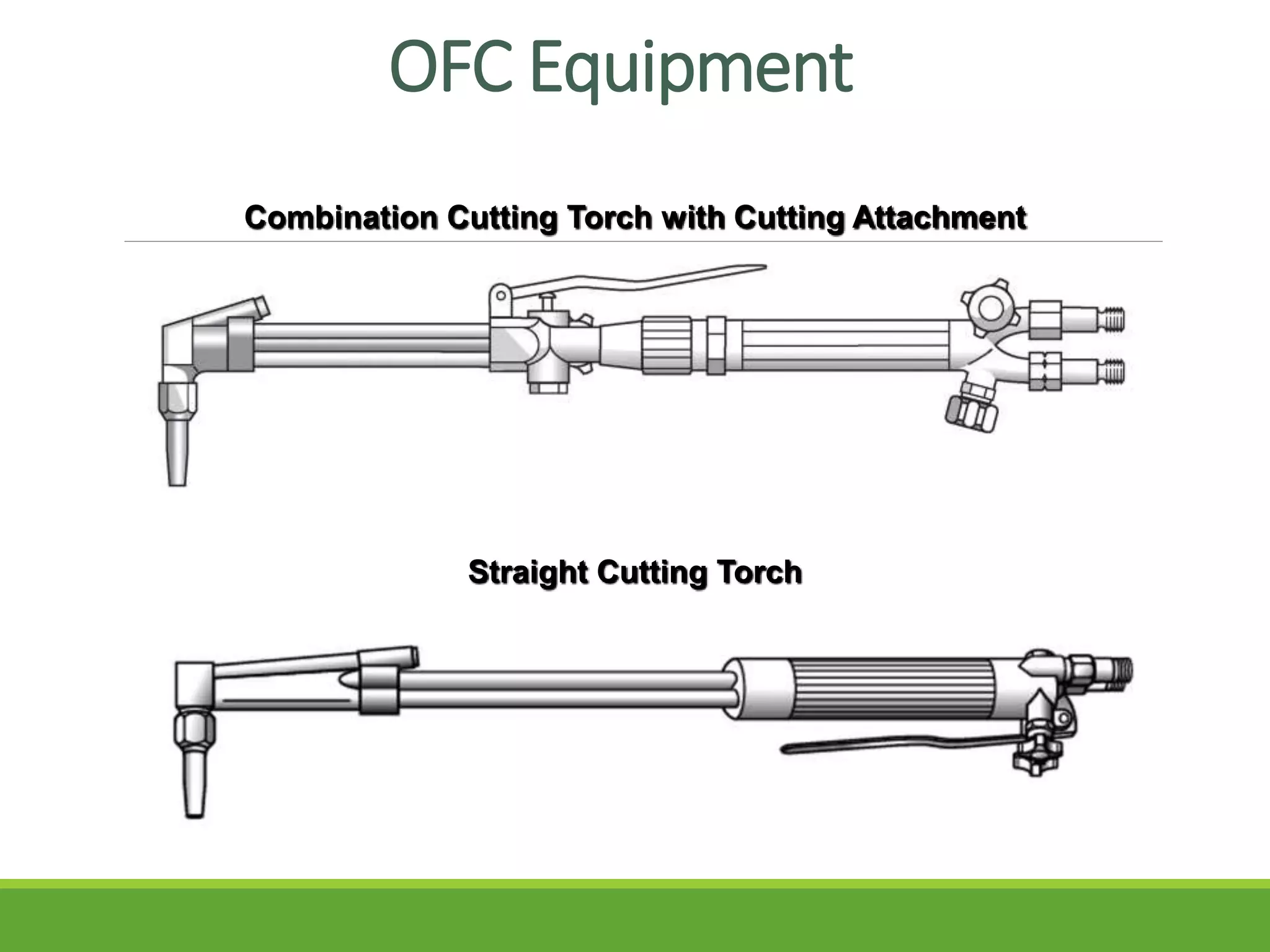
This document discusses the essential elements of oxy-fuel cutting. It explains that oxy-fuel cutting involves heating metal to its ignition point with a flame and then using high-pressure oxygen to burn and remove the metal. It provides details on equipment setup and inspection, selecting cutting tips, adjusting gas pressures, and maintaining a neutral flame for cutting. The document also outlines the advantages of oxy-fuel cutting, such as its ability to cut complex shapes and various metals, along with its disadvantages like slower speed and less accuracy compared to other cutting methods.