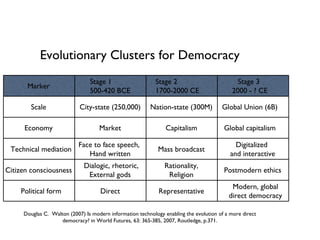
The document discusses democracy and the public sphere in the context of cyberpolitics. It defines democracy as rule by the people and outlines Robert Dahl's five principles of democracy. Three approaches to democracy are described: liberal individualism, communitarianism, and deliberative democracy. The internet is discussed as potentially enhancing each approach through information sharing, online communities, and as an electronic public sphere for deliberation. Habermas' concept of the public sphere and agora is also introduced. The document poses questions about whether the internet has transformed Habermas' idea of the public sphere and asks for examples of how this may contribute to the development of democracy.