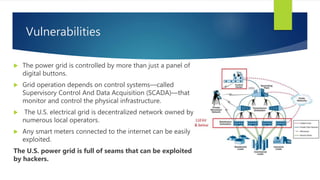
The document discusses cyber security threats to the US power grid. It notes that the power grid consists of over 300,000 km of transmission lines operated by 500 companies. Cyber attacks on critical infrastructure like the power grid are increasing in frequency and sophistication, which could have severe consequences. For example, a DDoS attack costing just $40 could overwhelm network links and cause a blackout. The document also provides examples of past cyber attacks on energy systems like Stuxnet and the 2015 attack on Ukraine's power grid that left 700,000 residents without electricity for 7 hours.