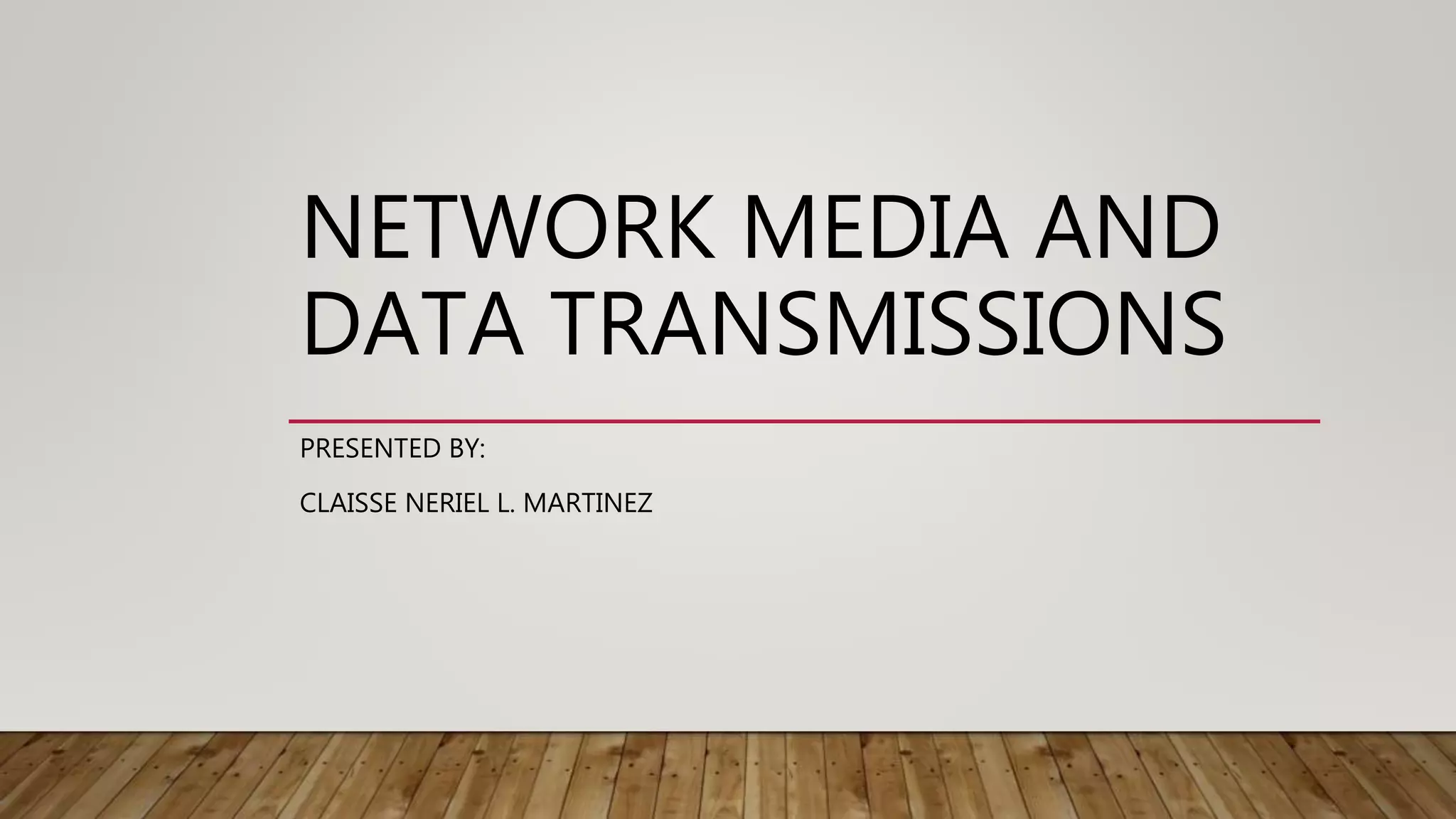
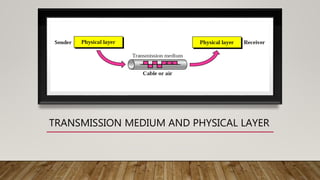
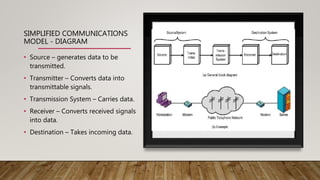
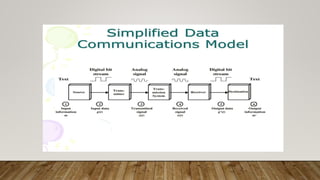
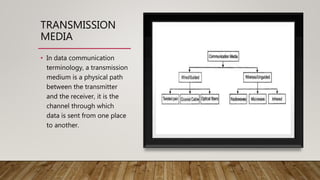
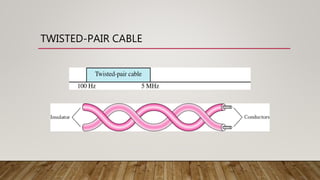
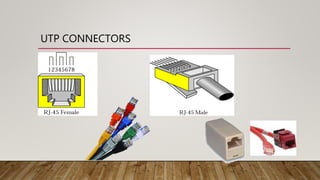
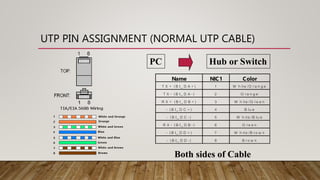
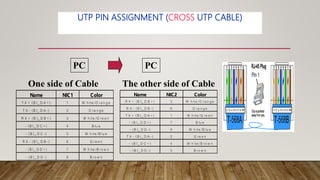
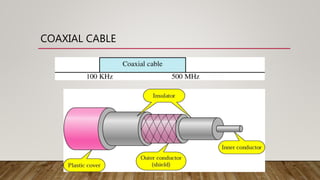
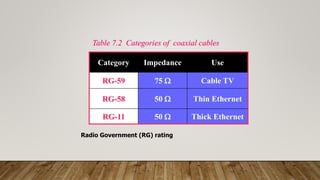
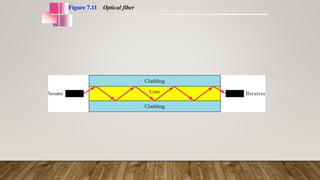
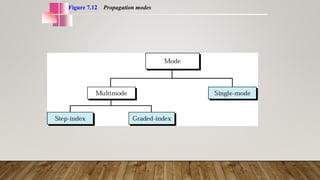
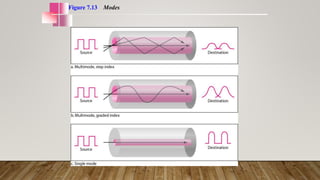
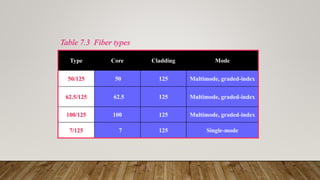
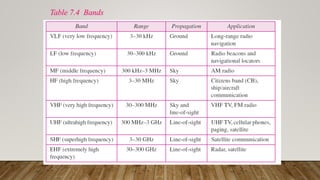
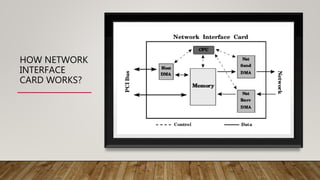
The document discusses network media and data transmissions. It describes different types of transmission media including guided/wired media like twisted pair cable, coaxial cable, and optical fiber cable. It also discusses unguided/wireless media like radio waves, microwaves, and infrared waves. It provides details on the components of data transmission including source, transmitter, transmission system, receiver, and destination. It also explains network interface cards and how they allow devices to communicate on a network.