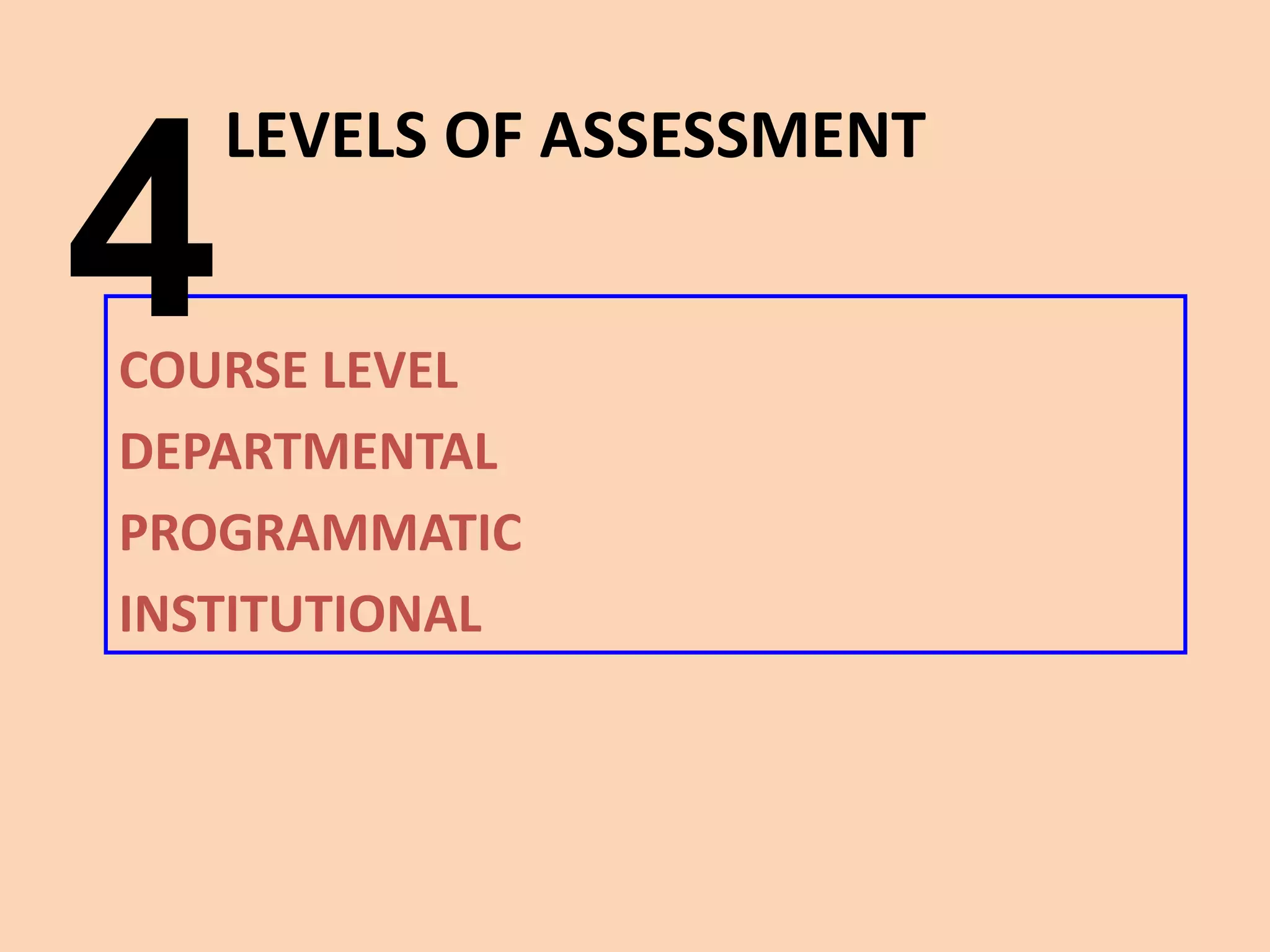
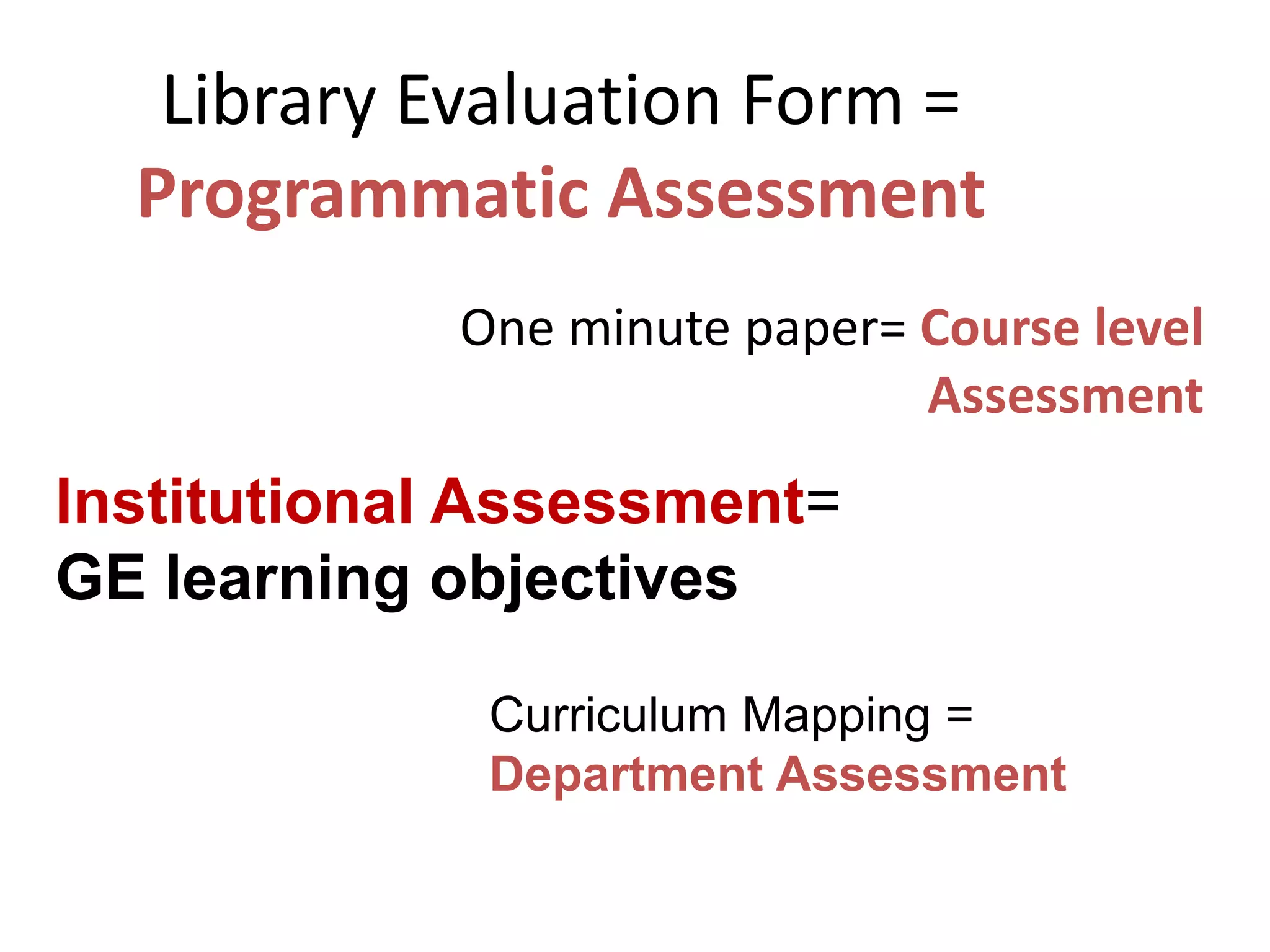
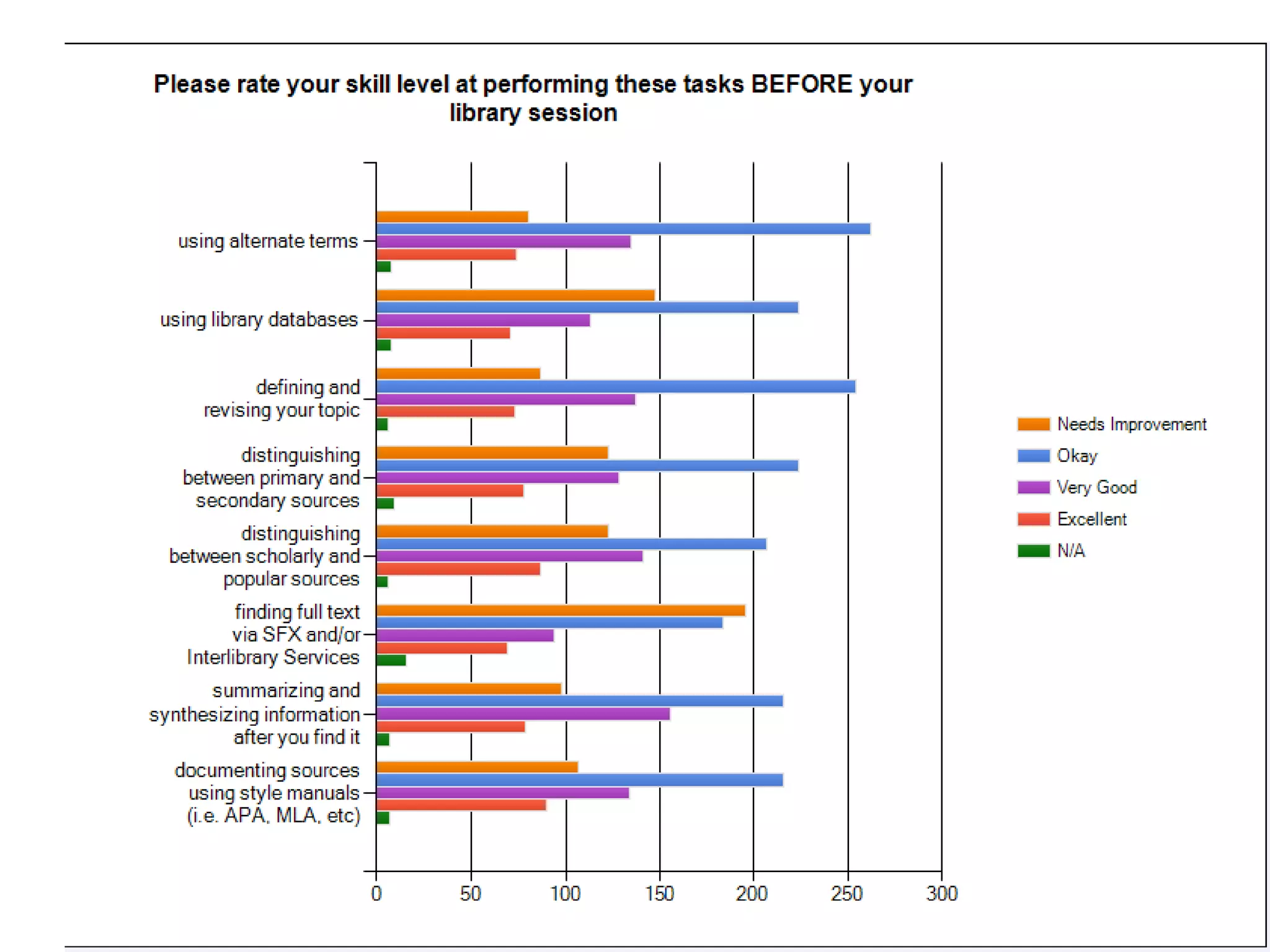
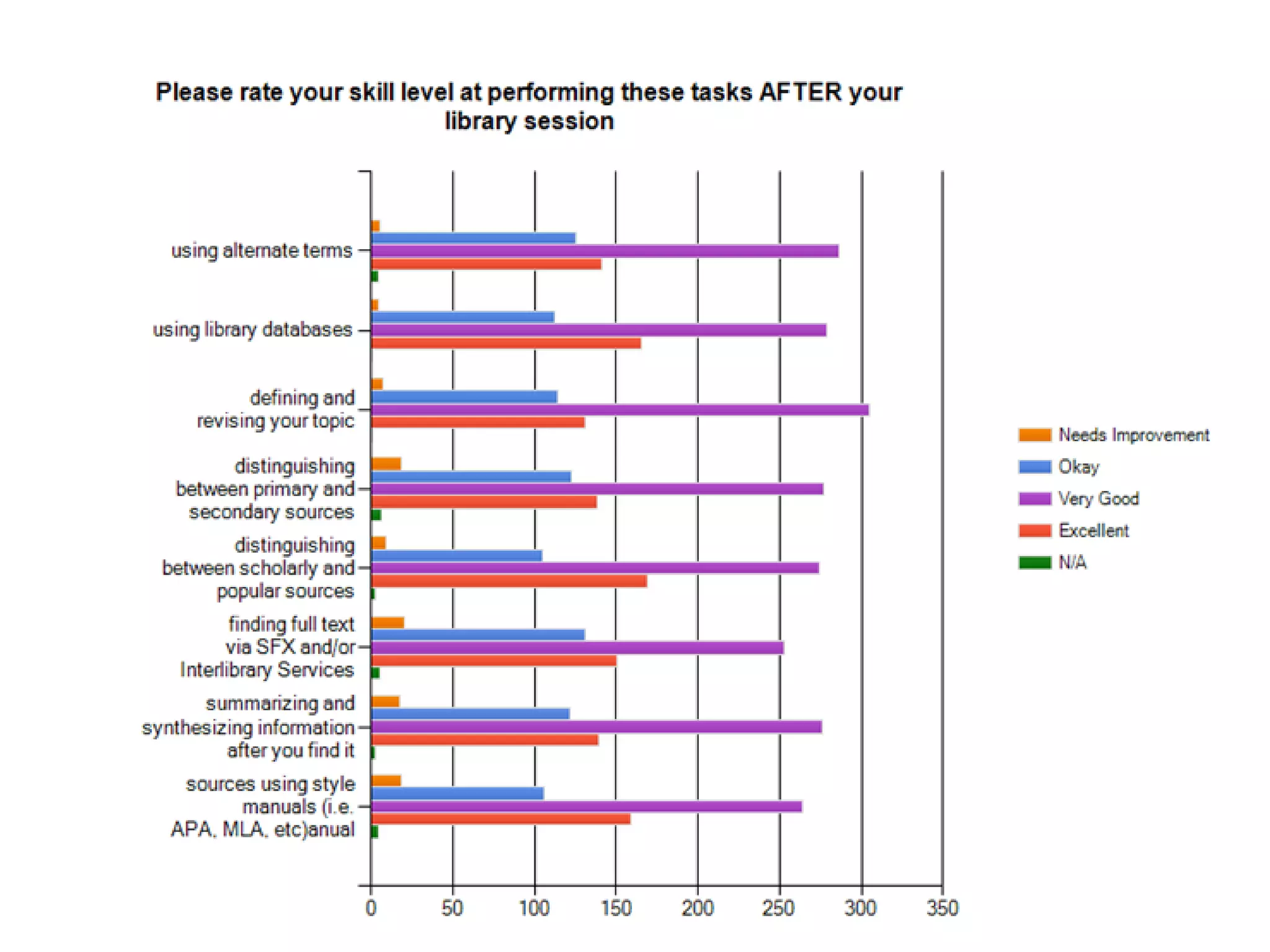
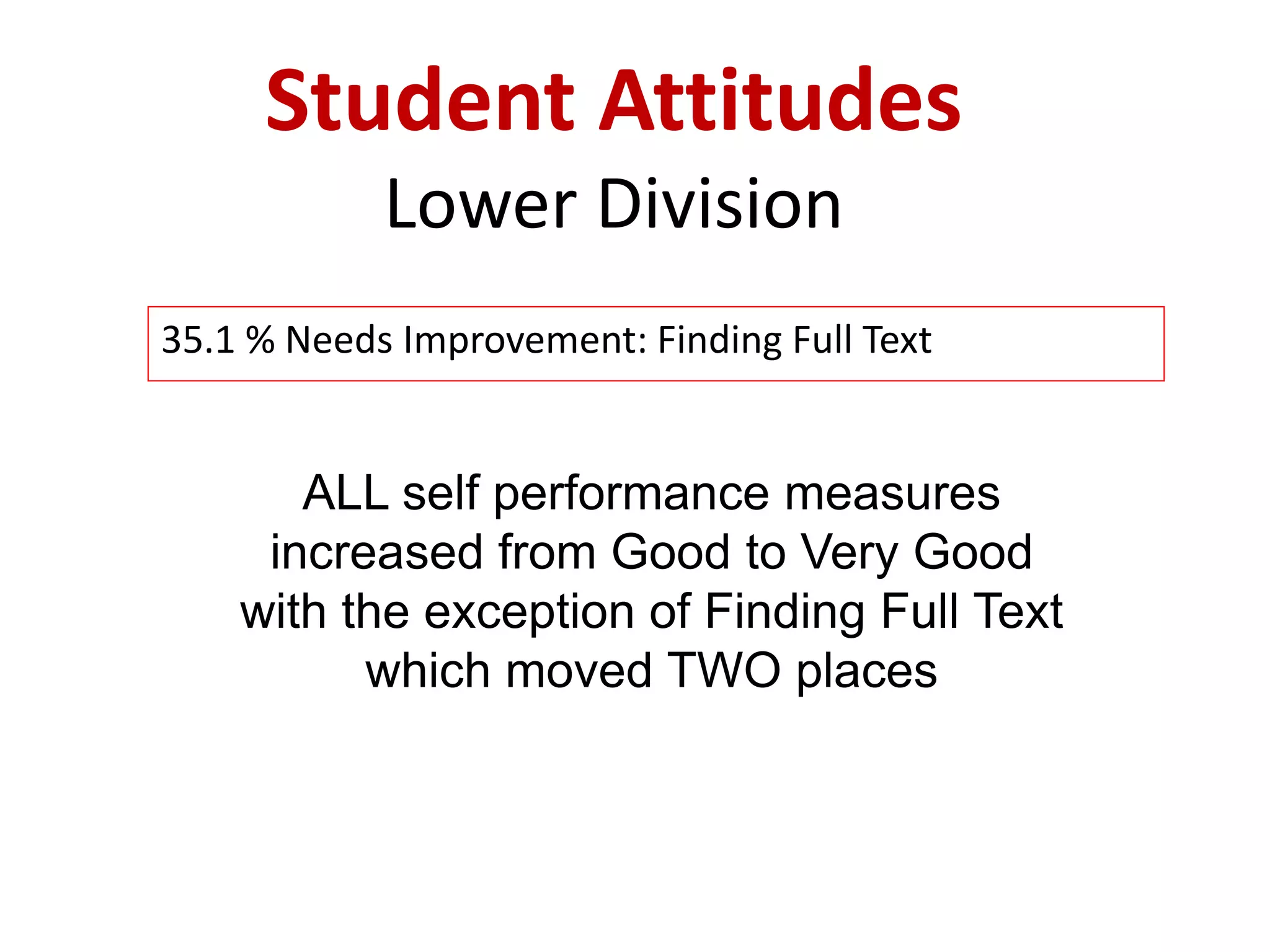
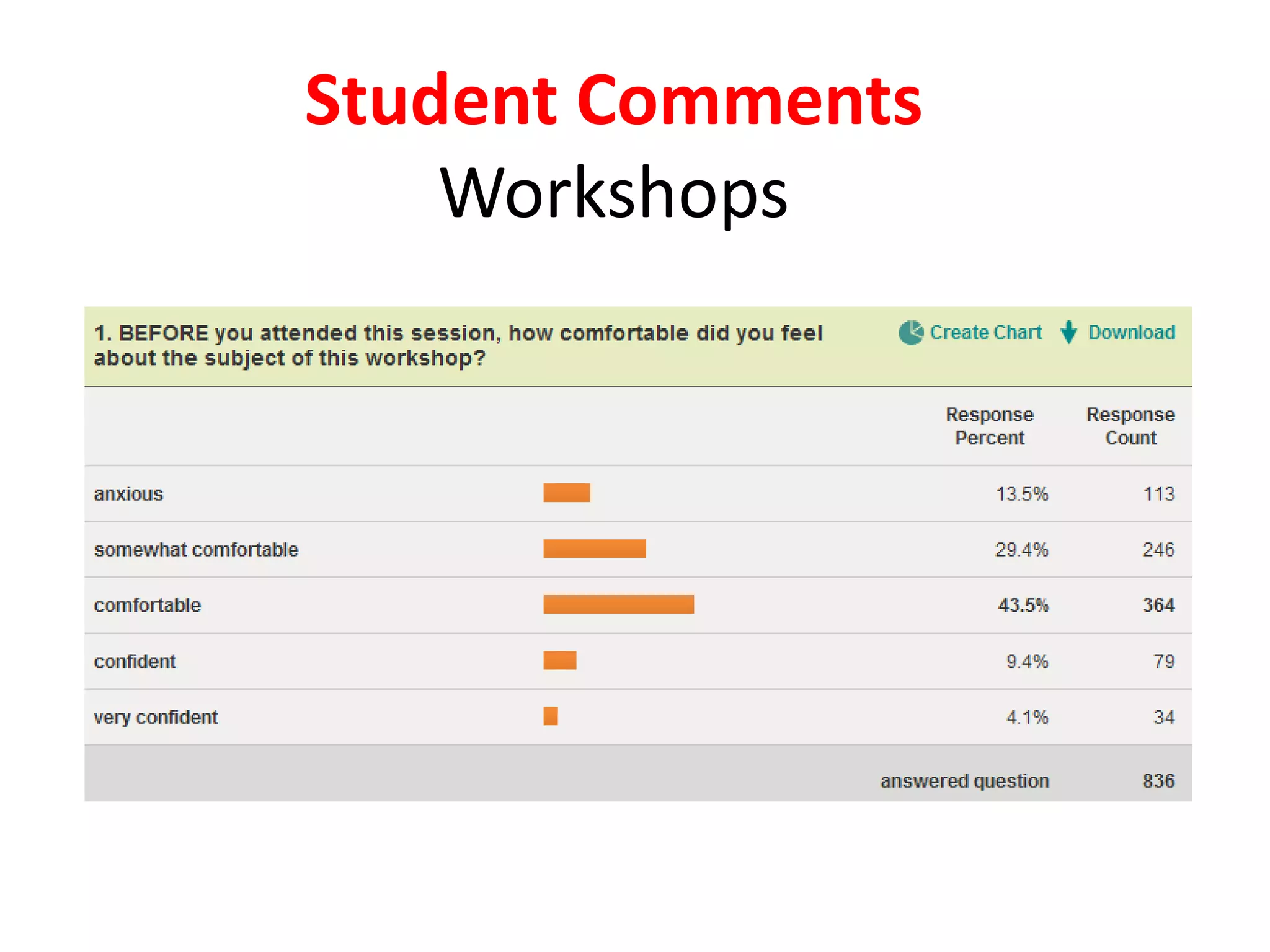
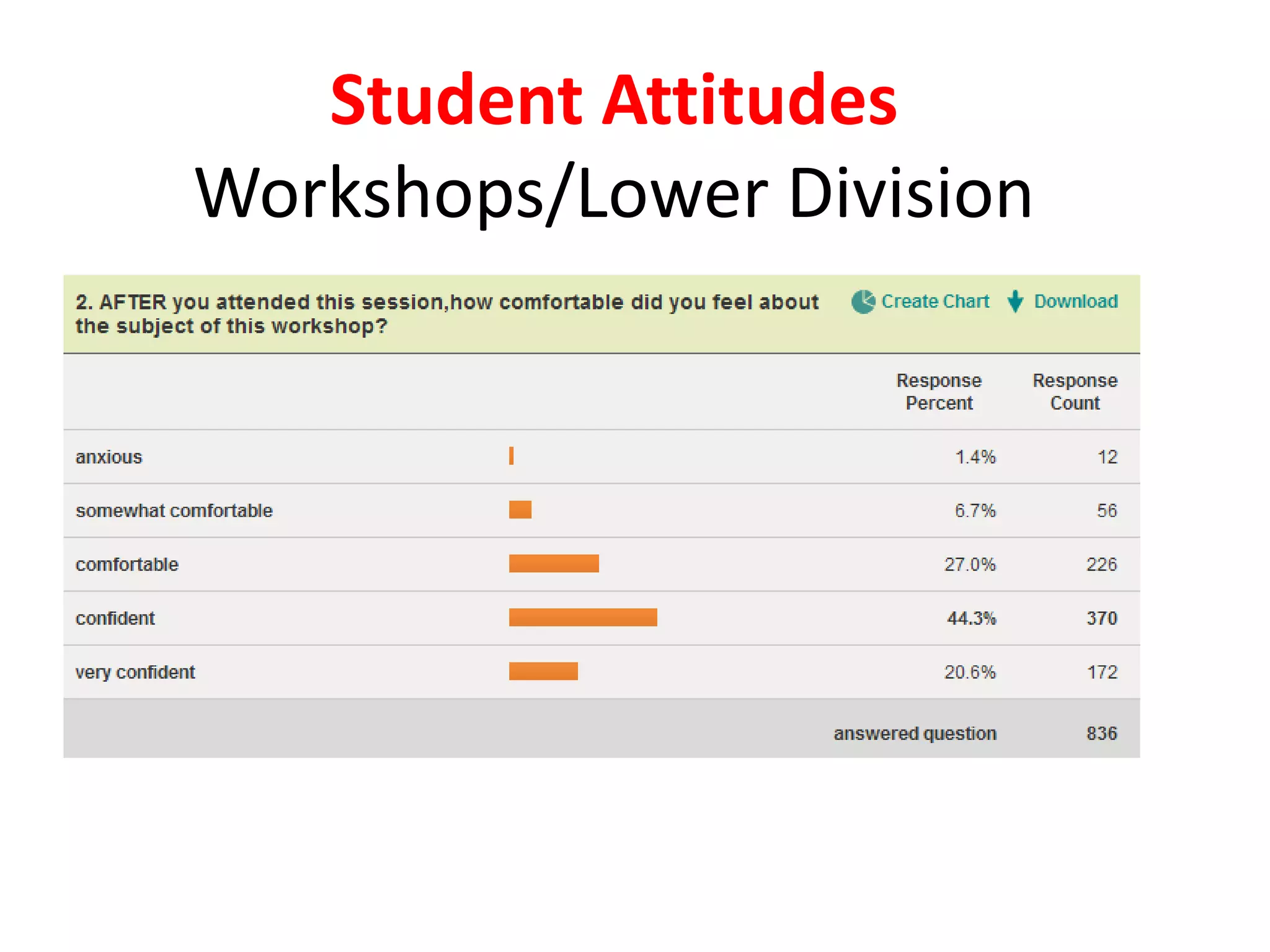
This document provides an overview of the content to be covered on day two of an art center information literacy and curriculum development workshop. It includes recapping day one, curriculum mapping, understanding learners, significant learning experiences, teaching styles, lesson planning, and assessment. Faculty will apply what they have learned by developing curriculum maps and lesson plans. The goal is to help faculty design effective instruction that engages students and assesses learning outcomes.