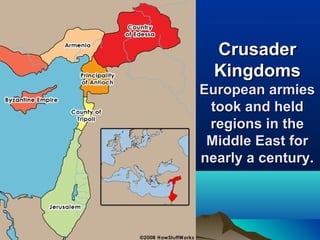
The Crusades were a series of military campaigns from the 1090s to the 1400s where European armies traveled to the Byzantine Empire and Middle East to regain Christian lands and pilgrimage routes. Pope Urban II gave a speech outlining religious, political, economic, and social reasons for Christians to join the Crusades, such as gaining forgiveness of sins and wealth. The Crusades weakened the Byzantine Empire but increased trade between Europe and the Middle East while also exposing Europe to Islamic knowledge. However, the Crusades had little lasting impact on politics and culture in the Middle East.