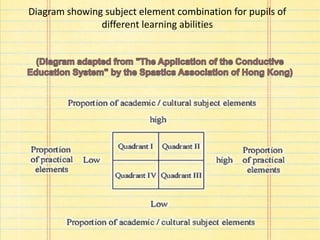
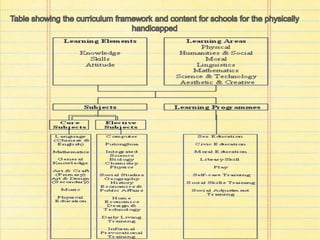
The document discusses considerations for designing curriculums for children with physical disabilities. It notes that while some have unaffected learning abilities, over half have additional mental or physical limitations. When planning, individual differences in movement, communication, daily living skills, social skills, and career development must be accounted for. The curriculum should be pupil-oriented, emphasize total development, integrate learning across subjects and school life, and prepare students for integration after school. Core subjects include languages, math, general knowledge, art/design, music, and PE, with electives like computer science, Mandarin, science courses and social studies. Learning programs outside class time focus on skills like sex education, library skills, self-care, and social adjustment