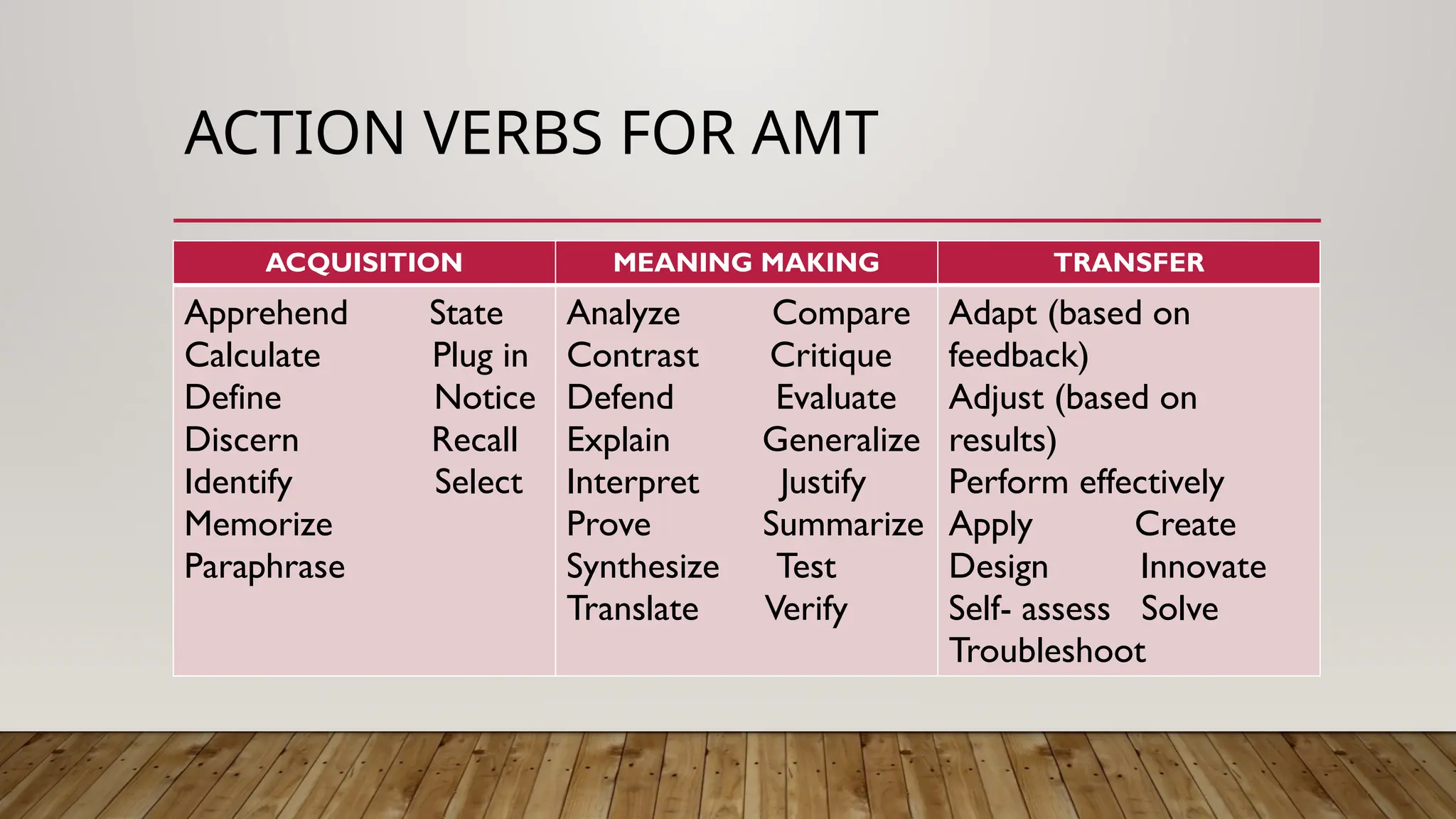
The document outlines a curriculum map developed by Jeorge O. Hugno, focusing on ensuring that acquisition, meaning, and transfer goals are incorporated in the learning plan. It describes various teaching strategies aligned with each goal: direct instruction for acquisition, facilitative teaching for meaning-making, and coaching for transfer. Strategies include diverse methods such as lectures, graphic organizers, and problem-based learning to enhance student learning outcomes.