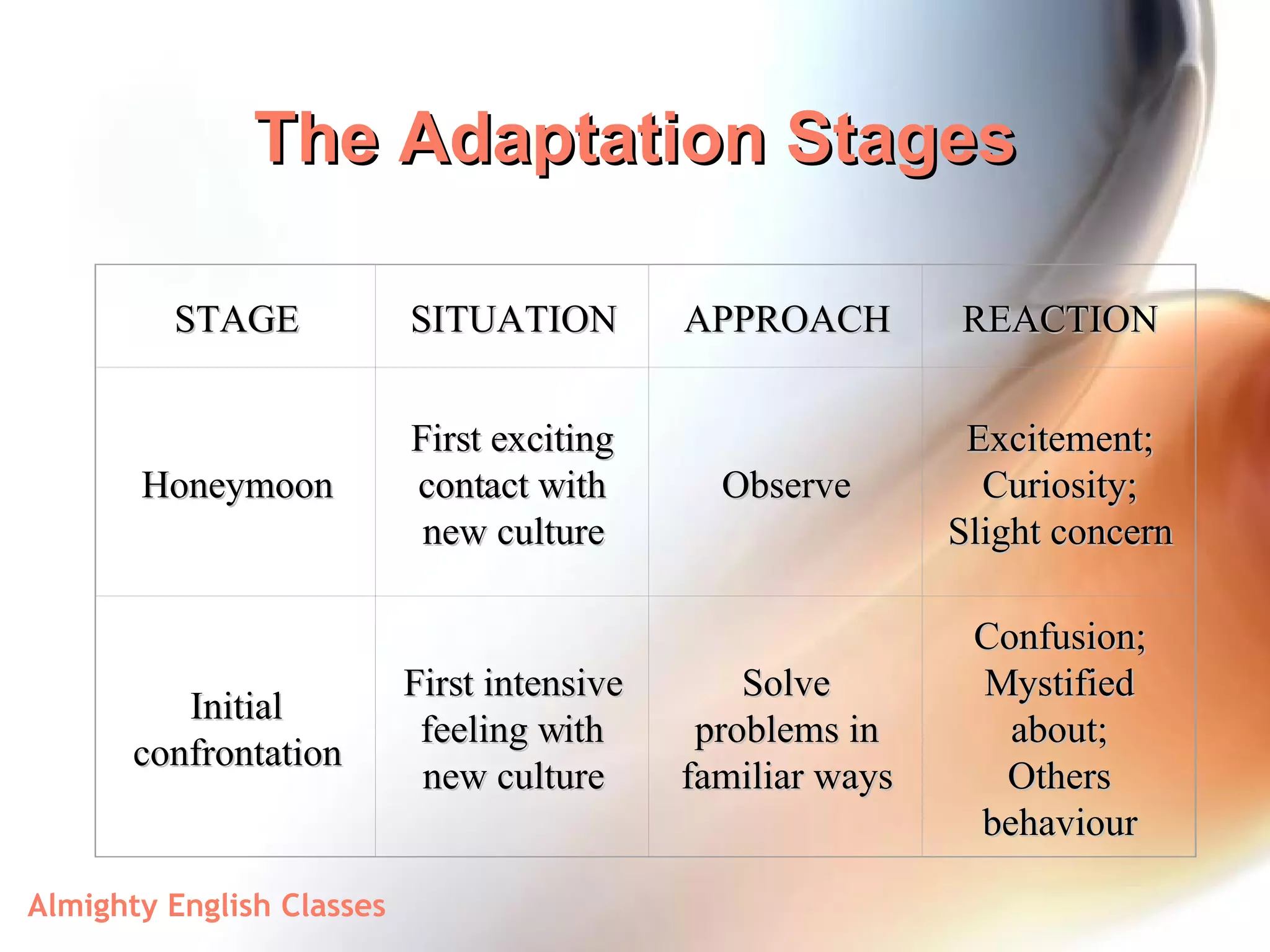
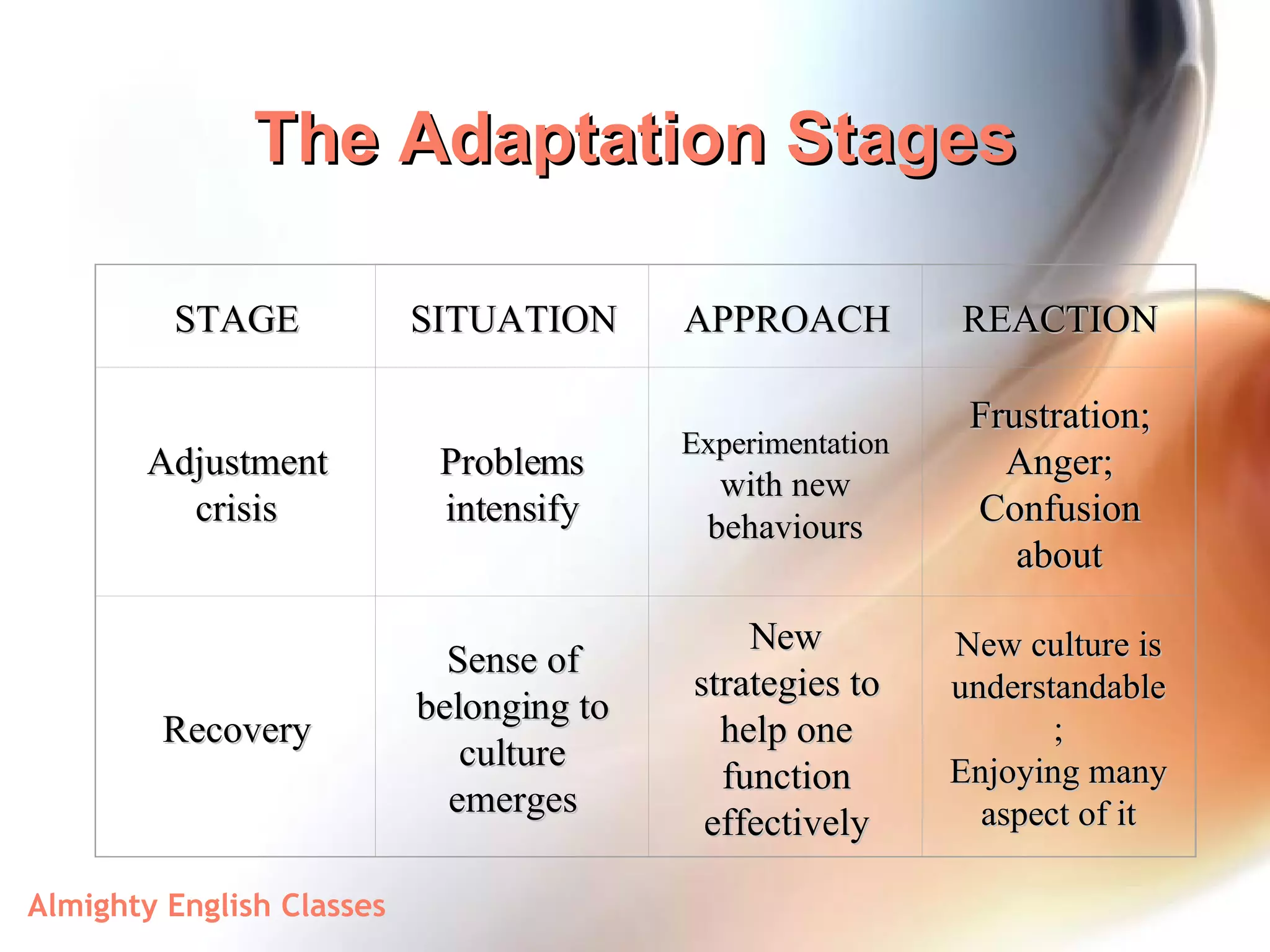
This document discusses cultural awareness and differences. It begins by defining culture and explaining that it is relative, learned, and changes over time. It then discusses some forces that shape individual cultures like values, beliefs, education, and religion. The document outlines some dangers of stereotypes and ethnocentrism. It provides examples of cultural differences in areas like eating habits, religion, family structures, communication, and time. It stresses the importance of understanding other cultural frameworks and seeing cultural differences as creative problem-solving opportunities. The document also discusses the stages of cultural adaptation like honeymoon, initial confrontation, adjustment crisis, and recovery.