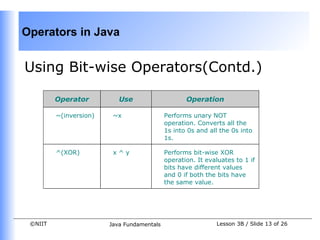
The document discusses operators in Java, including unary, binary, arithmetic, bitwise, shift, and instanceof operators. It provides examples of how to use various operators like increment, decrement, arithmetic assignment, bitwise AND, OR, NOT, XOR, right shift, left shift, and unsigned shift. It also covers operator precedence and demonstrates how operators in an expression are evaluated based on their predetermined precedence order.




















![Operators in Java
Operators Precedence
• Each operator in an expression is evaluated in a predetermined order called
operator precedence.
• Operators on the same line have equal precedence.
Operators Category
[], (), . , expr++, expr-- Array index, method call, member
access, and postfix operators
++expr, --expr, +, -, !, ~ Unary postfix operators
*, /, % Multiplicative Arithmetic operators
+, - Additive Arithmetic operators
©NIIT Java Fundamentals Lesson 3B / Slide 22 of 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dacj-1-3b-120518023106-phpapp01/85/Dacj-1-3-b-22-320.jpg)



