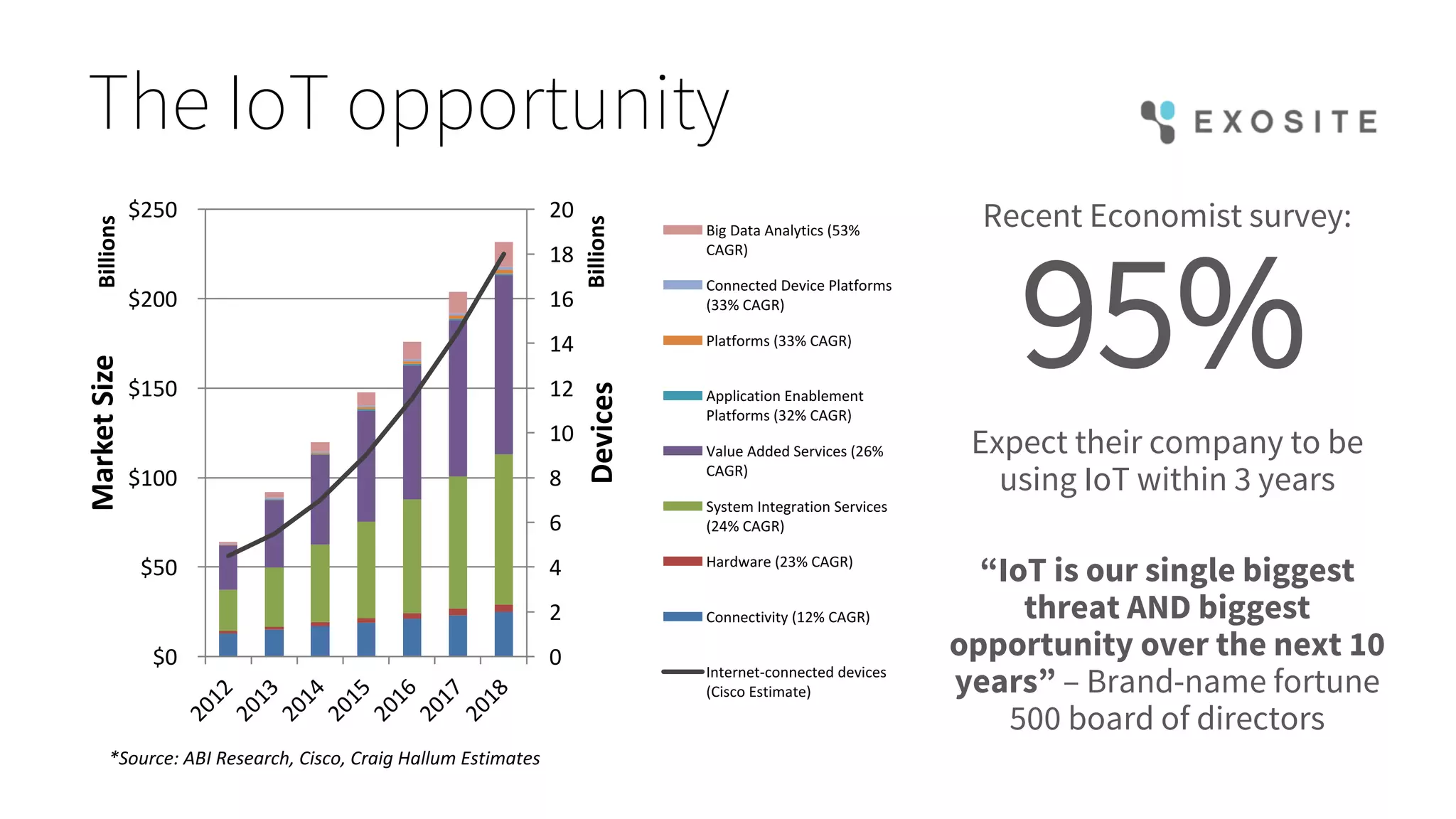
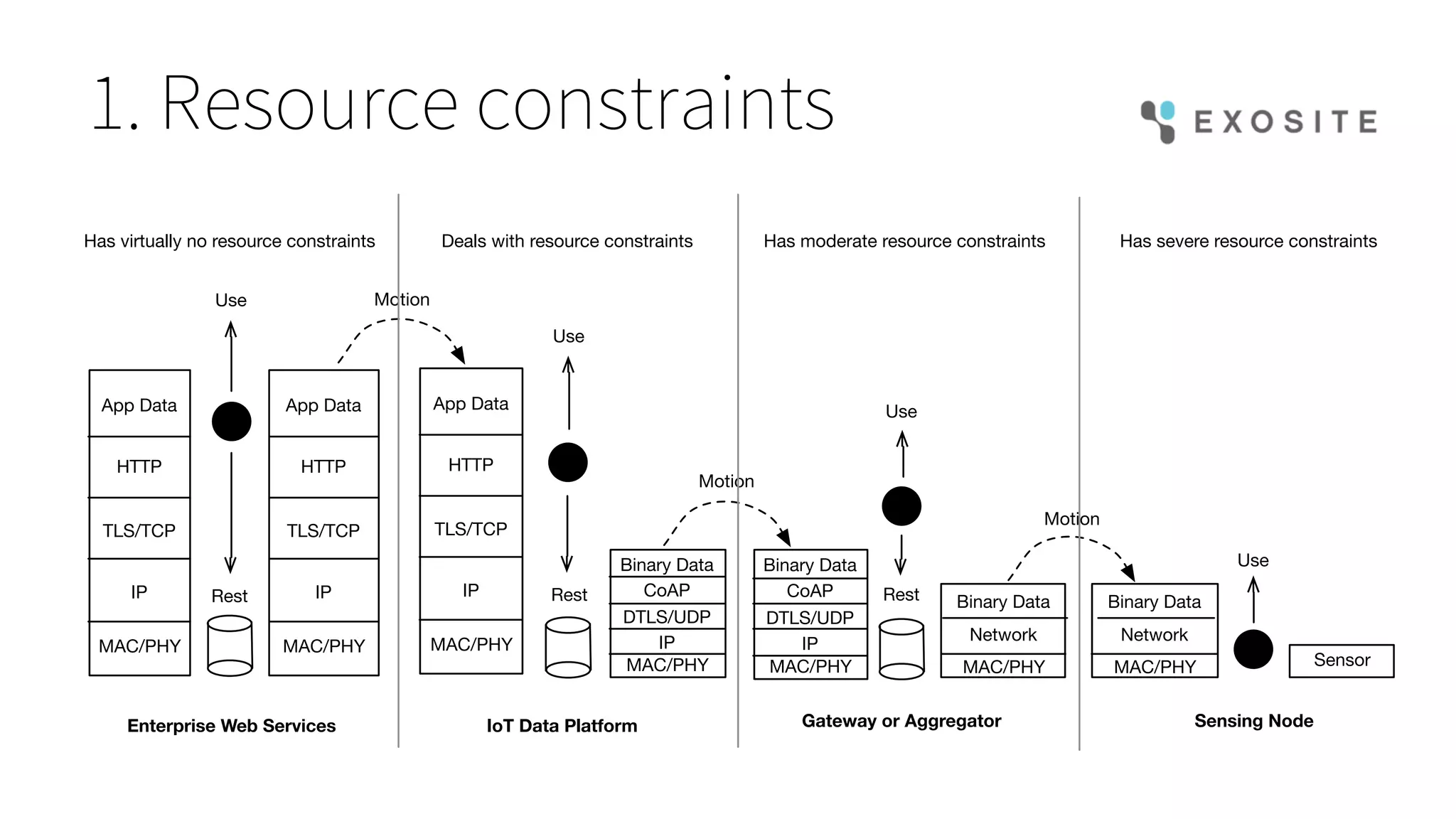
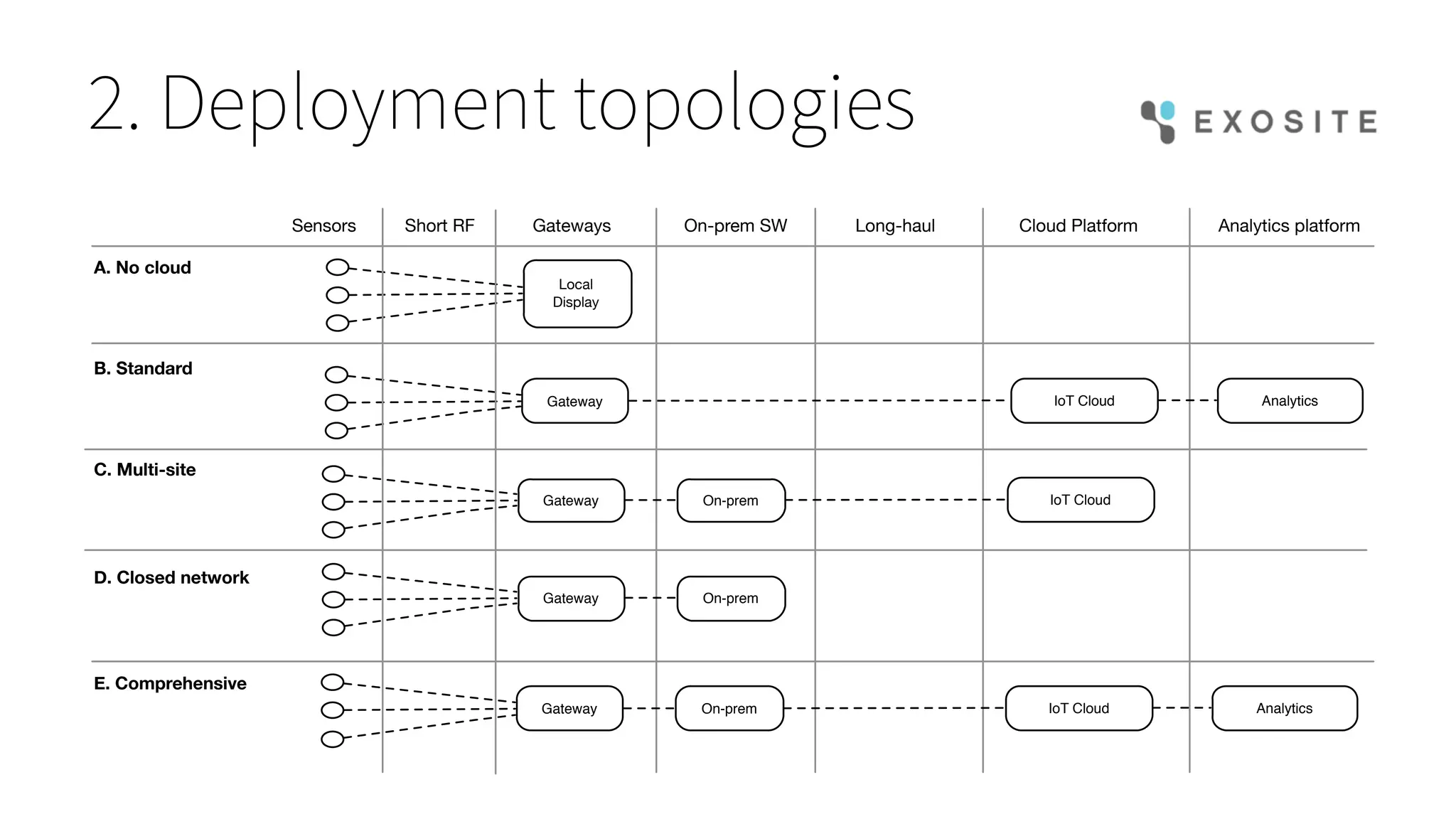
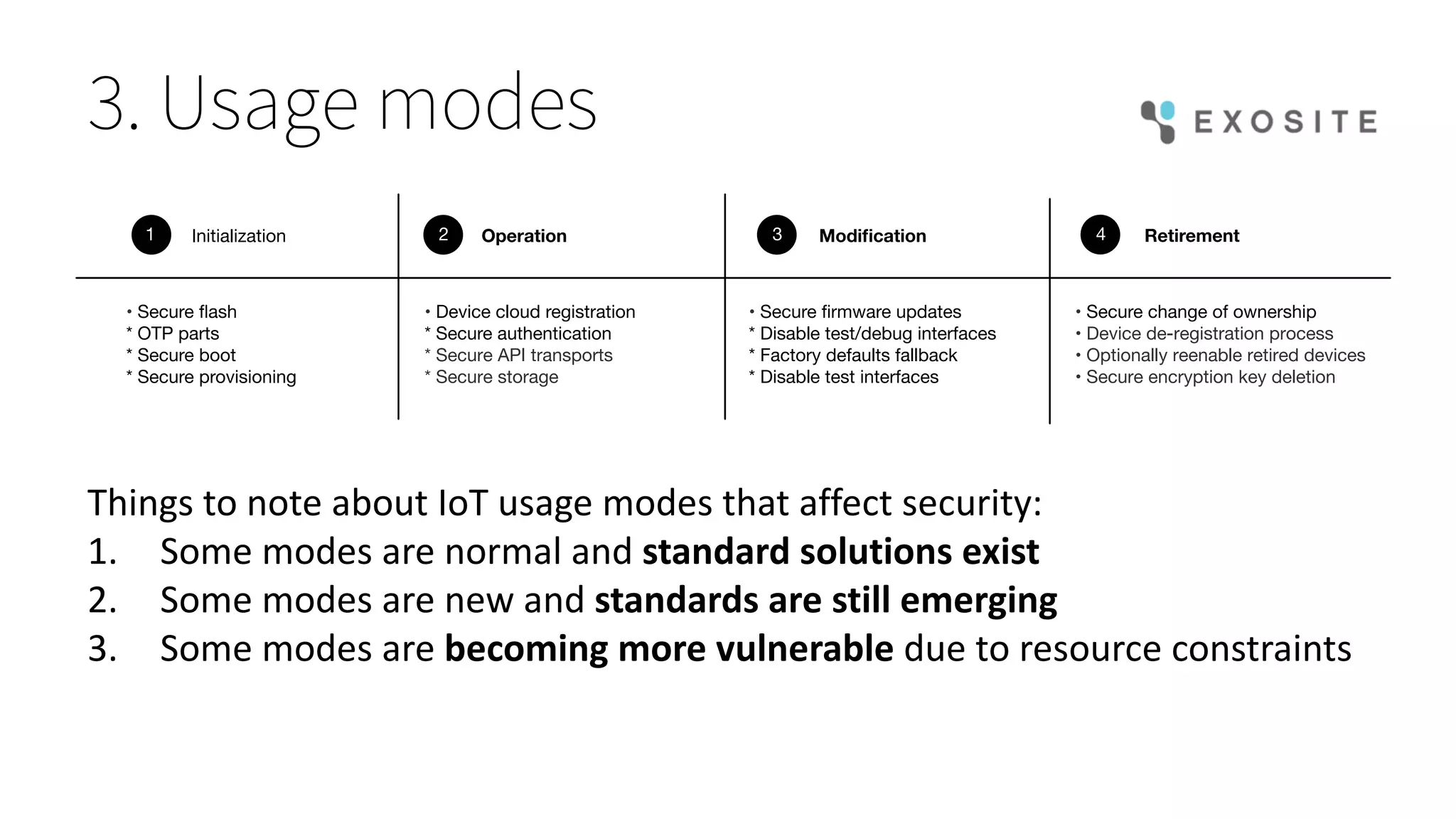
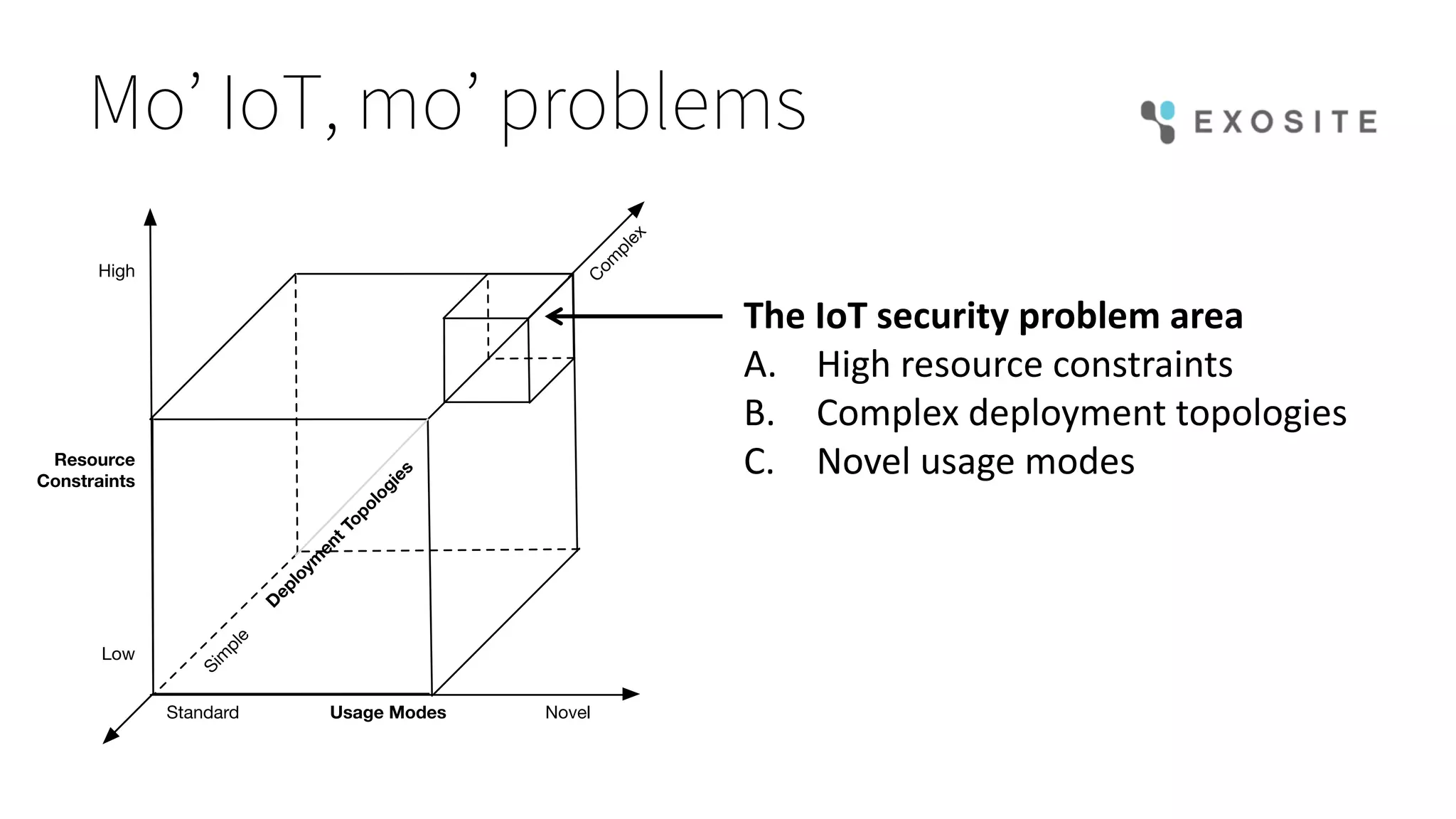
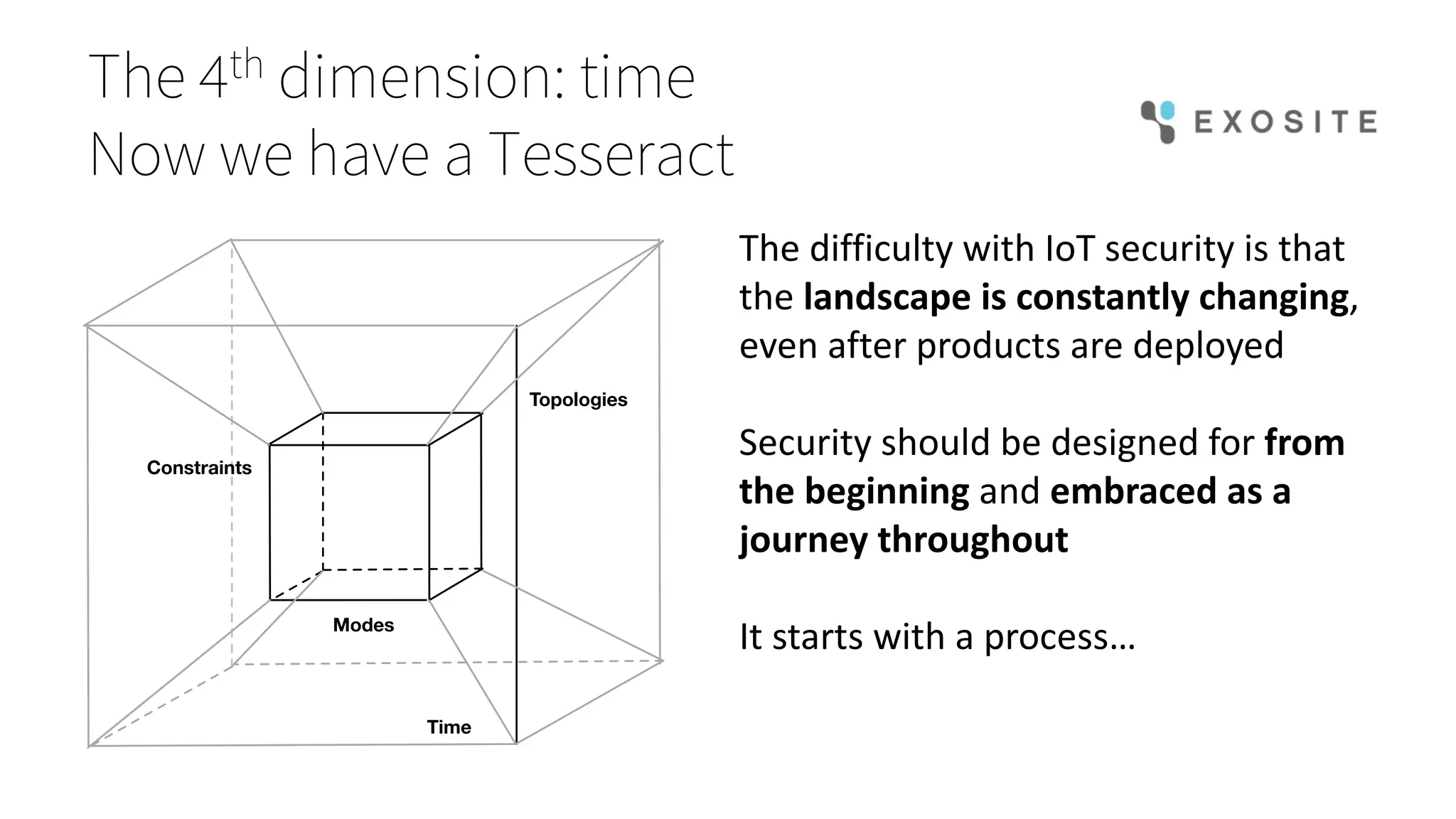
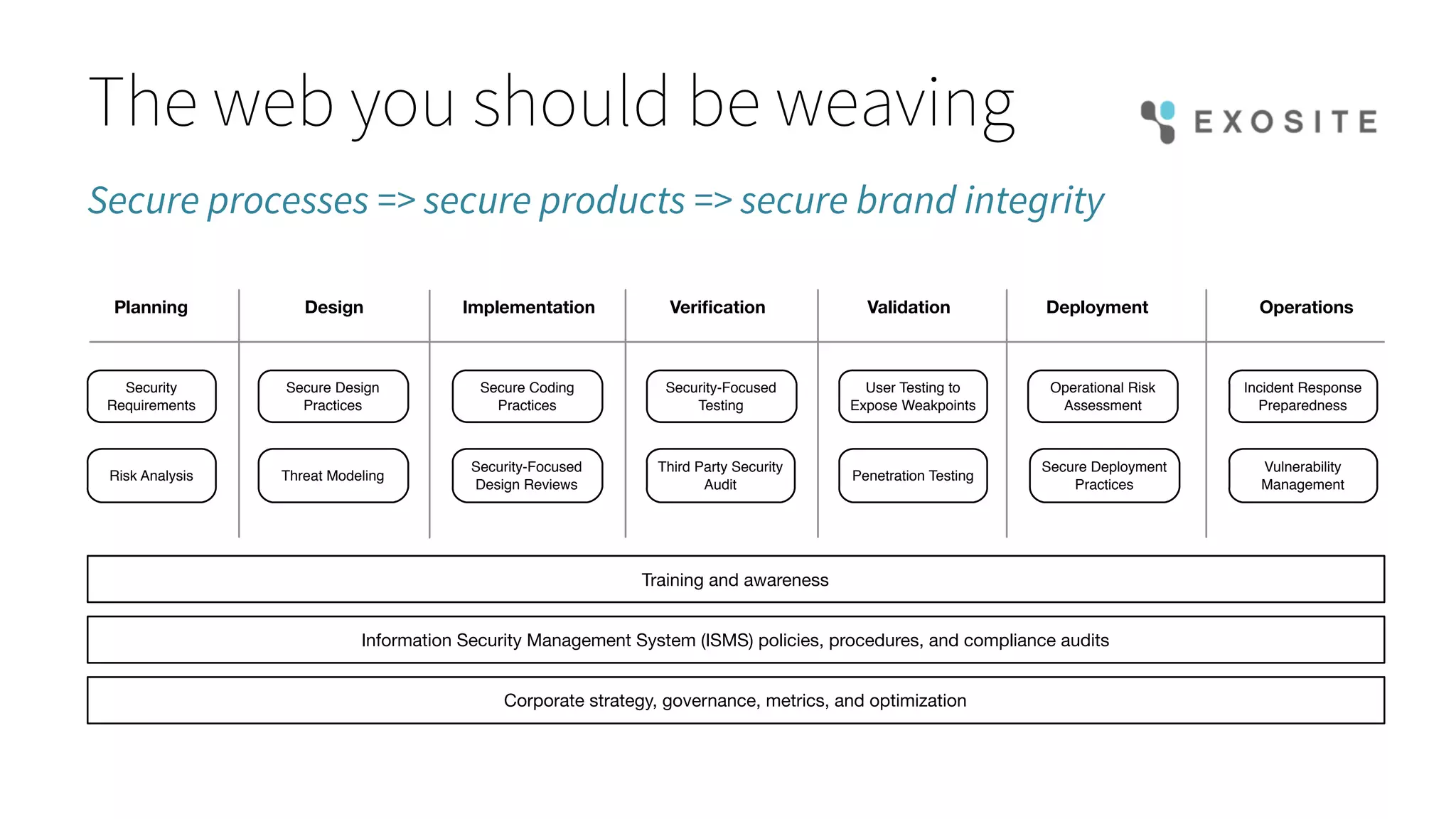
Mark Benson's presentation at the IoT Stream Con discusses the significant security challenges posed by the Internet of Things (IoT), highlighting concerns such as growing attack surfaces, consumer privacy, and severe breach consequences. The document outlines three main dimensions of IoT security—resource constraints, deployment topologies, and usage modes—along with a focus on the evolving nature of security needs over time. Key takeaways emphasize the necessity of integrating security processes from the start, selecting appropriate technologies, and planning operational responses to potential security incidents.