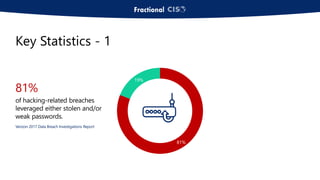
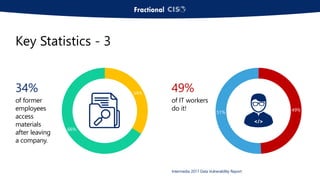
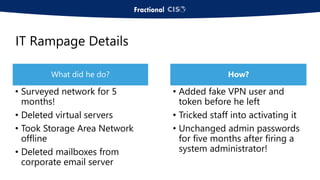
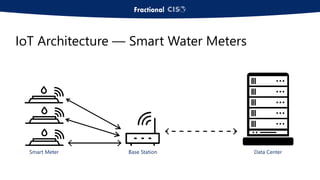
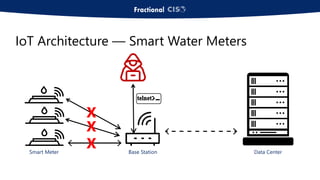
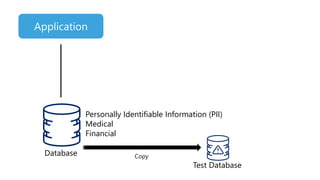
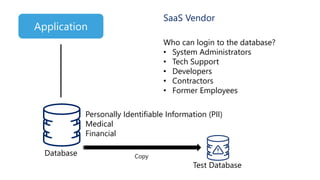
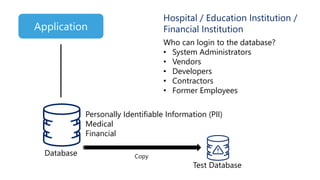
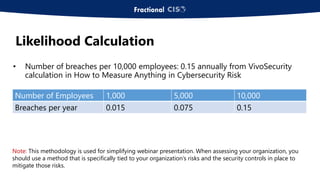
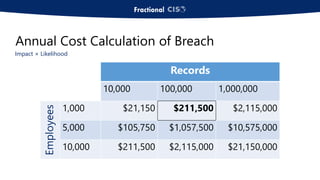
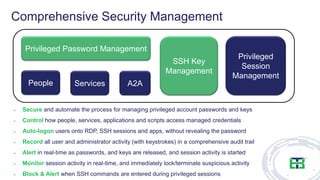
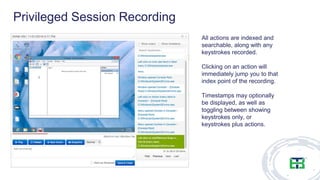
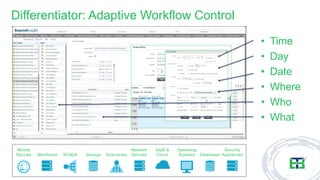
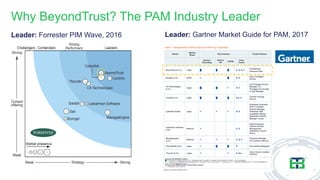
The document discusses the importance of privileged access management (PAM) in mitigating cybersecurity threats, particularly from disgruntled employees and evolving IoT security challenges. Key statistics highlight that a significant number of breaches stem from weak or stolen passwords, underscoring the need for better credential management. The presentation outlines both the risks and the potential return on investment for implementing PAM solutions to secure organizational assets.