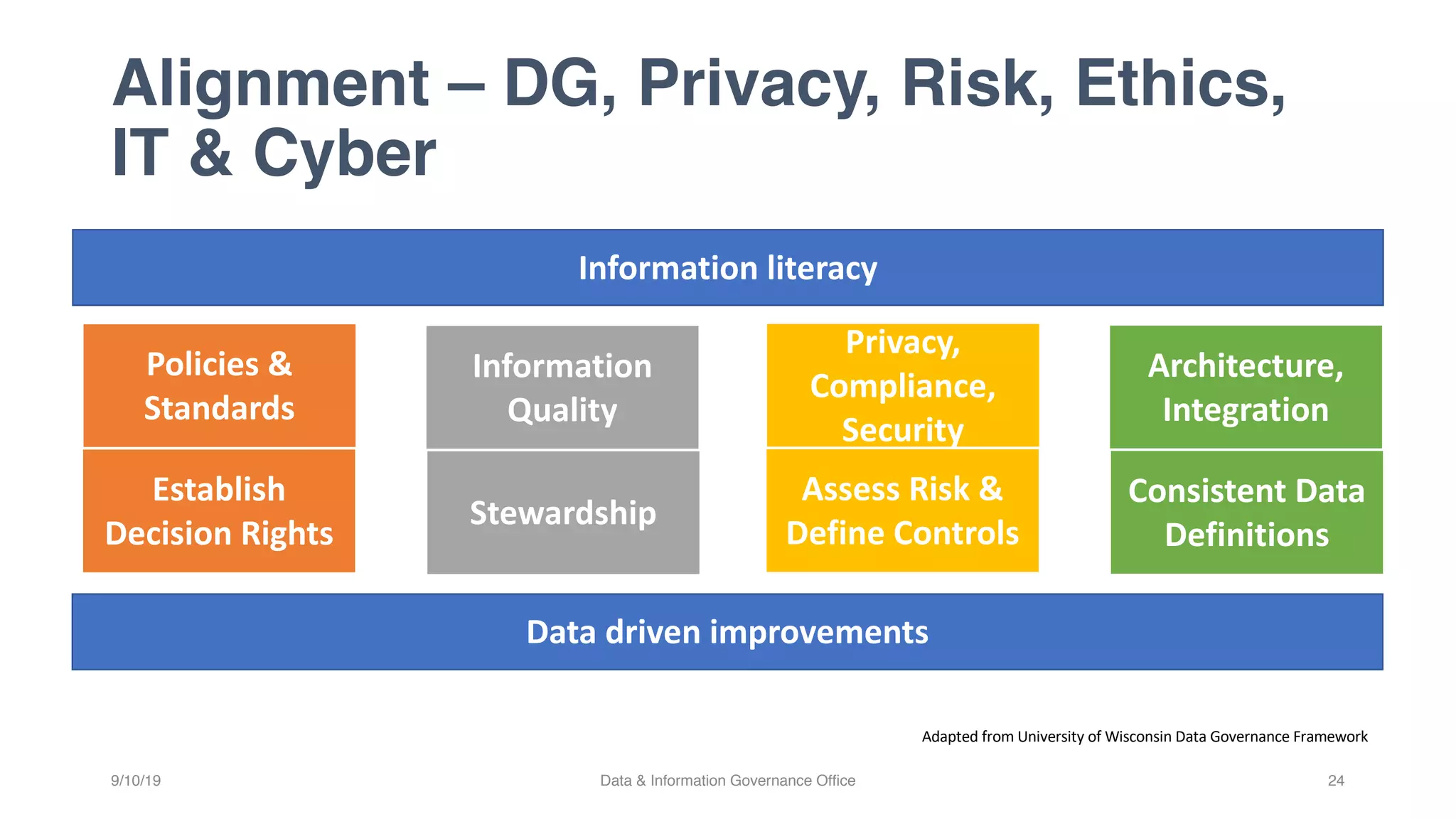
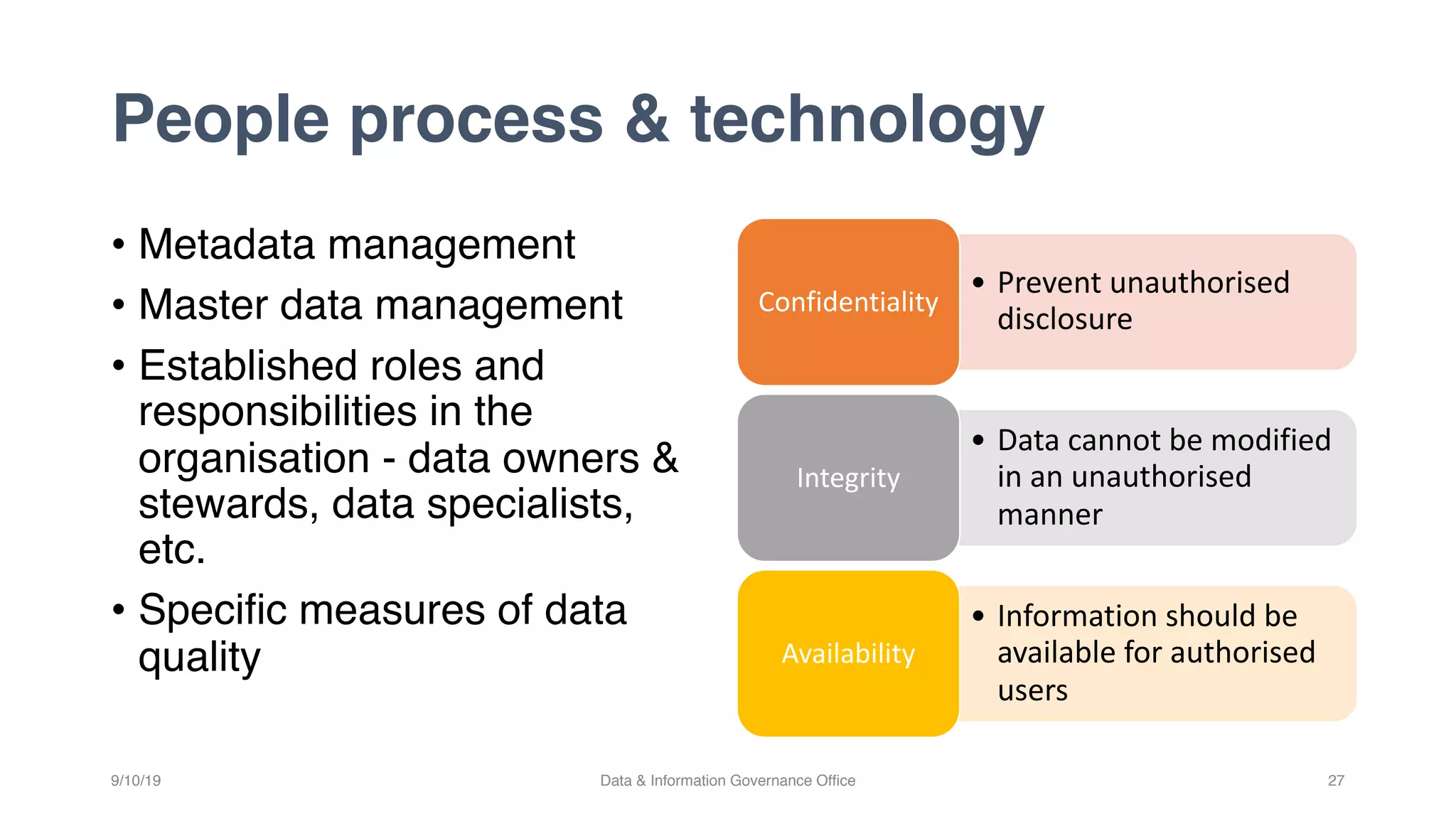
The document discusses how data governance is an essential foundation for effective cyber security. It establishes that a data governance program enables investment in cyber security, effective data risk management, and efficient allocation of cyber resources. The document then provides definitions of data governance, cyber security, and information security. It explains how data governance, when aligned with privacy, risk management, ethics, IT, and cyber security functions, helps implement defense in depth for organizations by identifying at-risk data, data access management, and establishing roles and responsibilities for data ownership. Establishing foundational elements of data governance such as policies, classifications, and guidelines is important for building collaborative risk management functions.