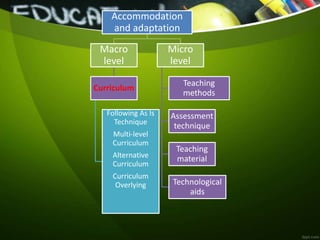
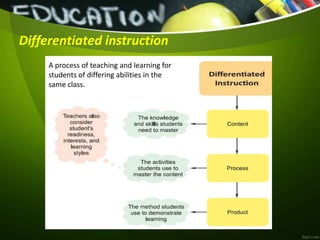
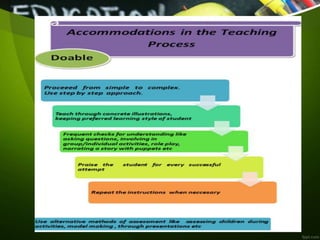
The document outlines a syllabus for inclusive education, focusing on instructional design and collaboration strategies for diverse learners. It emphasizes the importance of curriculum adaptations, differentiated instruction, and the use of assistive technologies to create inclusive learning environments. Additionally, it addresses the necessity of fostering social competence and providing equal opportunities for students with special needs through effective teaching methods and support systems.


![Practical: Critical study of any Special teacher
training college or Institutes
• Study following Points of special teacher training institute need to include
in file:
• 1] Introduction
• 2] Objectives
• 3] Vision
• 4] Mission
• 5] Infrastructural Facilities
• 6] Section wise work: Administration and academic work
• 7] Other activities of institute
• 8] Educational Importance
• 9] Special features of institute
• 9] Interview/ Questionnaire analysis
• 10] Report writing of visit
• 11] photos of visit](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inclusivecurriculum-230914114426-7bb13de1/85/Inclusive-curriculum-pptx-3-320.jpg)