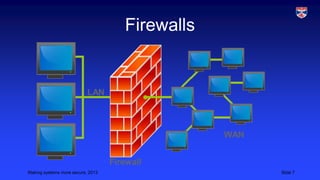
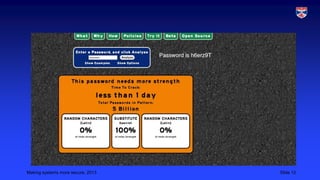
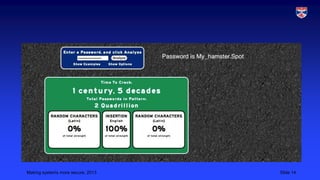
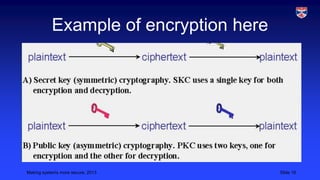
This document outlines strategies for improving cybersecurity, including deterrence, awareness, procedures, and monitoring/logging. Deterrence aims to increase the costs and risks of attacks so attackers are discouraged. Awareness involves educating all users about security risks and improving security culture. Procedures should be realistic and tailored to asset values. Monitoring and logging tracks all system access to detect anomalies and deter insider threats. The overall goal is a multifaceted approach to strengthen defenses through multiple layers of security controls.