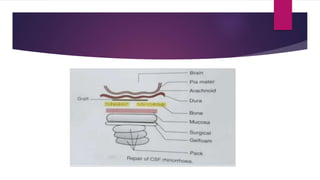
CSF rhinorrhoea is caused by trauma, infections, tumors, or congenital defects that damage the skull base and allow cerebrospinal fluid to leak into the nose. It is diagnosed through history of clear nasal discharge, endoscopic examination, and tests to detect beta-2 transferrin or beta trace protein in nasal fluid. The leak site is localized using imaging studies like CT or MRI. Treatment involves conservative measures, antibiotics, lumbar drainage, and surgical repair using endoscopic or open approaches to reconstruct the skull base defect.