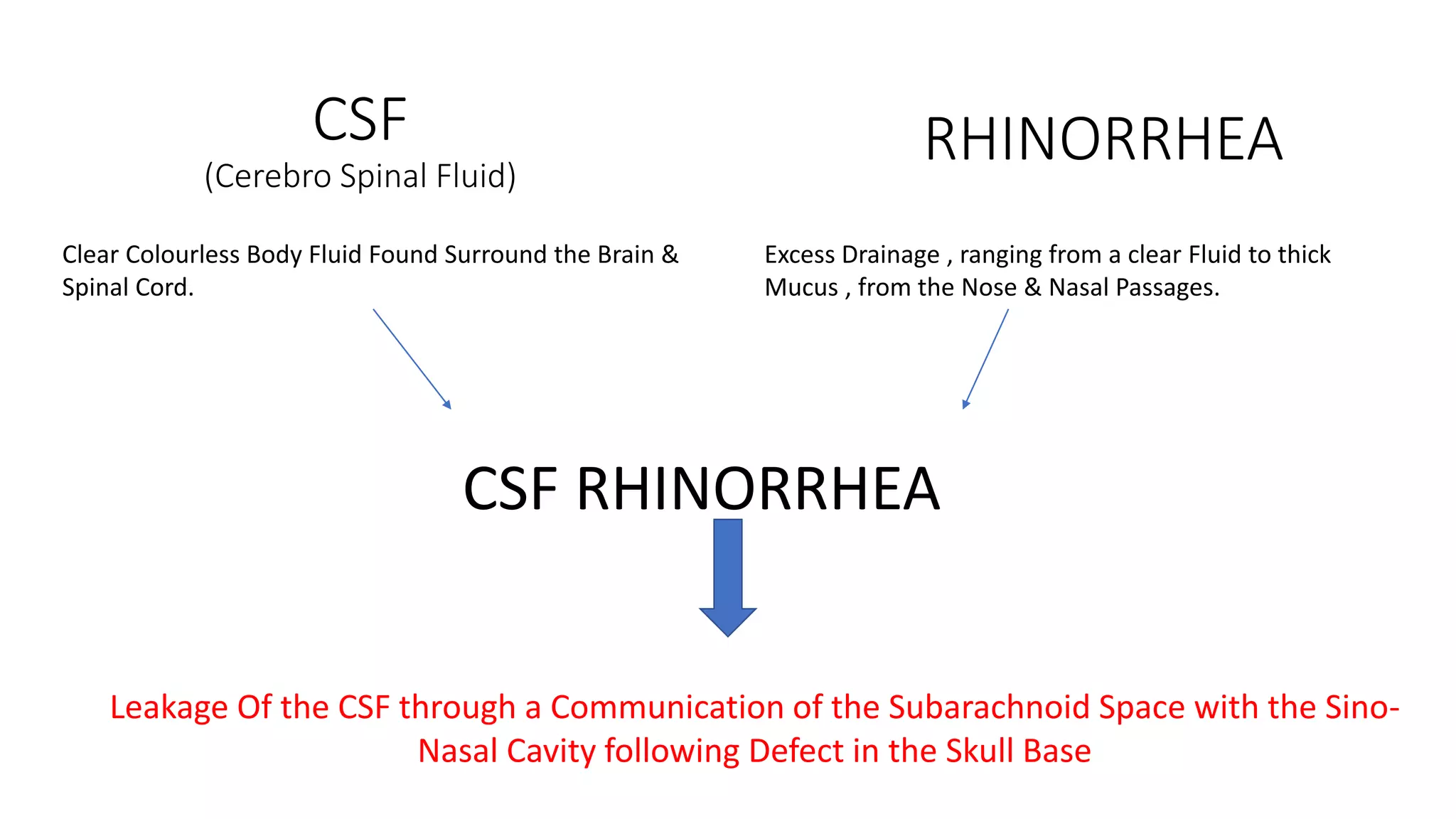
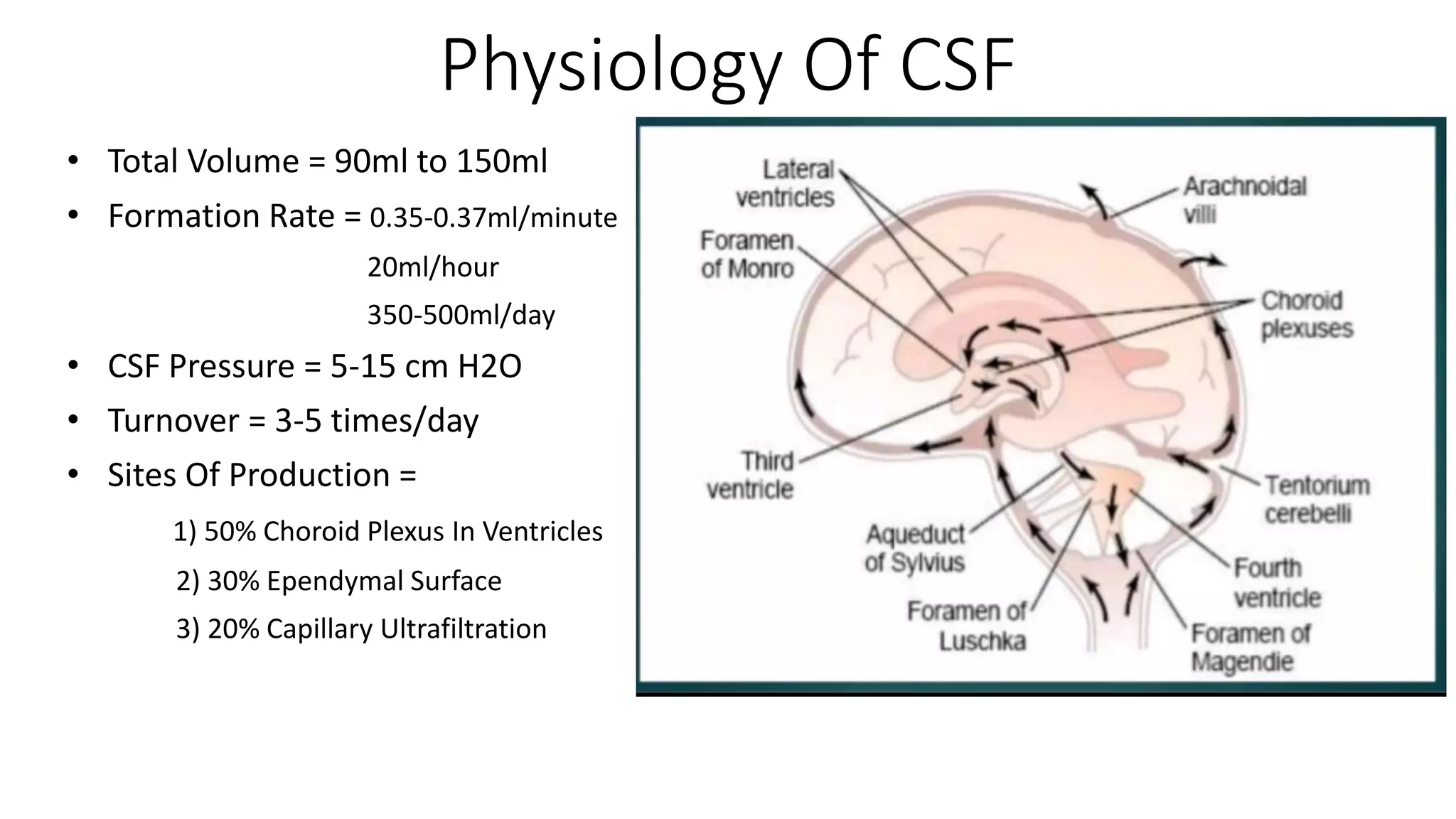
This document discusses cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) rhinorrhea, which is the leakage of CSF through the nose. It outlines the anatomy and physiology related to CSF, various causes of CSF leaks, clinical signs and symptoms, diagnostic tests including beta-2 transferrin and imaging, and management approaches including conservative treatment and surgical repair via an endoscopic or external approach. Surgical repair involves identifying and closing the defect using grafts such as fat, cartilage, or fascia and postoperative care including packing and bed rest is emphasized.
![CSF RHINORRHEA
Dr. Jeet M. Amin
Resident Doctor, ENT Department, PDU Medical College & Hospital, Rajkot
Dr. Manoj G. Amin[M. S., ENT]
JEET ENT Hospital, Deesa
HOD, ENT, AASHKA Multispecility Hospital, Gandhinagar](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csfrhinorrhea-210321134232/75/CSF-Rhinorrhea-1-2048.jpg)



![Clinically
• Watery Nasal Discharge [unilateral >> bilateral]
• Headache
• Anosmia
• Vertigo +/-
• Pulsatile Tinnitus
Lately Meningitis, Seizures, Fever](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csfrhinorrhea-210321134232/75/CSF-Rhinorrhea-7-2048.jpg)











![Conservative Management
• Bed Rest
• Head Elevation (15 Degree)
• Stool Softeners
• Diuretics [Azetazolamide]
• Avoid Coughing, Sneezing , Blowing
• Prophylactic Antibiotics
• Lumber Drain for High Pressure Leak(Hourly 10 ml drainage)
• Mostly for 7-10 Days.
Post-Traumatic CSF Leak](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csfrhinorrhea-210321134232/75/CSF-Rhinorrhea-19-2048.jpg)











![Post-Operative Care
• Nasal Packing
• Complete Bed Rest for At least 5 Days
• Higher Antibiotics
• Diuretics [Azetazolamide] to maintain the ICP
• FOLLOW UP CT SCAN @ 3 MONTHS to look for the Sinus Blockage](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/csfrhinorrhea-210321134232/75/CSF-Rhinorrhea-31-2048.jpg)

