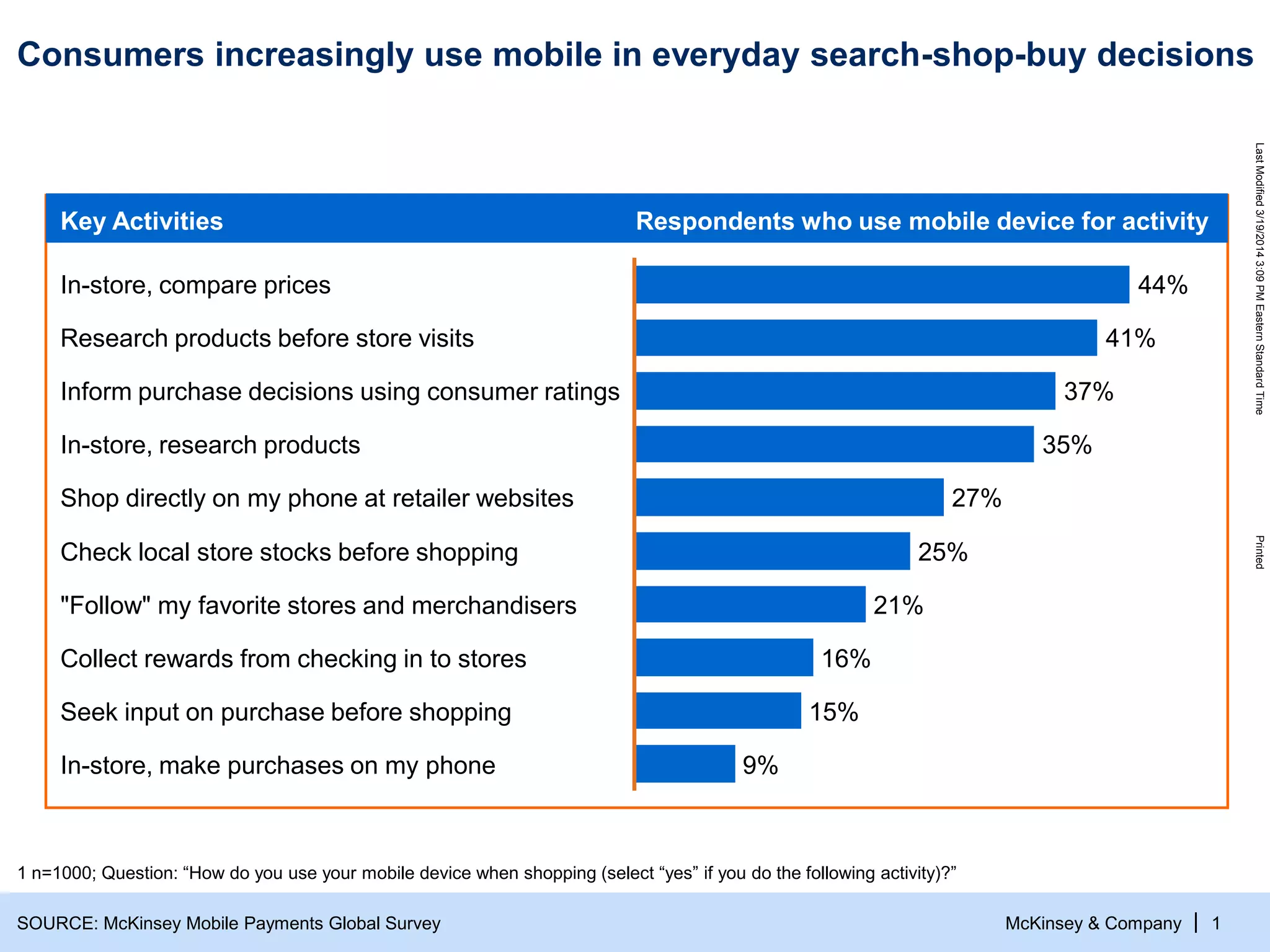
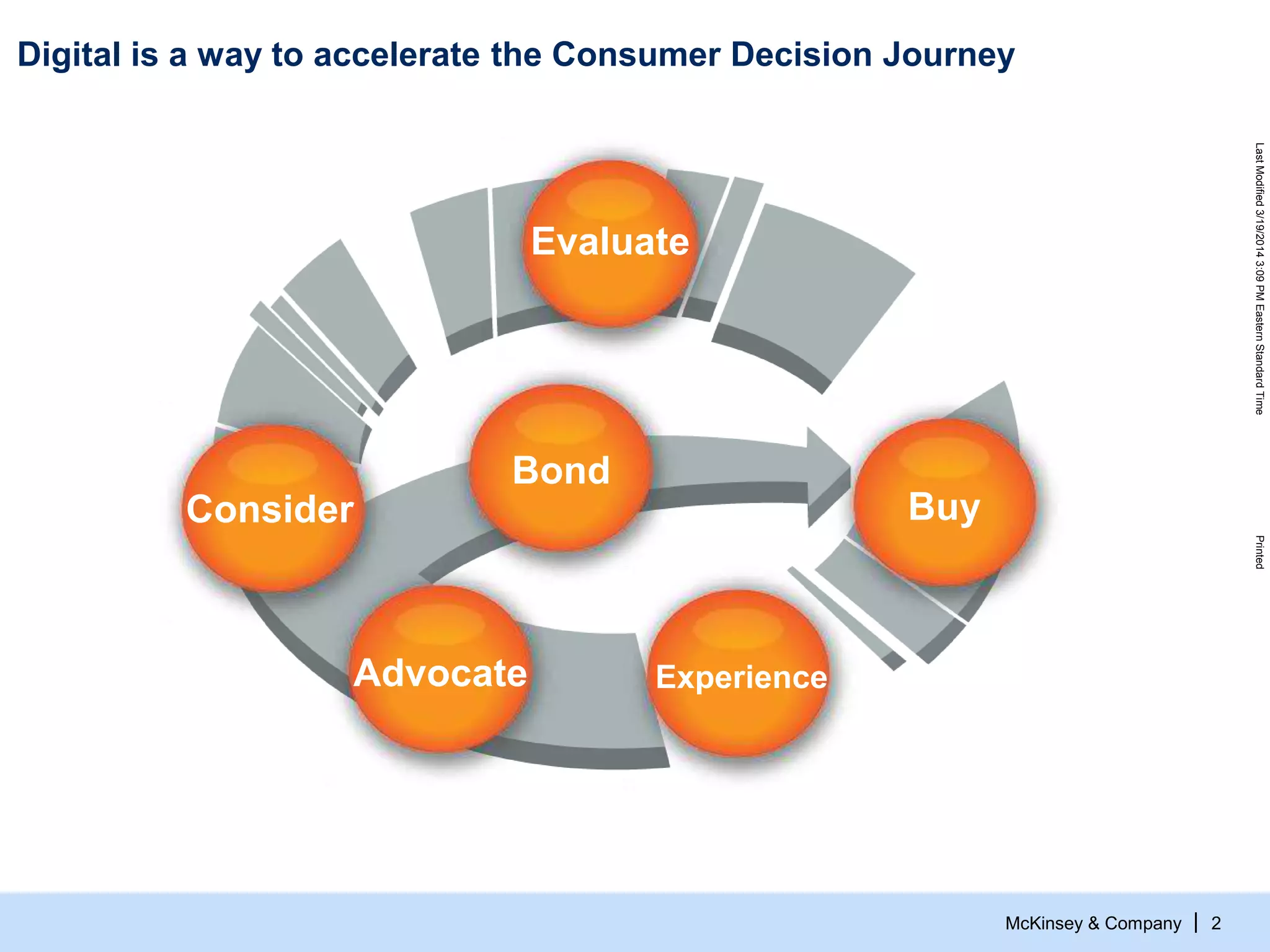
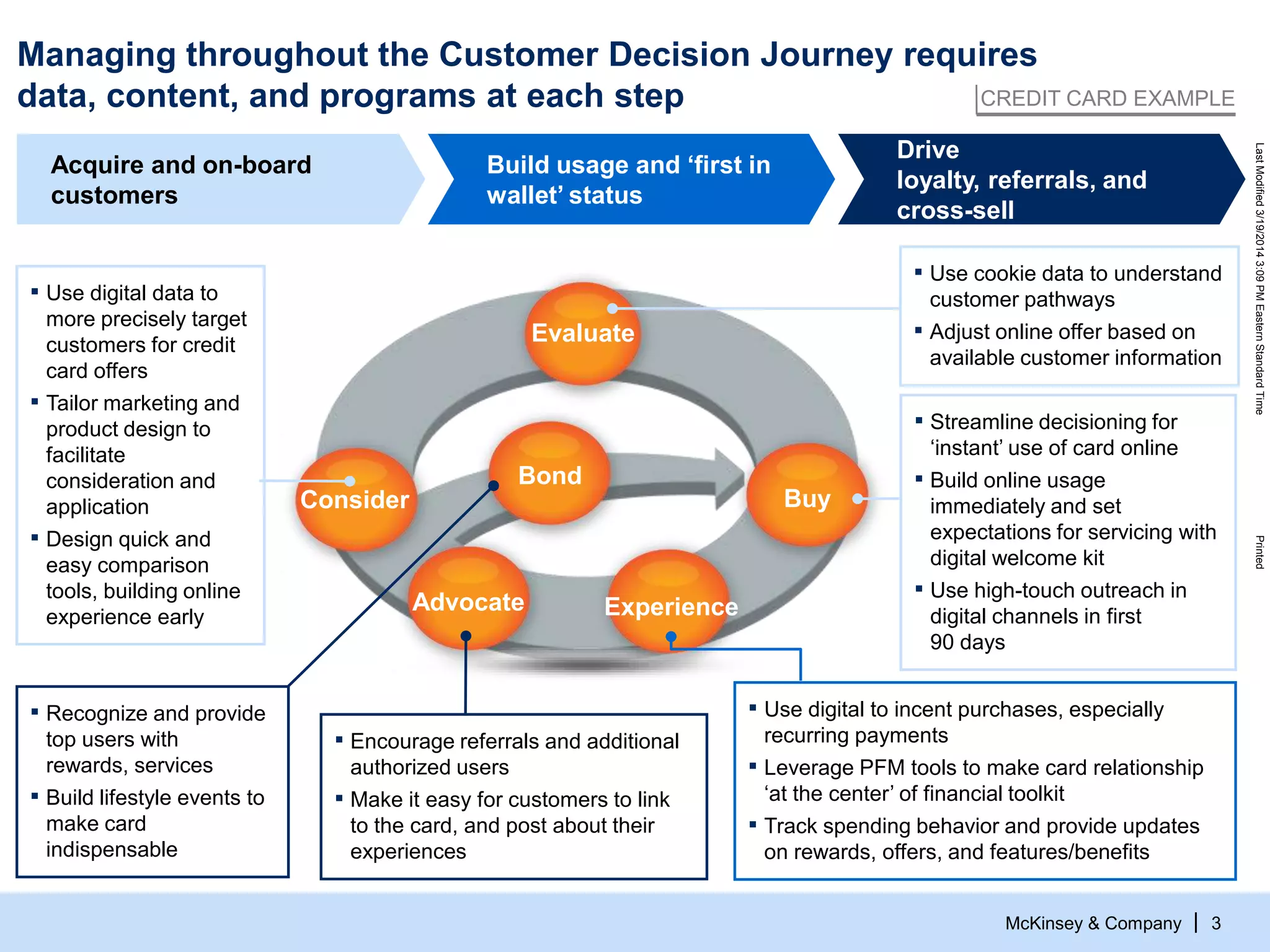
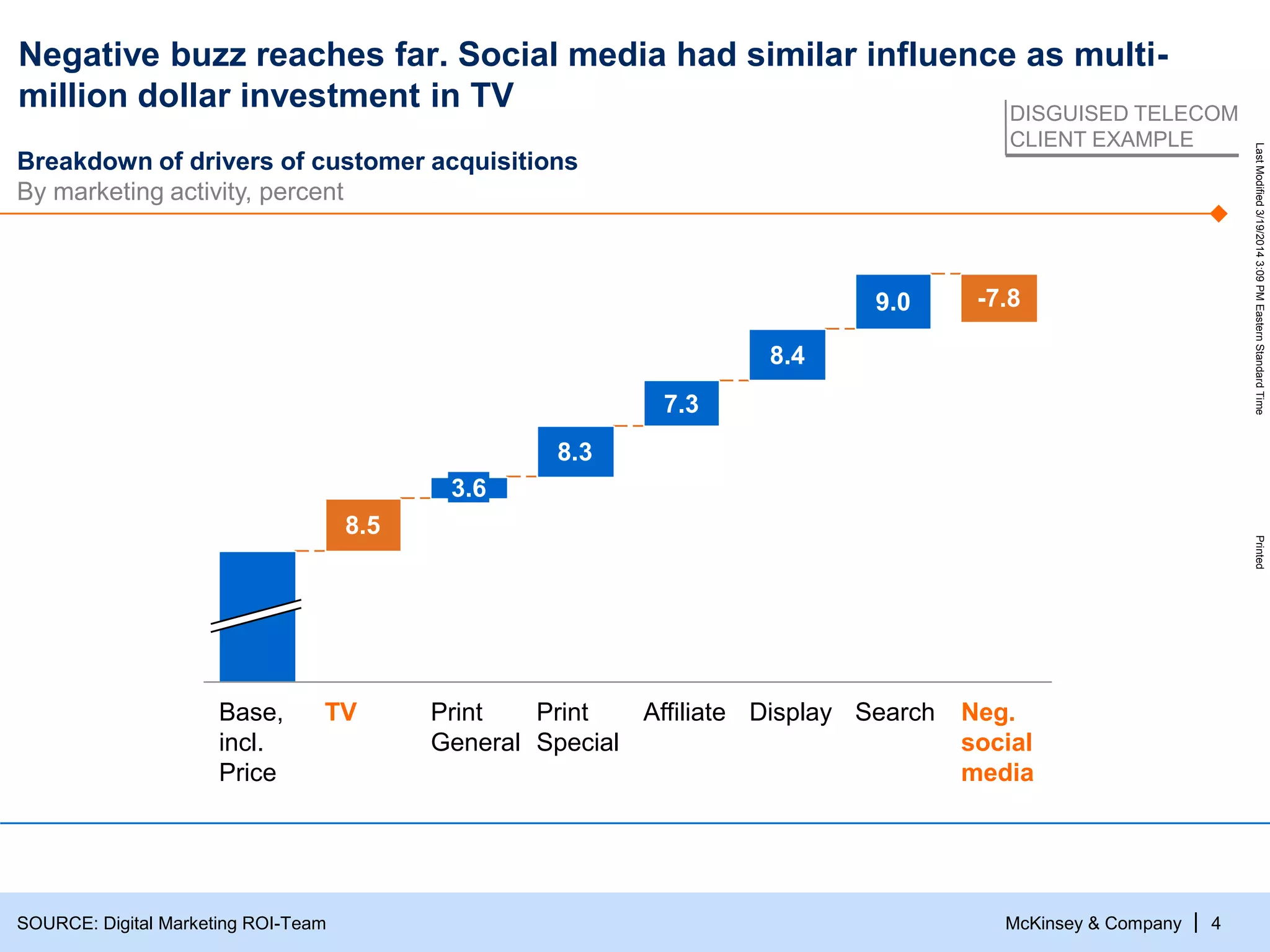
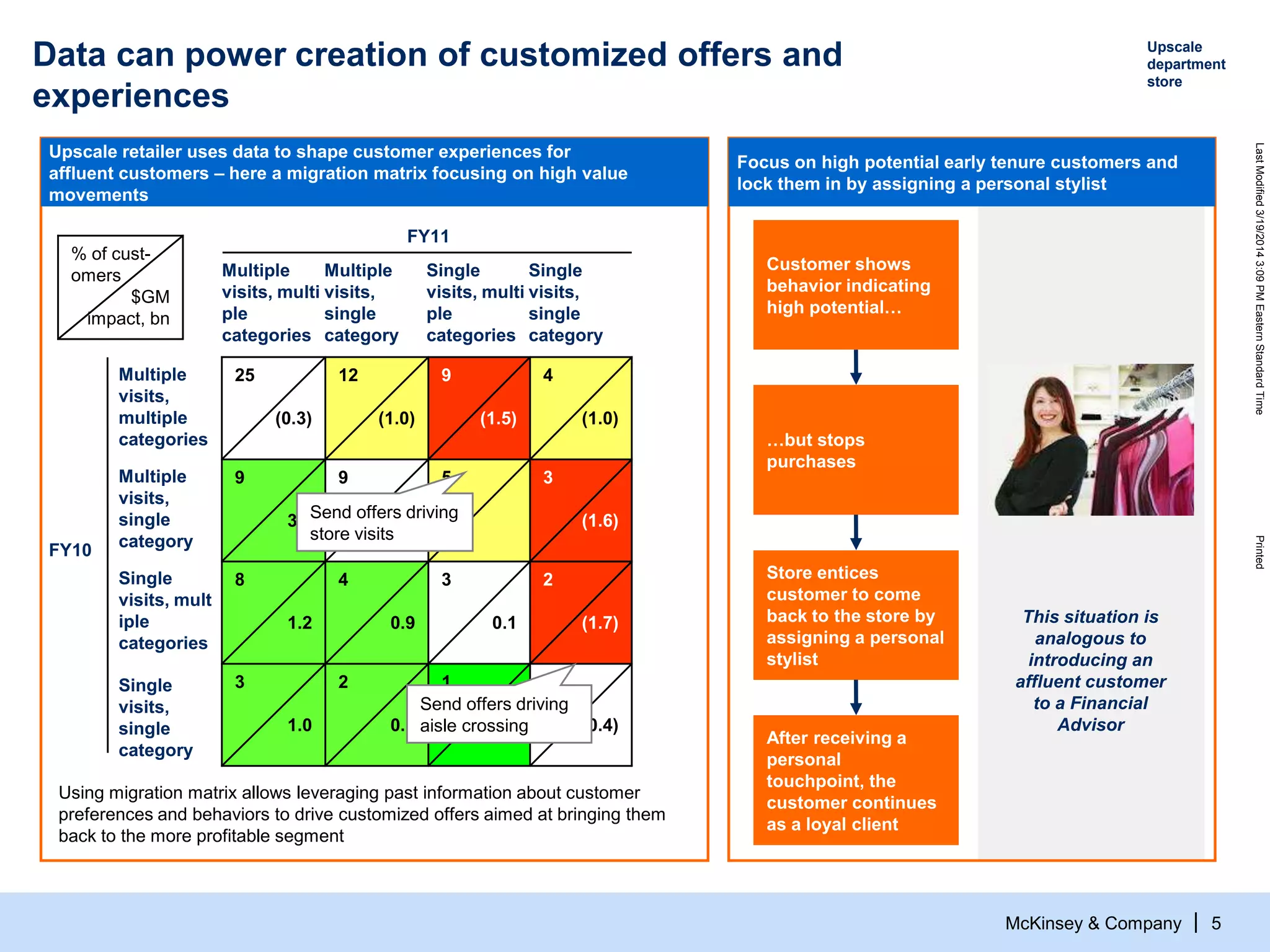
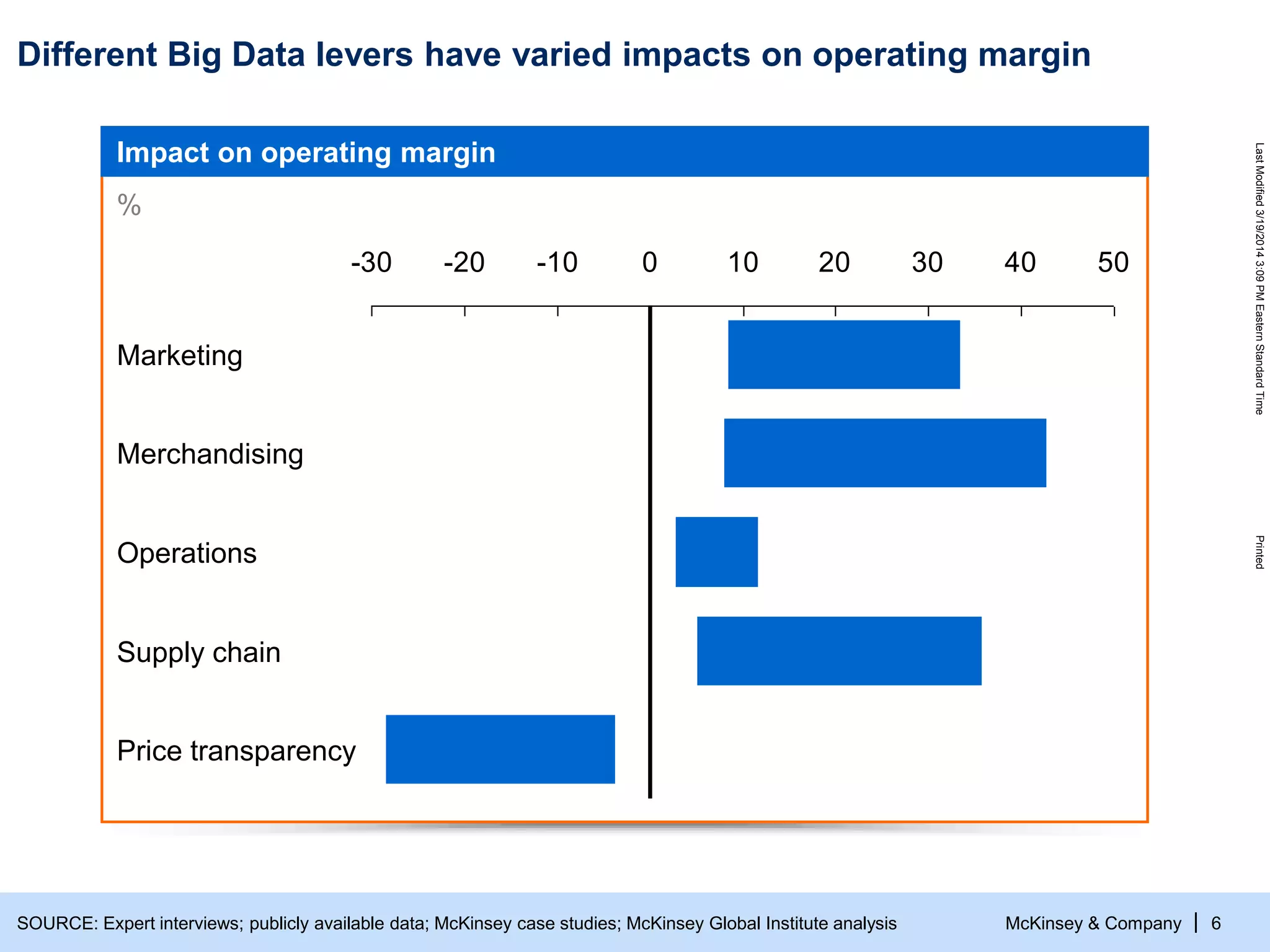
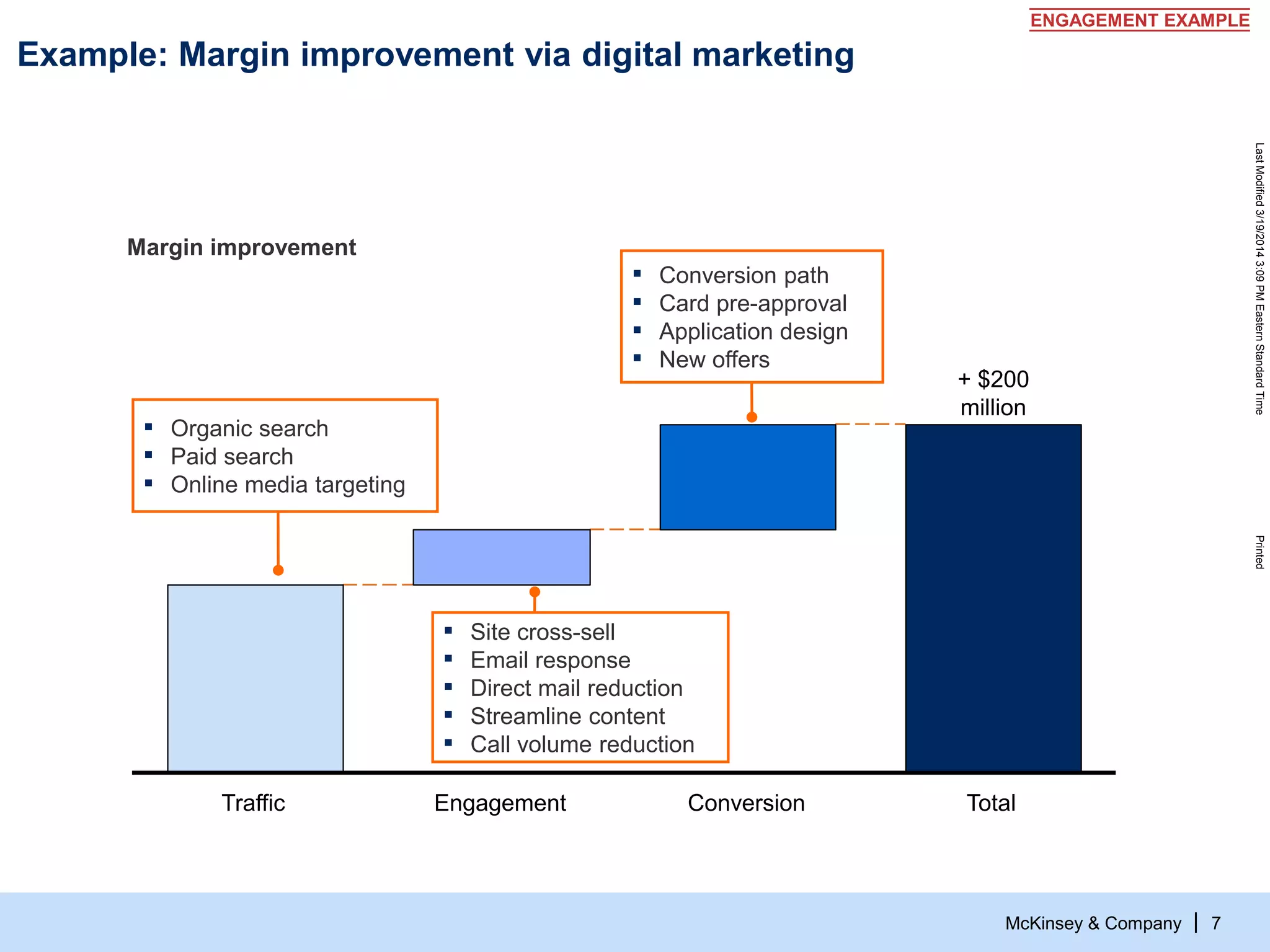
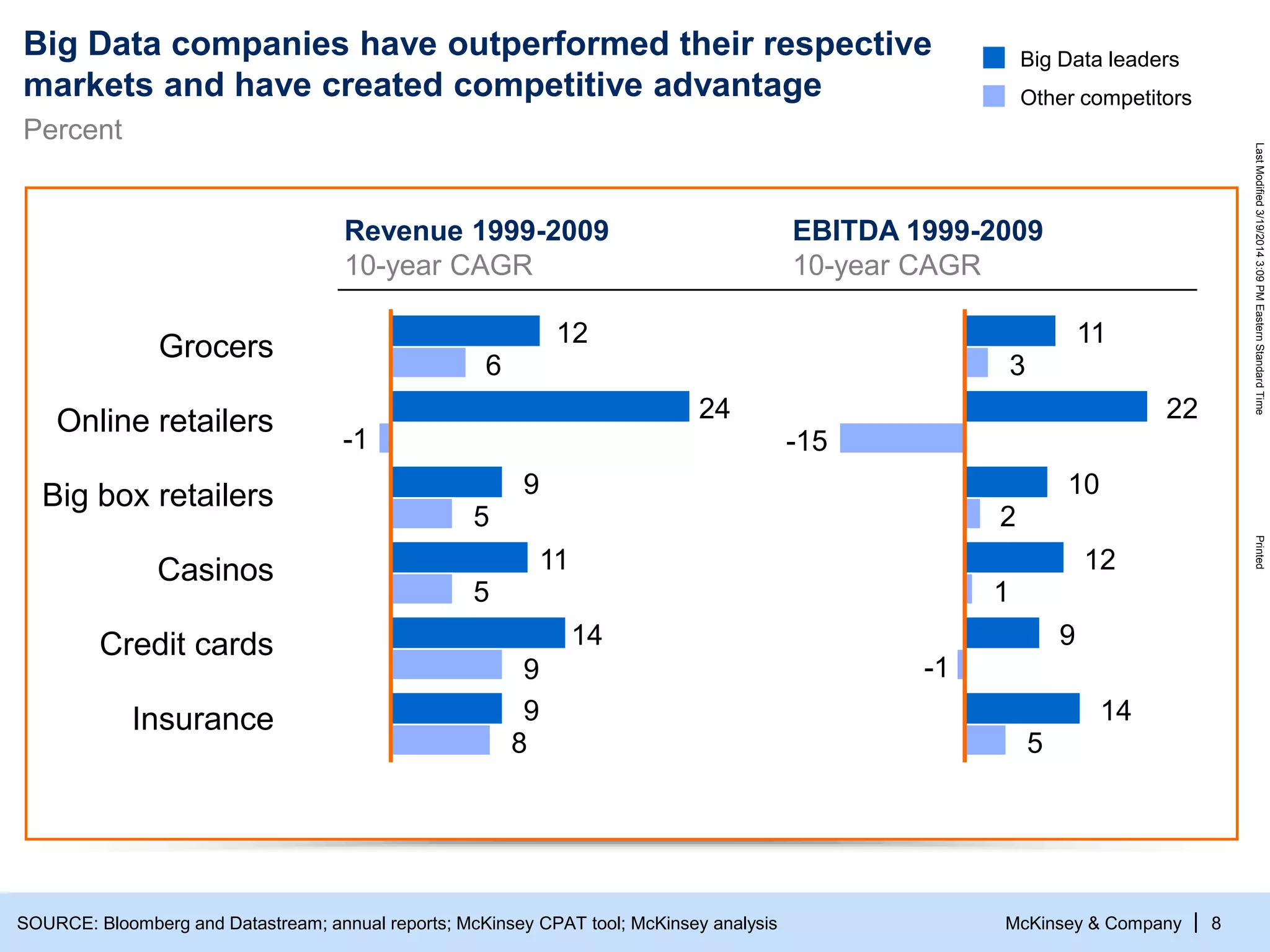
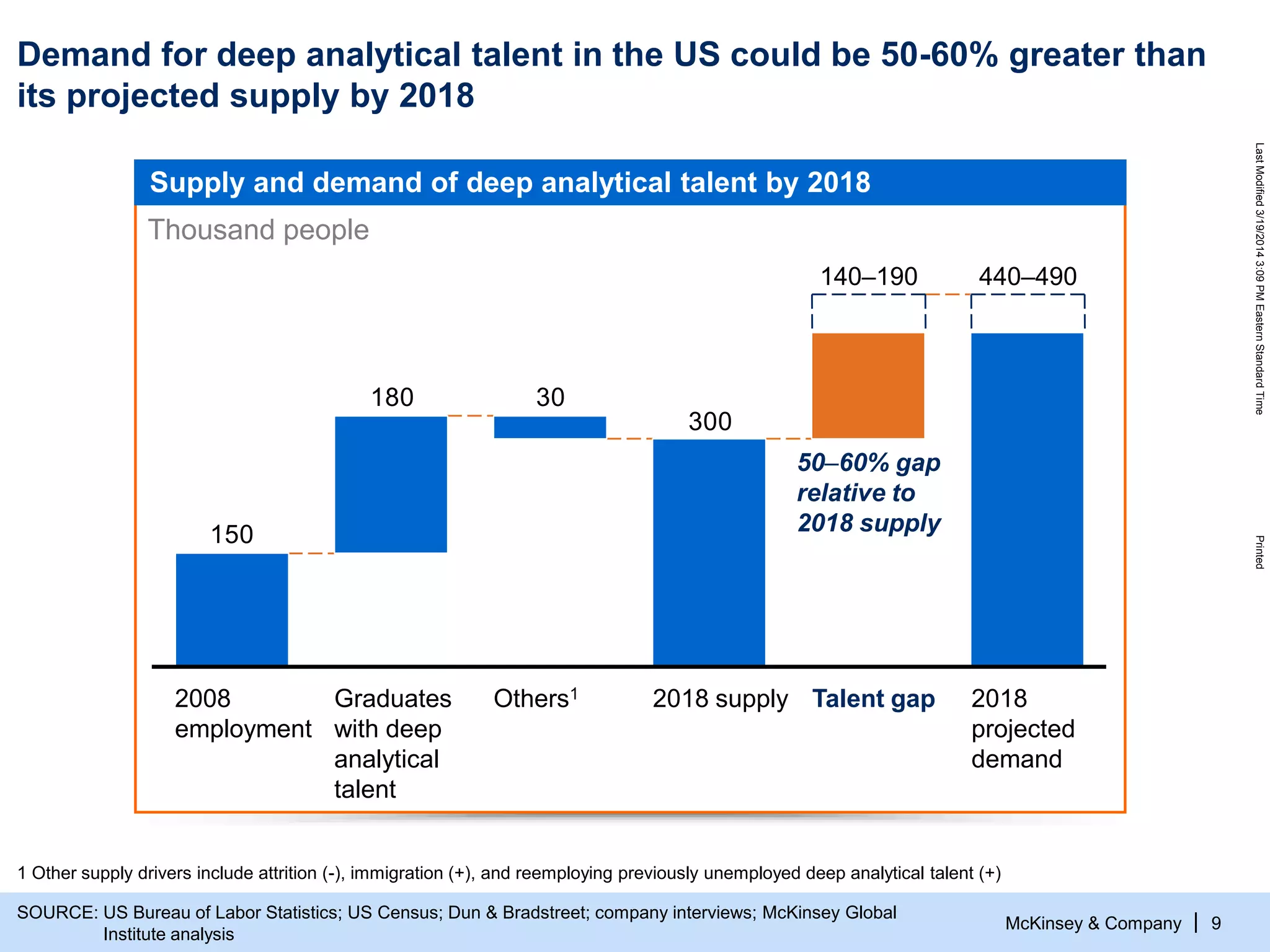
The document discusses the evolving role of digital channels in consumer decision-making, emphasizing the integration of mobile technology in shopping behaviors. It highlights the importance of leveraging data to create personalized customer experiences and to improve marketing strategies for customer acquisition and retention. Additionally, it notes a significant talent gap in deep analytical skills required for digital marketing success as organizations adapt to a more data-driven environment.