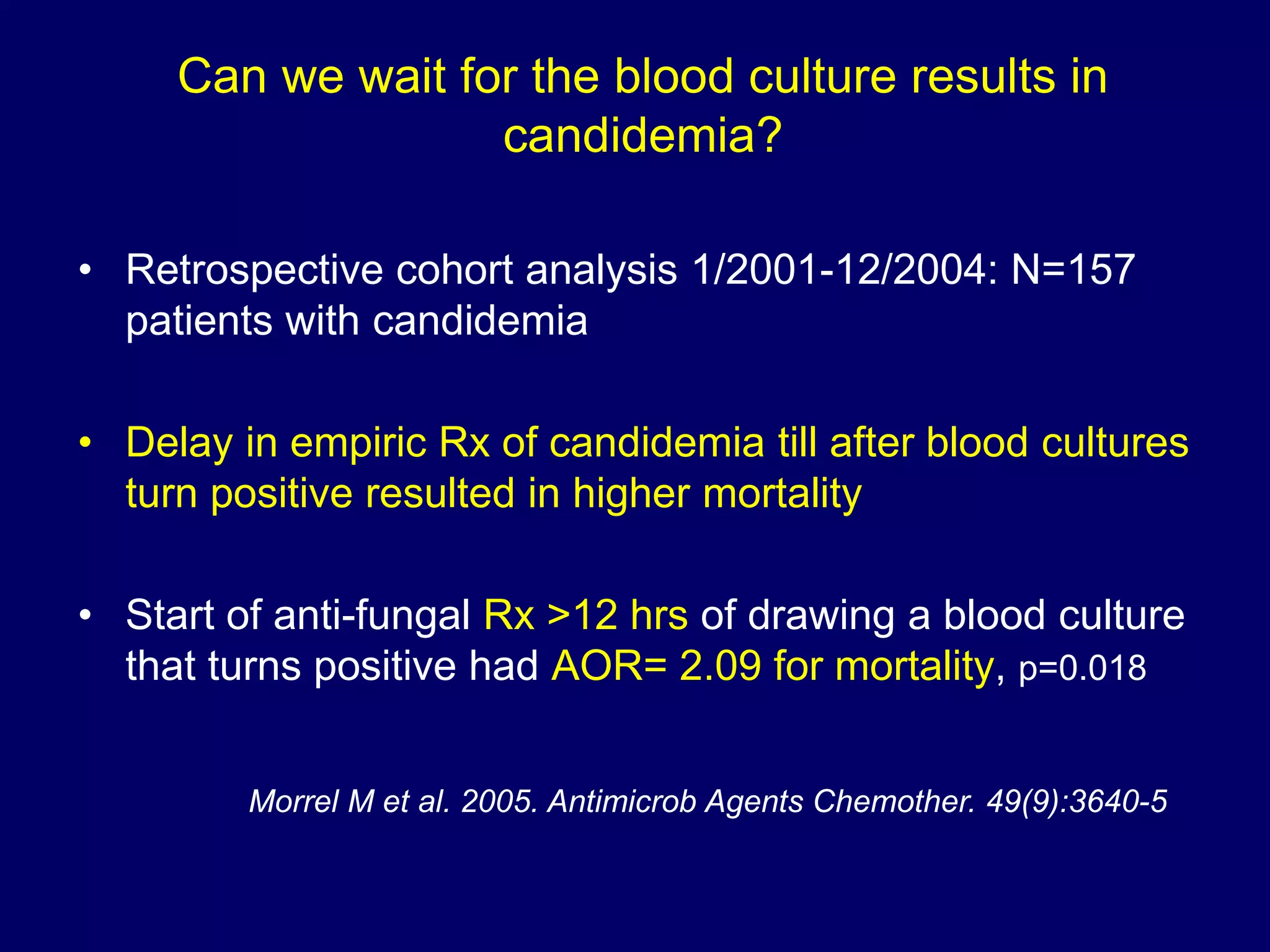
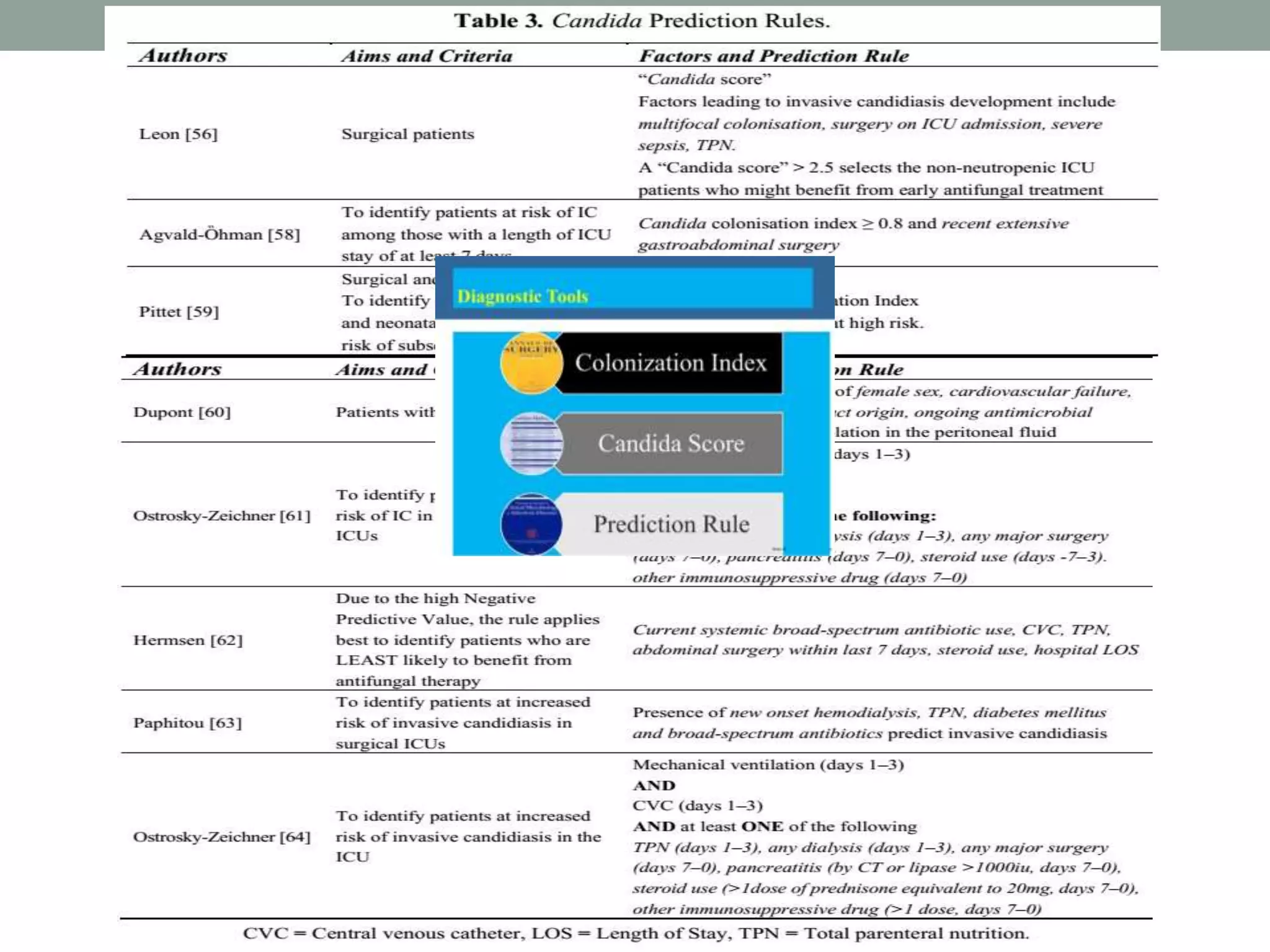
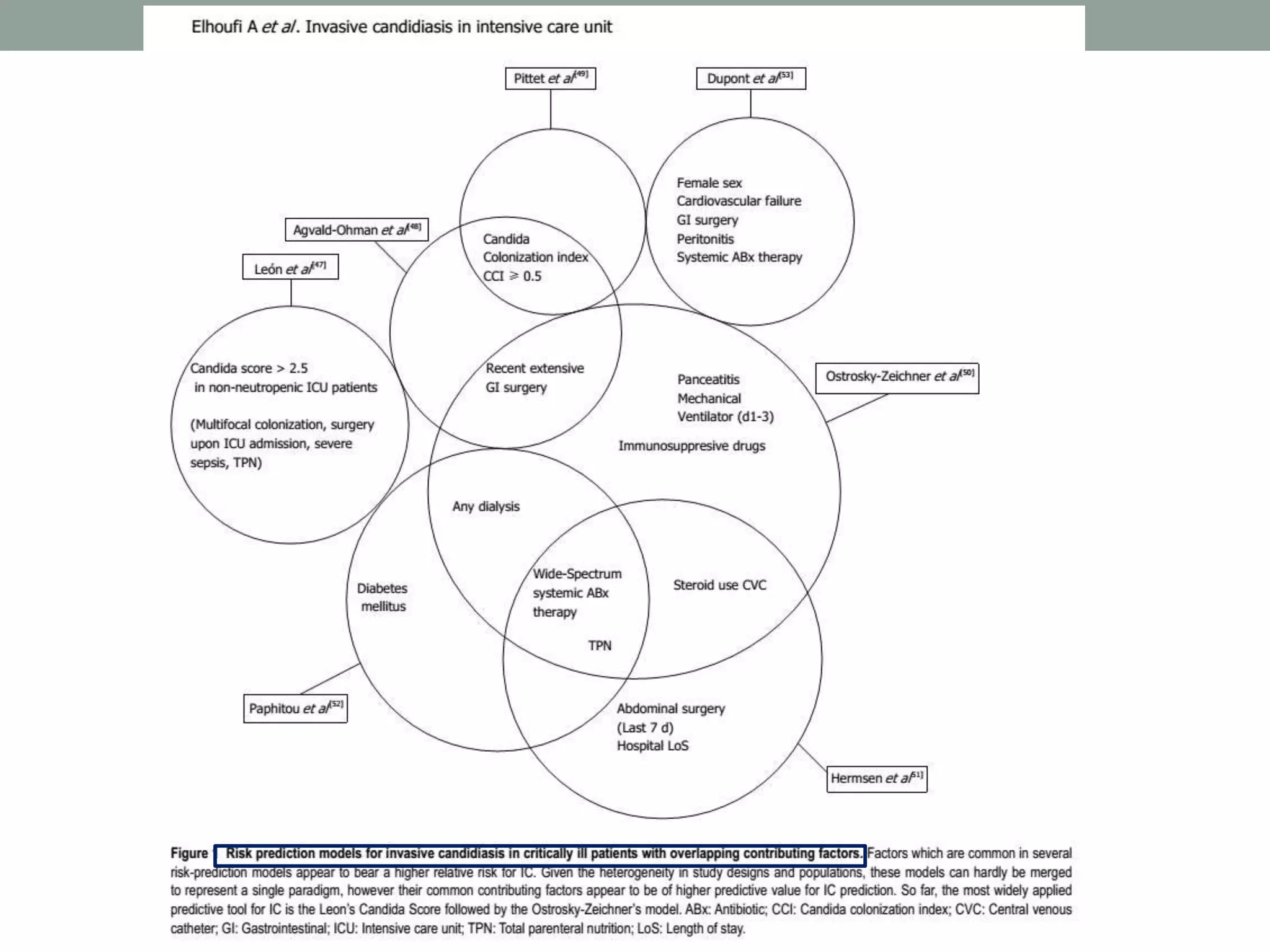
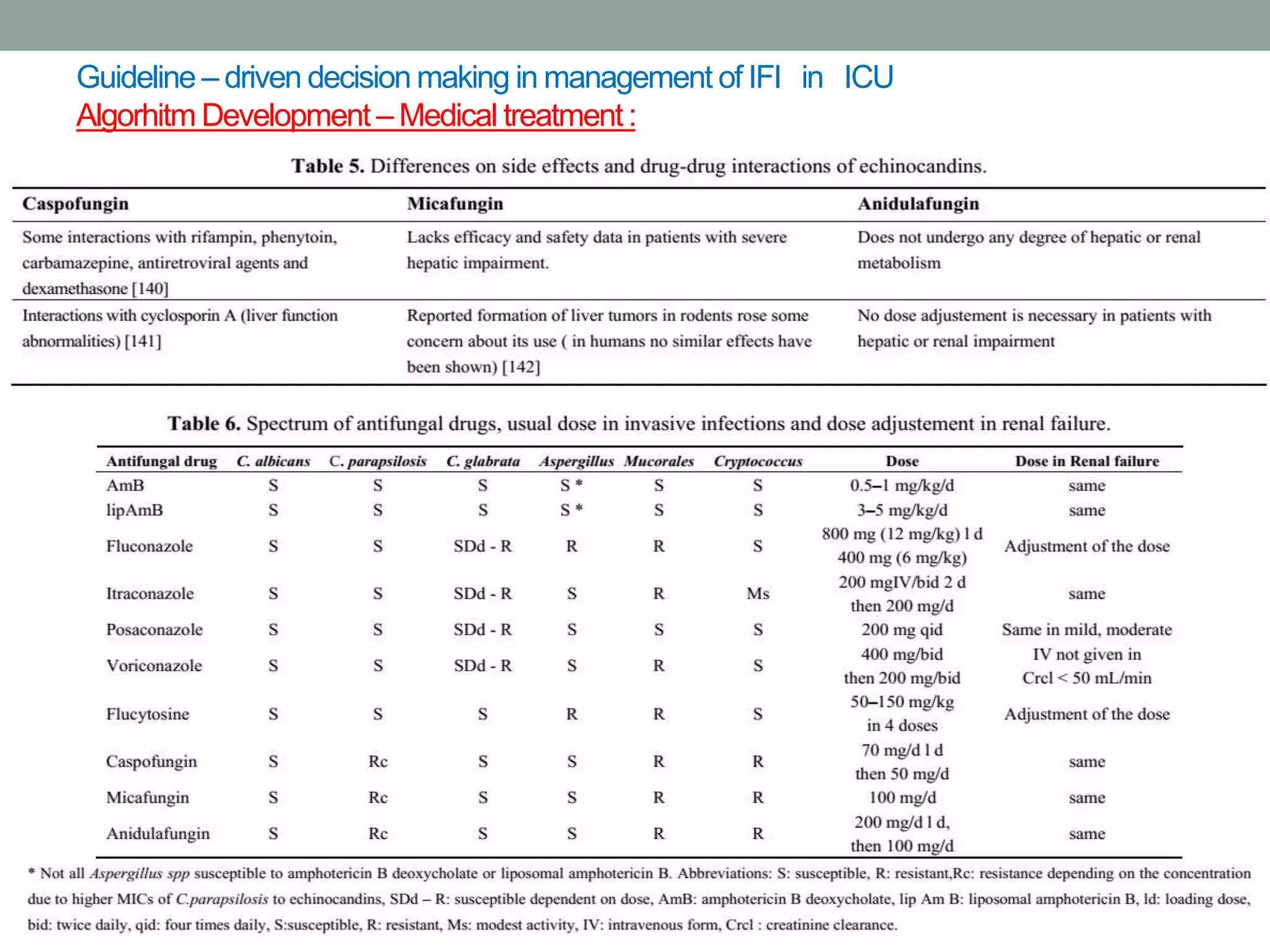
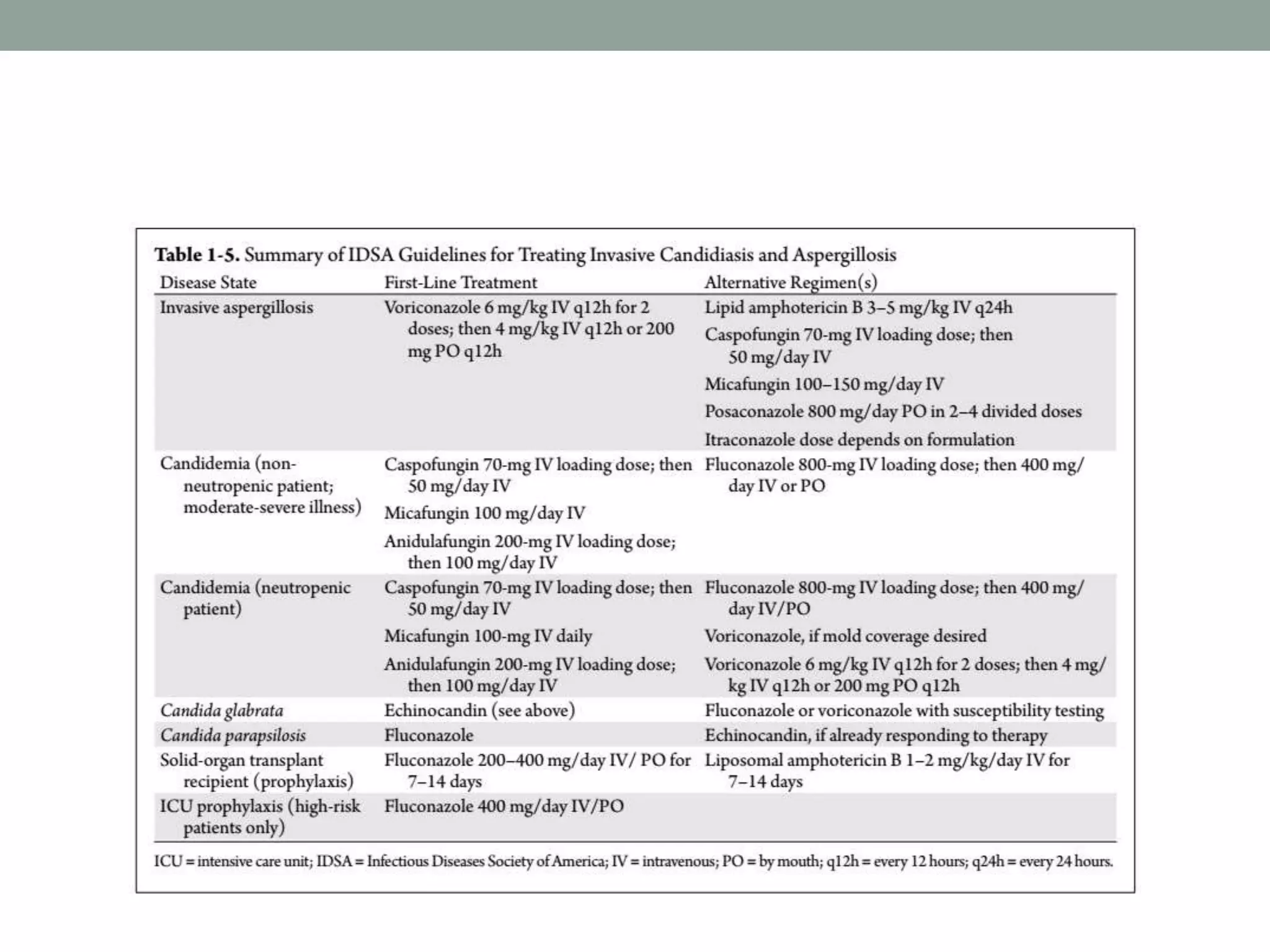
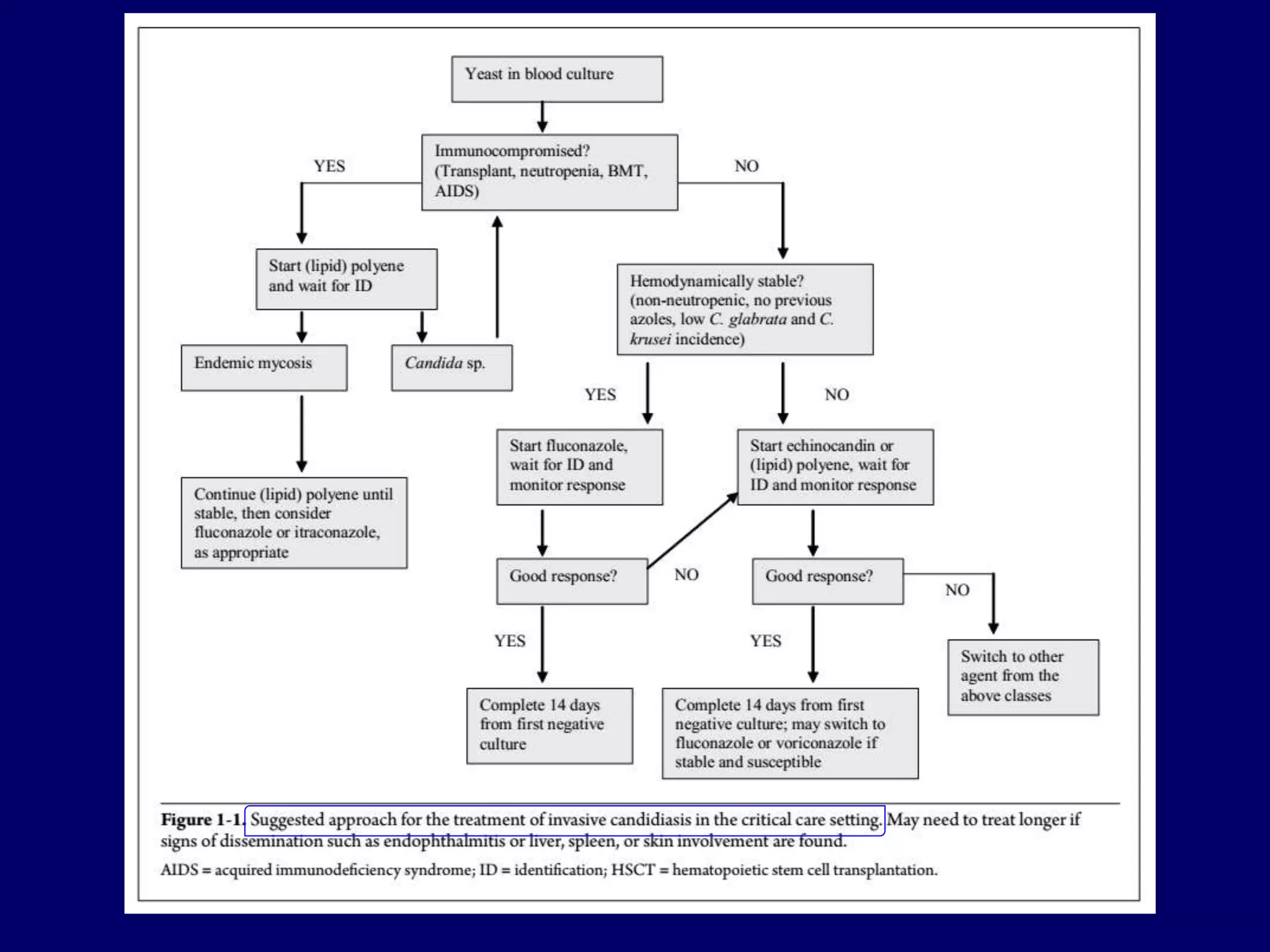
This document discusses the guideline-driven decision-making process for managing invasive fungal infections (IFI) in the ICU, highlighting the critical implications of IFI on patient morbidity and mortality. It emphasizes the importance of early diagnosis, appropriate antifungal therapy, and understanding local epidemiology to guide treatment strategies effectively. The document also presents treatment algorithms and stresses the negative outcomes associated with delays in antifungal therapy.