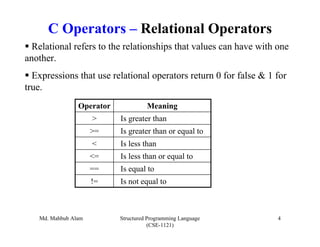
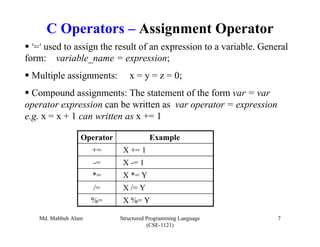
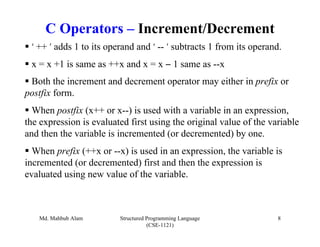
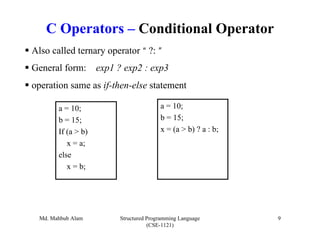
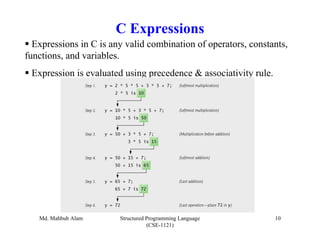
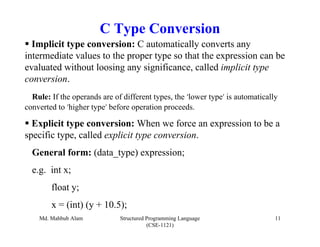
The document discusses C operators and expressions. It covers the different categories of C operators like arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, increment/decrement, and conditional operators. It explains operator precedence and associativity rules. It also discusses type conversion in C expressions, including implicit and explicit type conversion. The key topics covered are C operators, expression evaluation order, and type conversions.