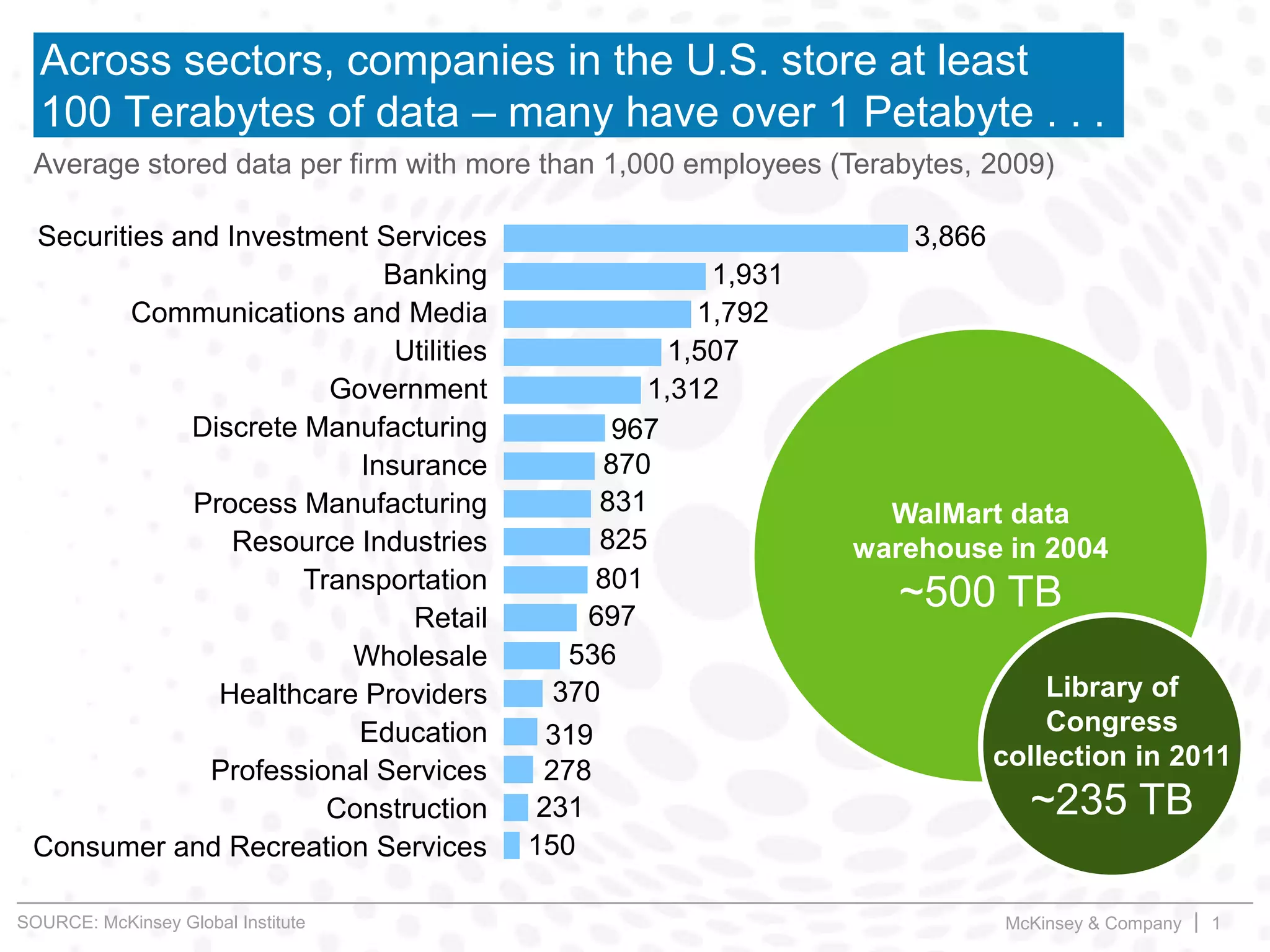
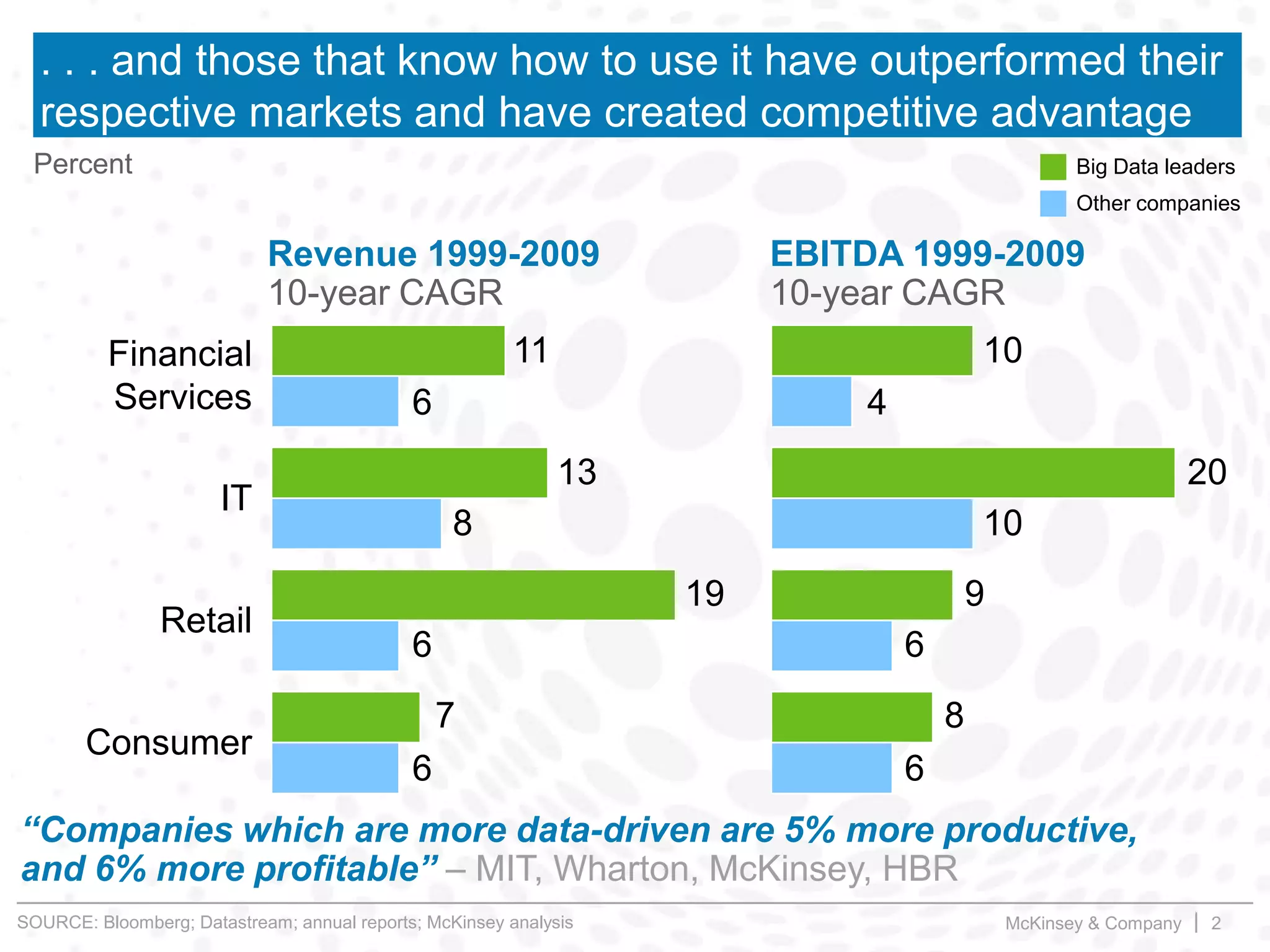
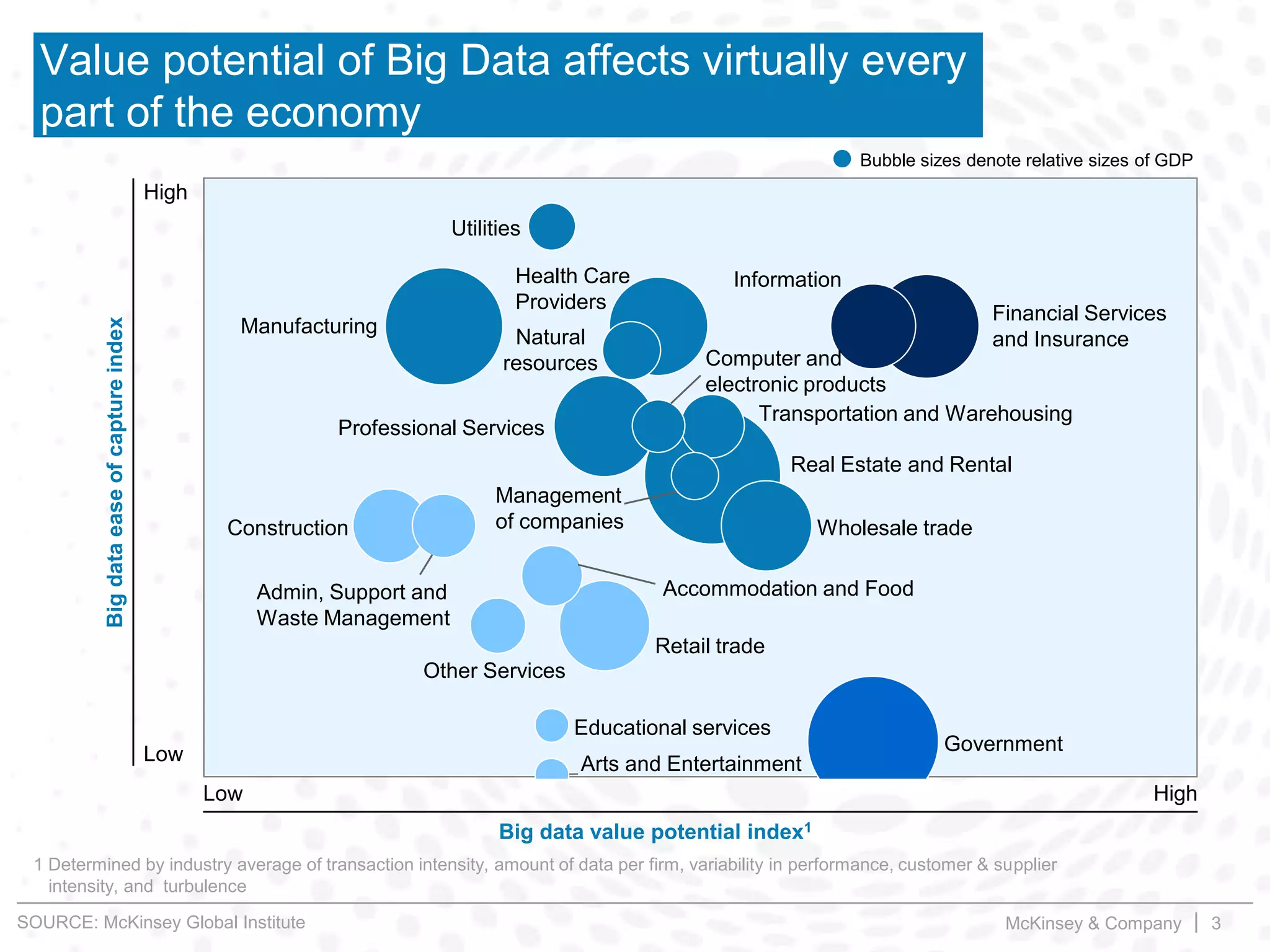
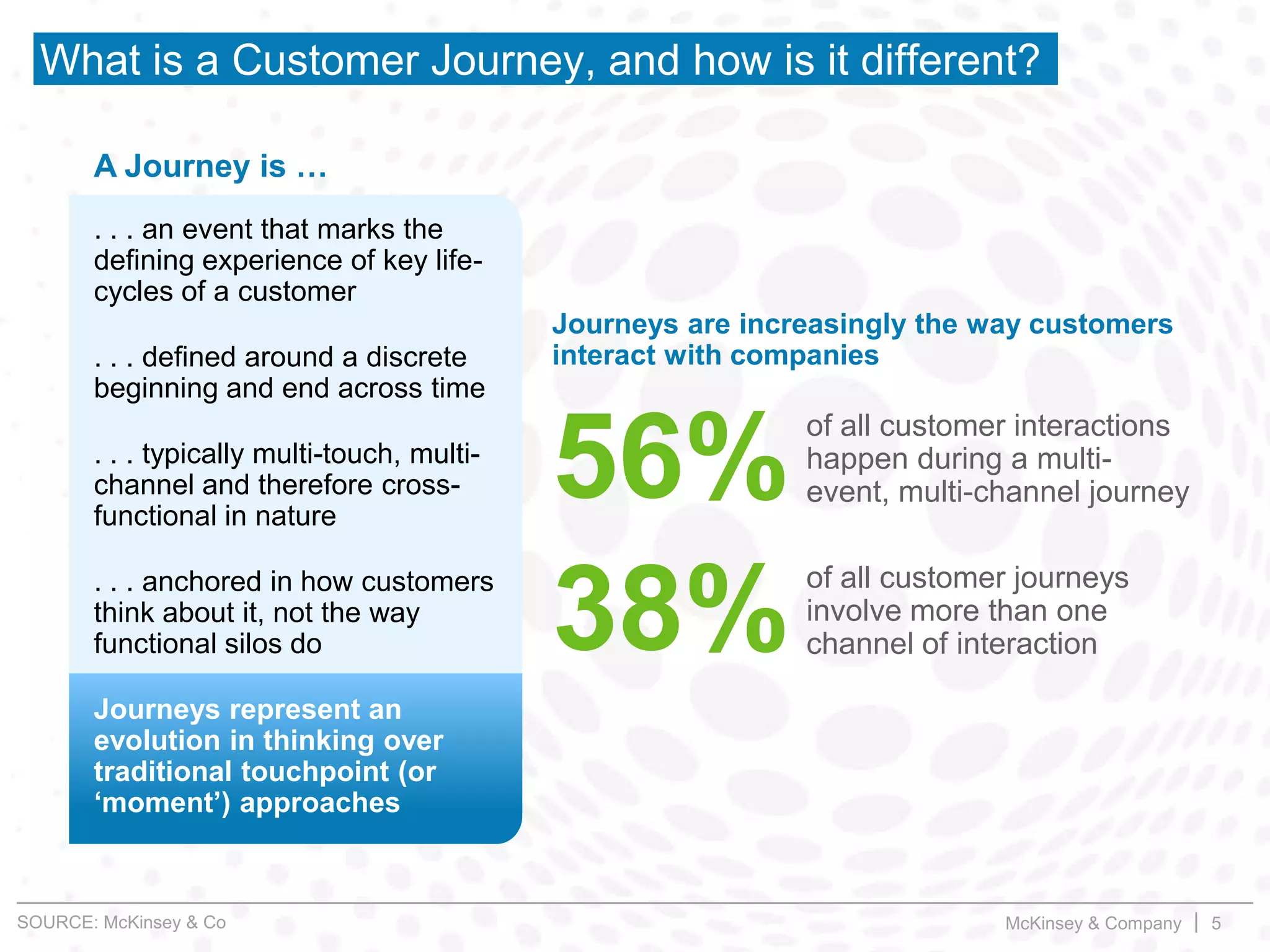
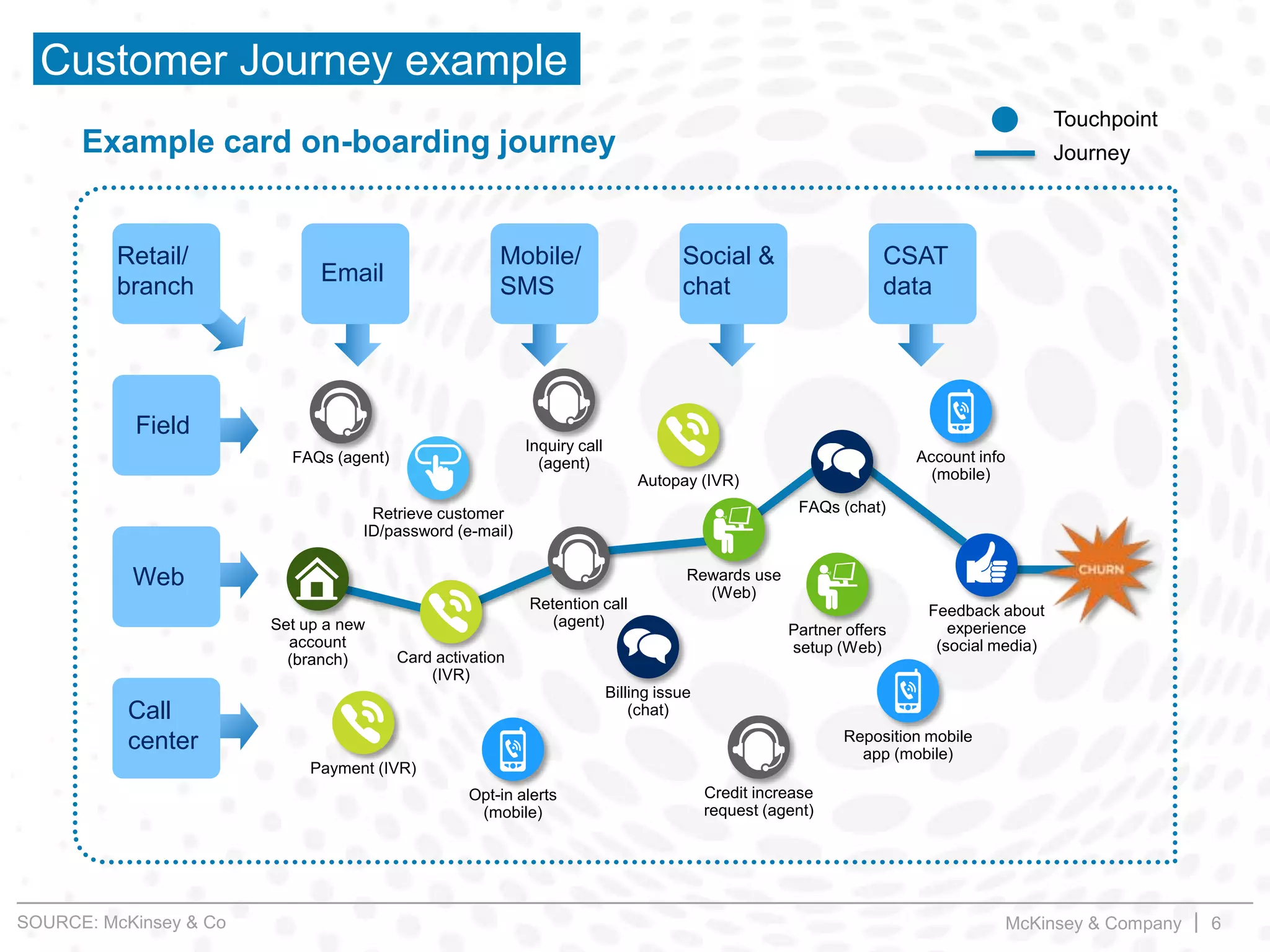
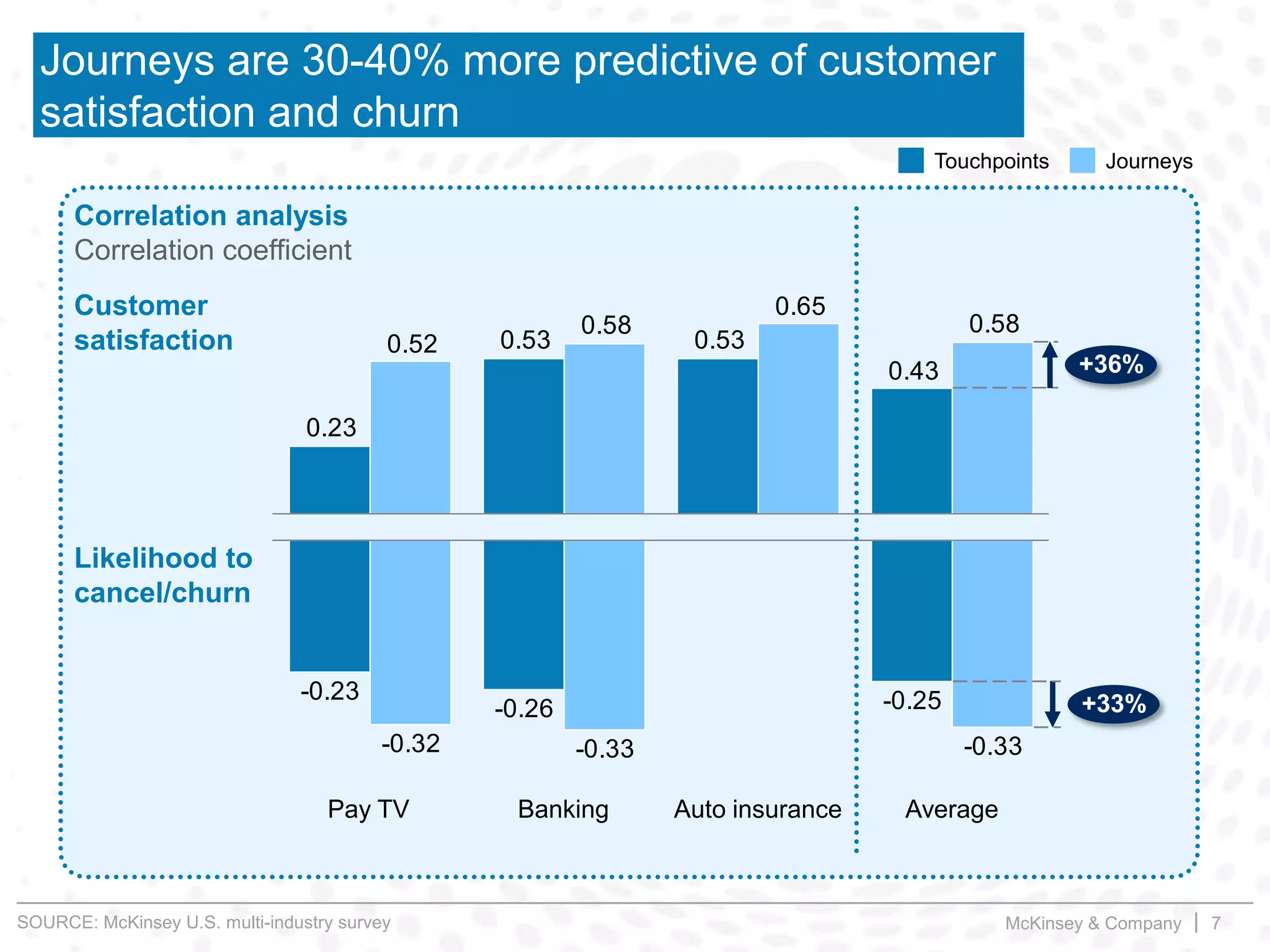
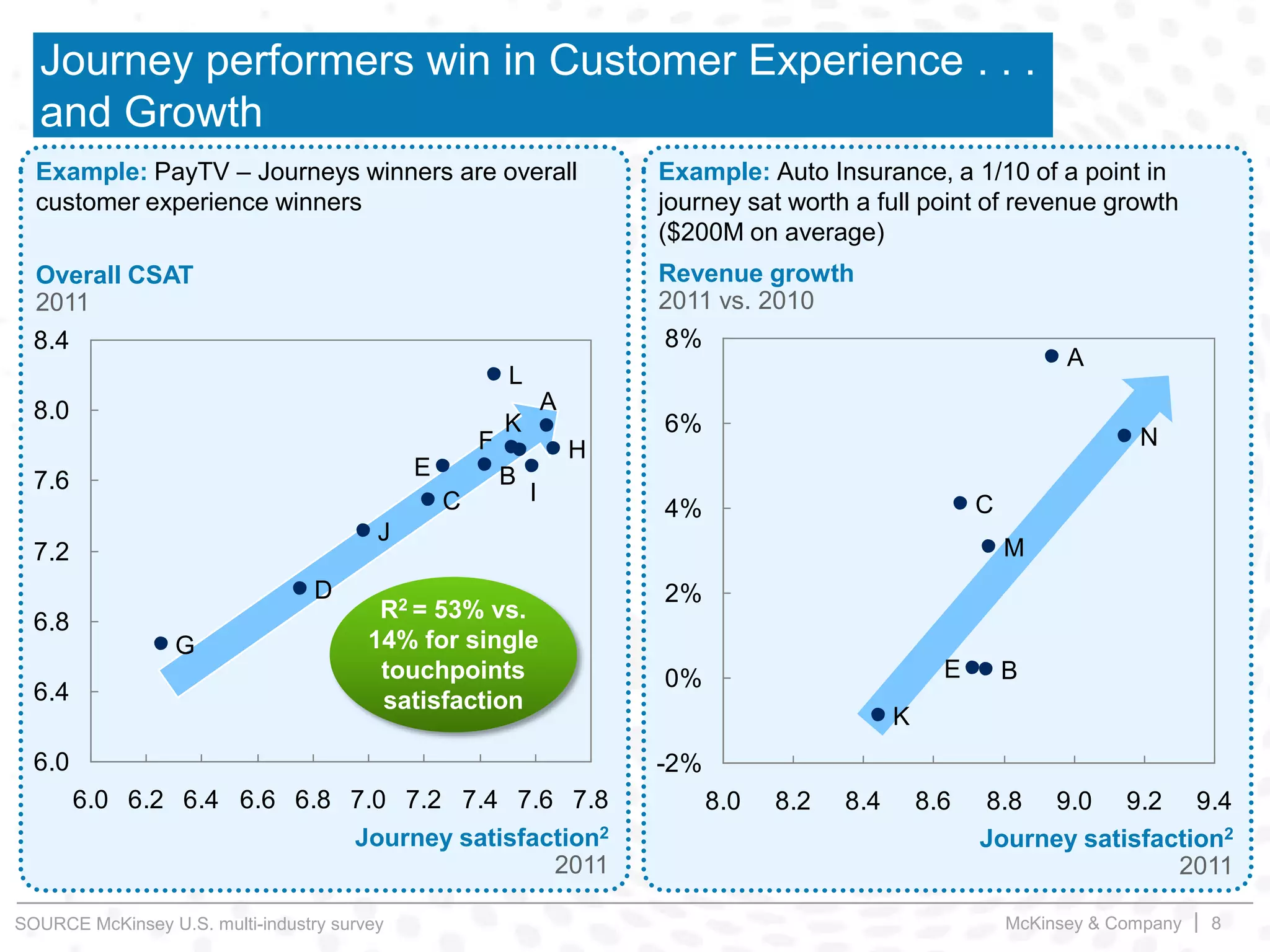
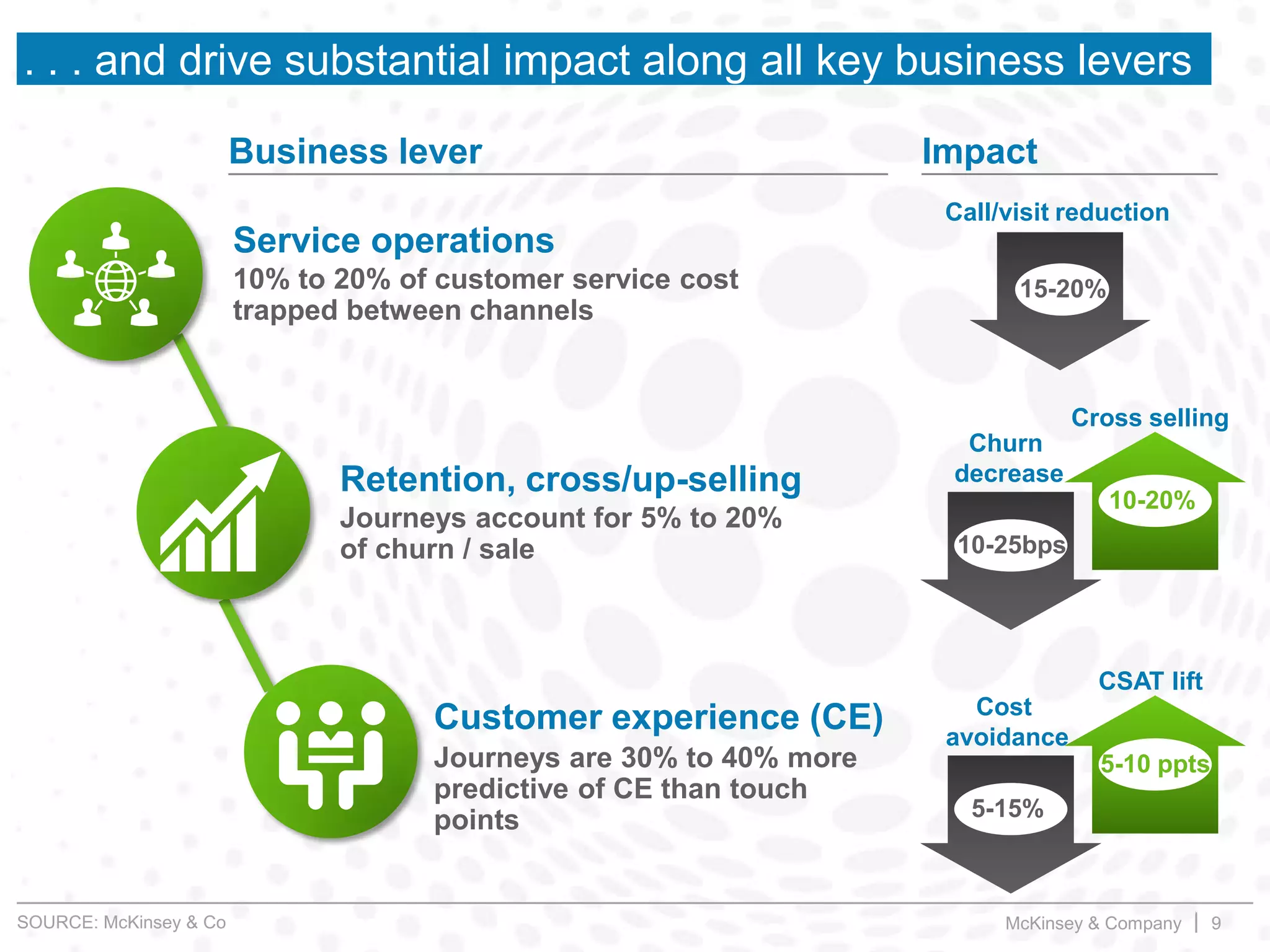
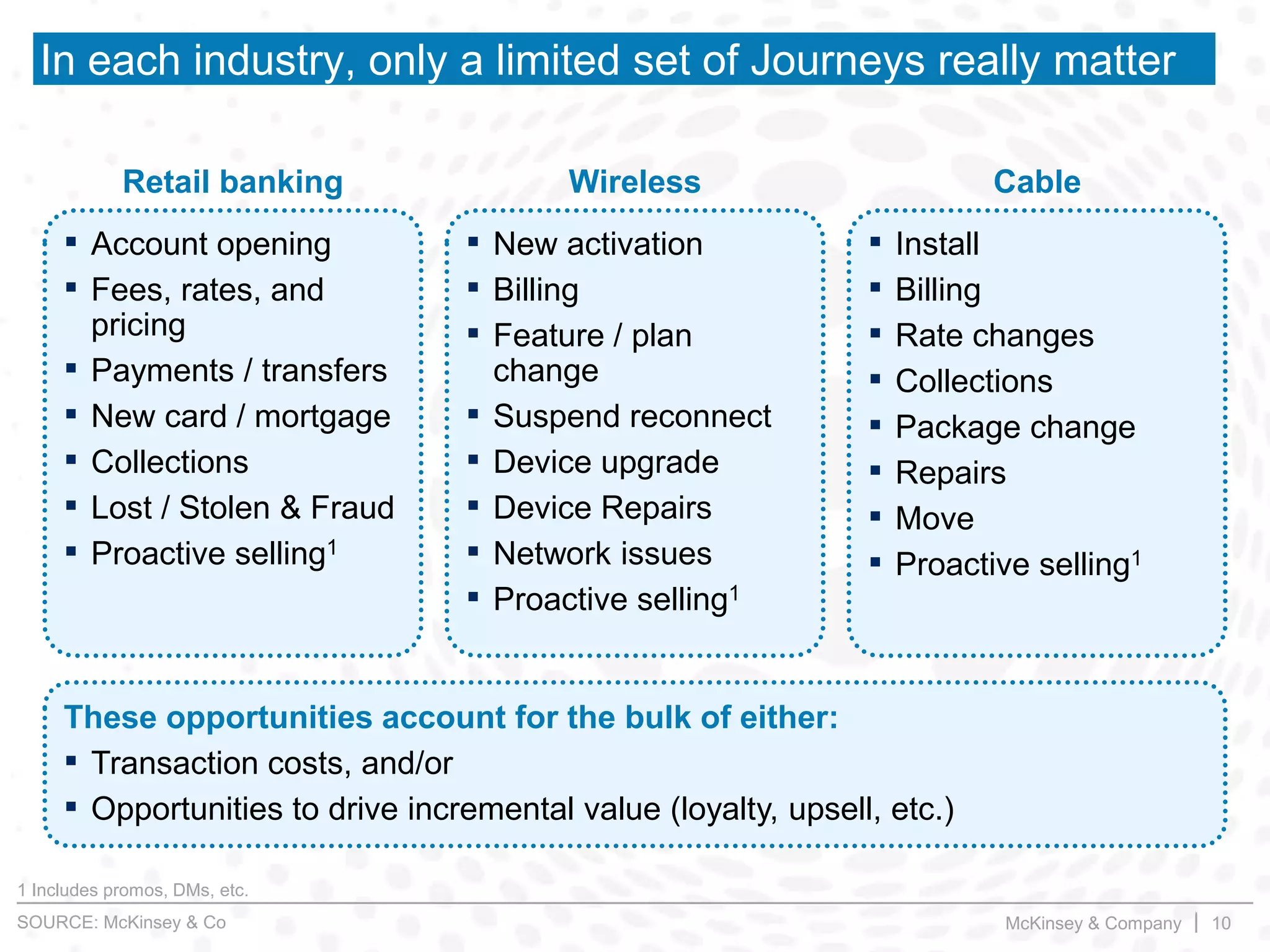
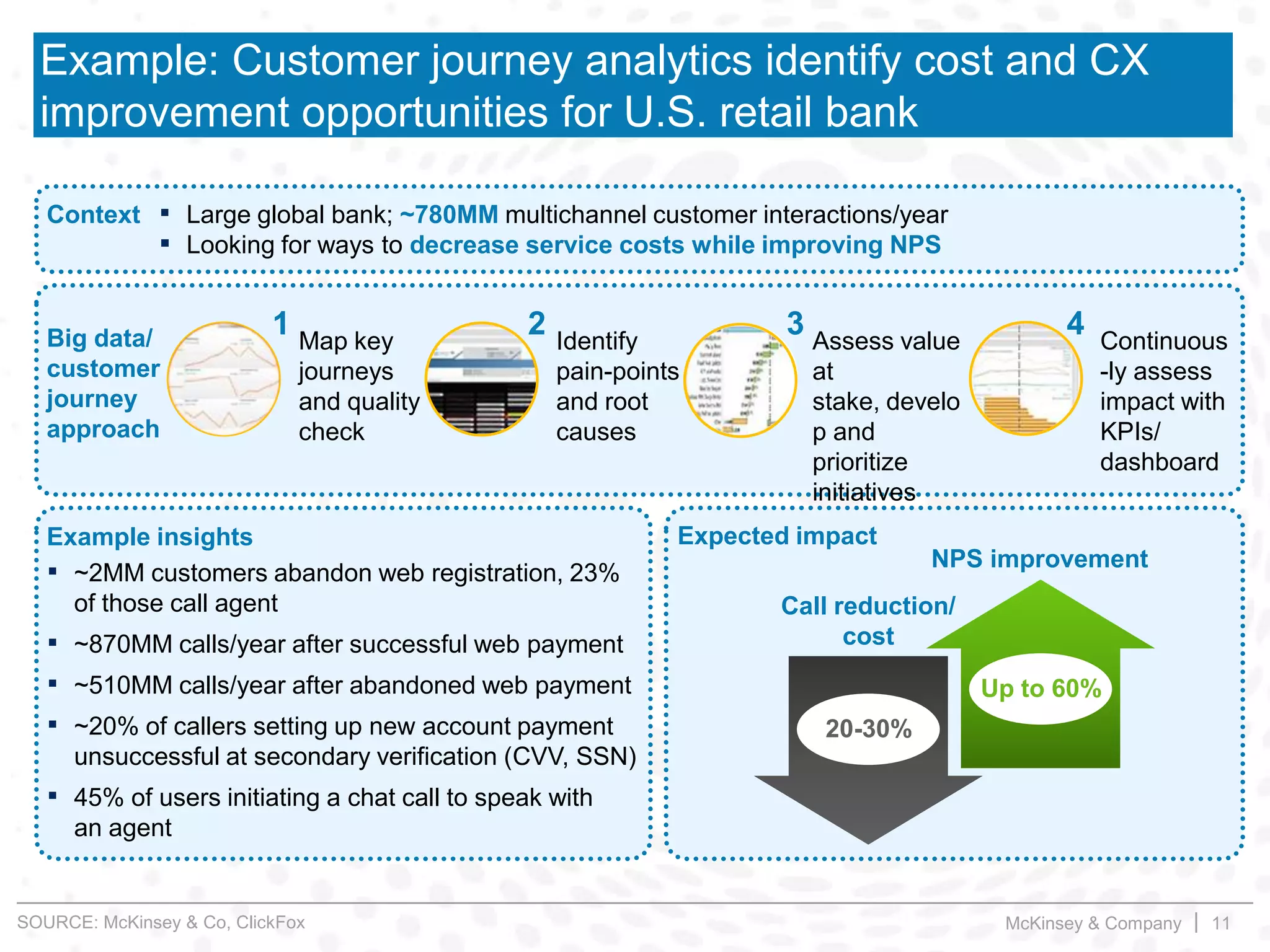
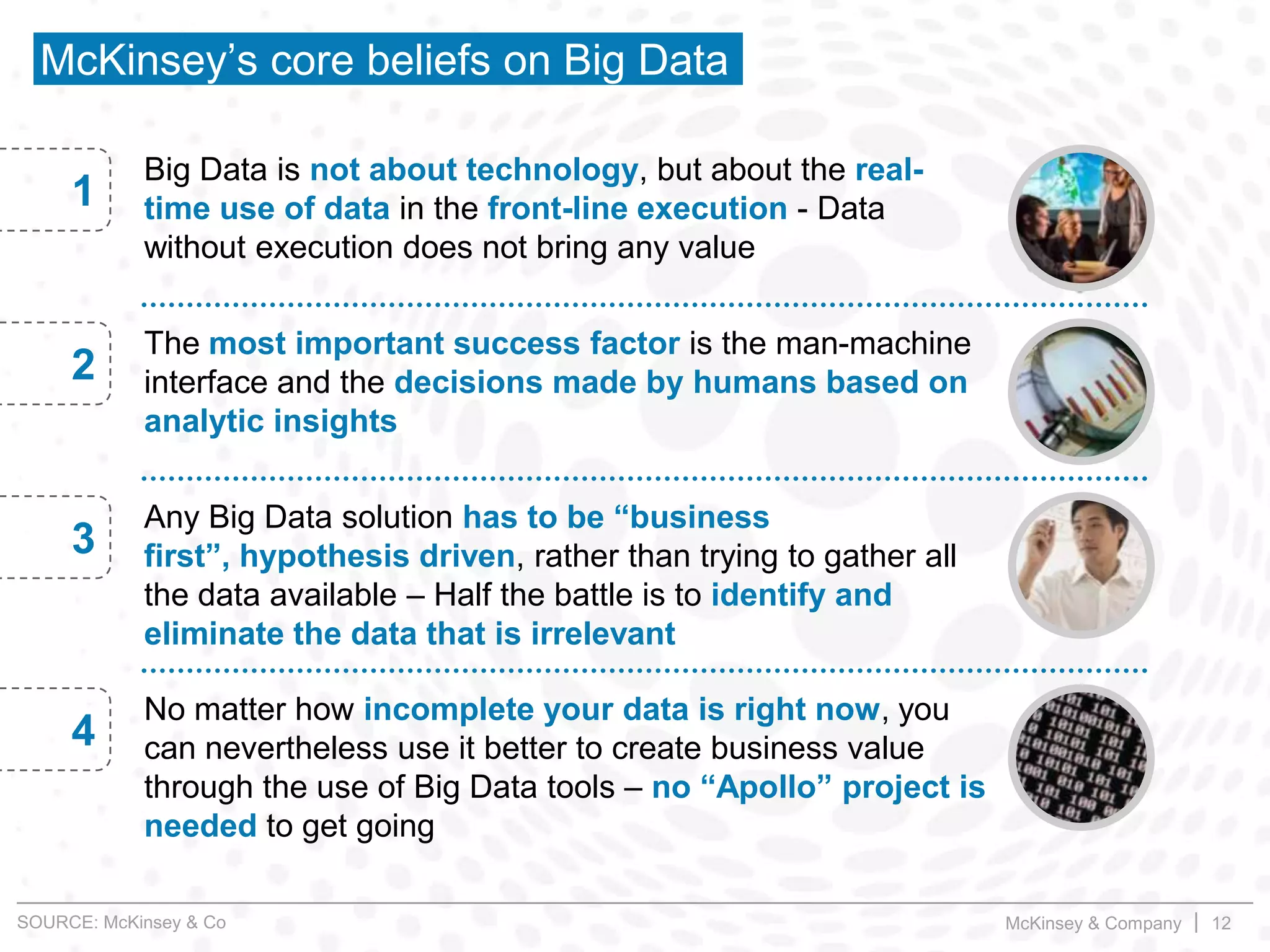
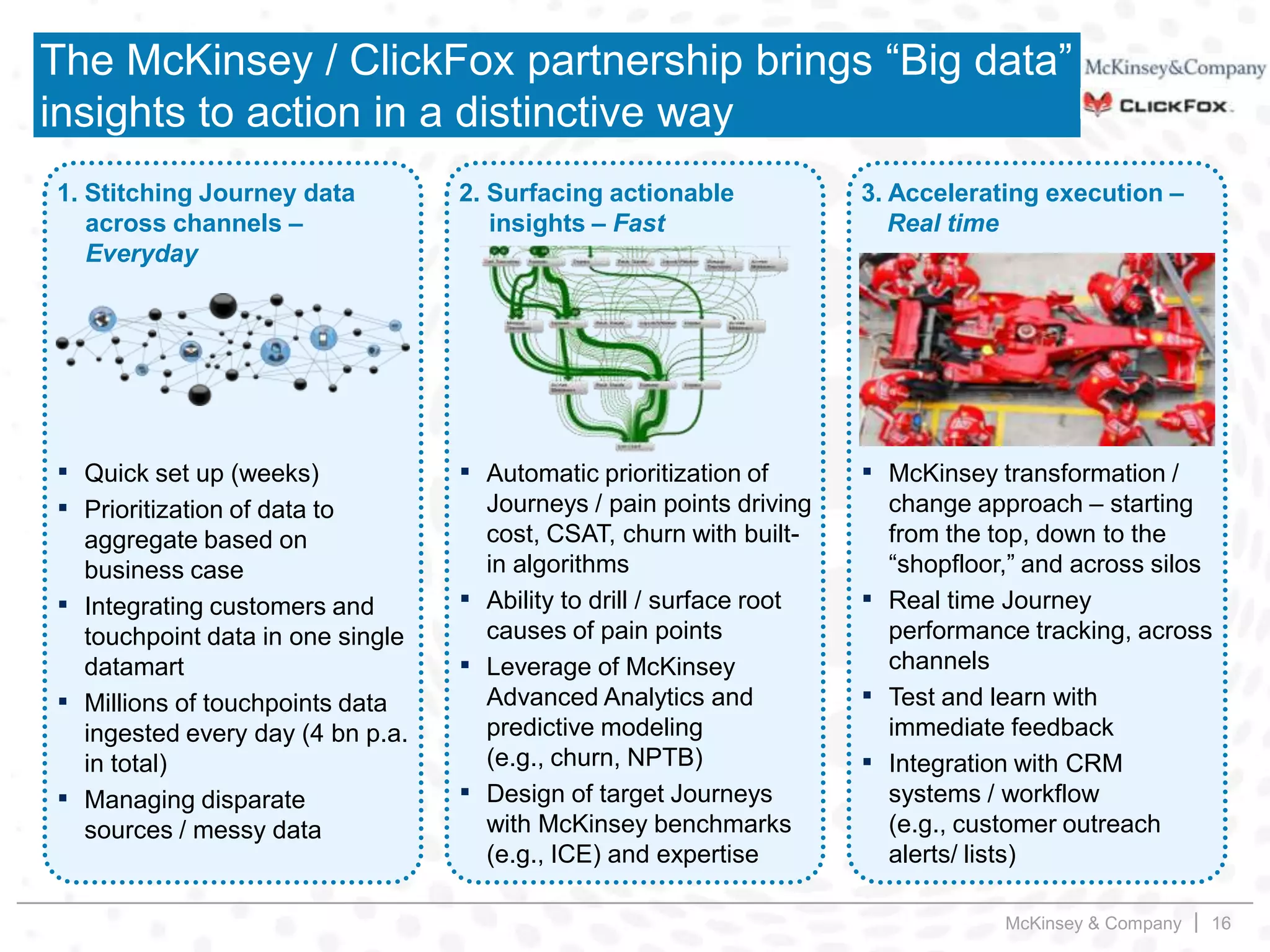
This document summarizes key insights from a McKinsey presentation on customer journey analytics and big data. It finds that companies are storing large amounts of data but few know how to extract value from it. Analyzing customer journeys rather than individual touchpoints provides more predictive insights into customer satisfaction and churn. Mapping important customer journeys in an industry reveals opportunities to improve the customer experience and reduce costs. The presentation provides an example of a retail bank that identified ways to decrease service costs and improve customer satisfaction by analyzing its customer journey data.