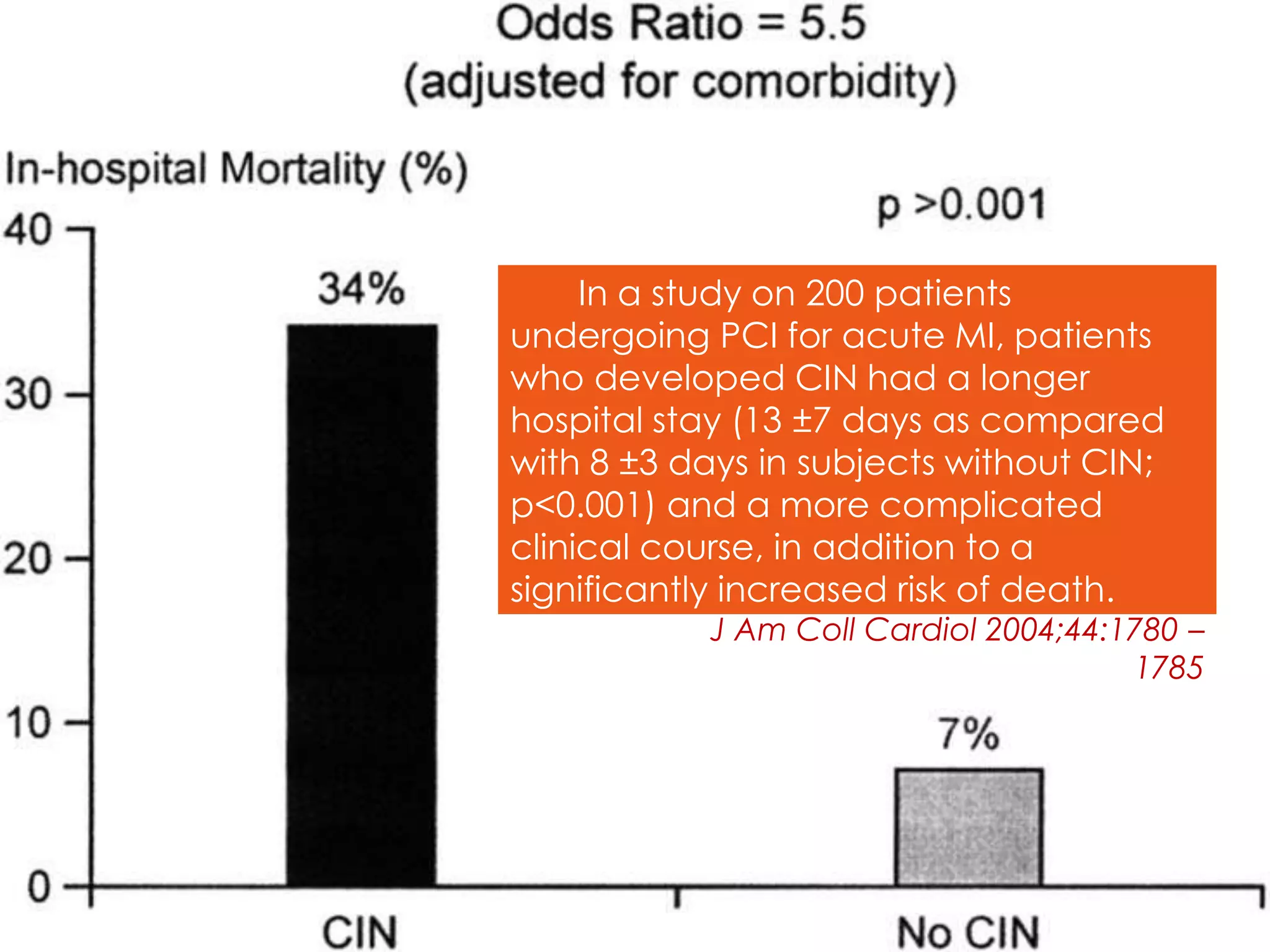
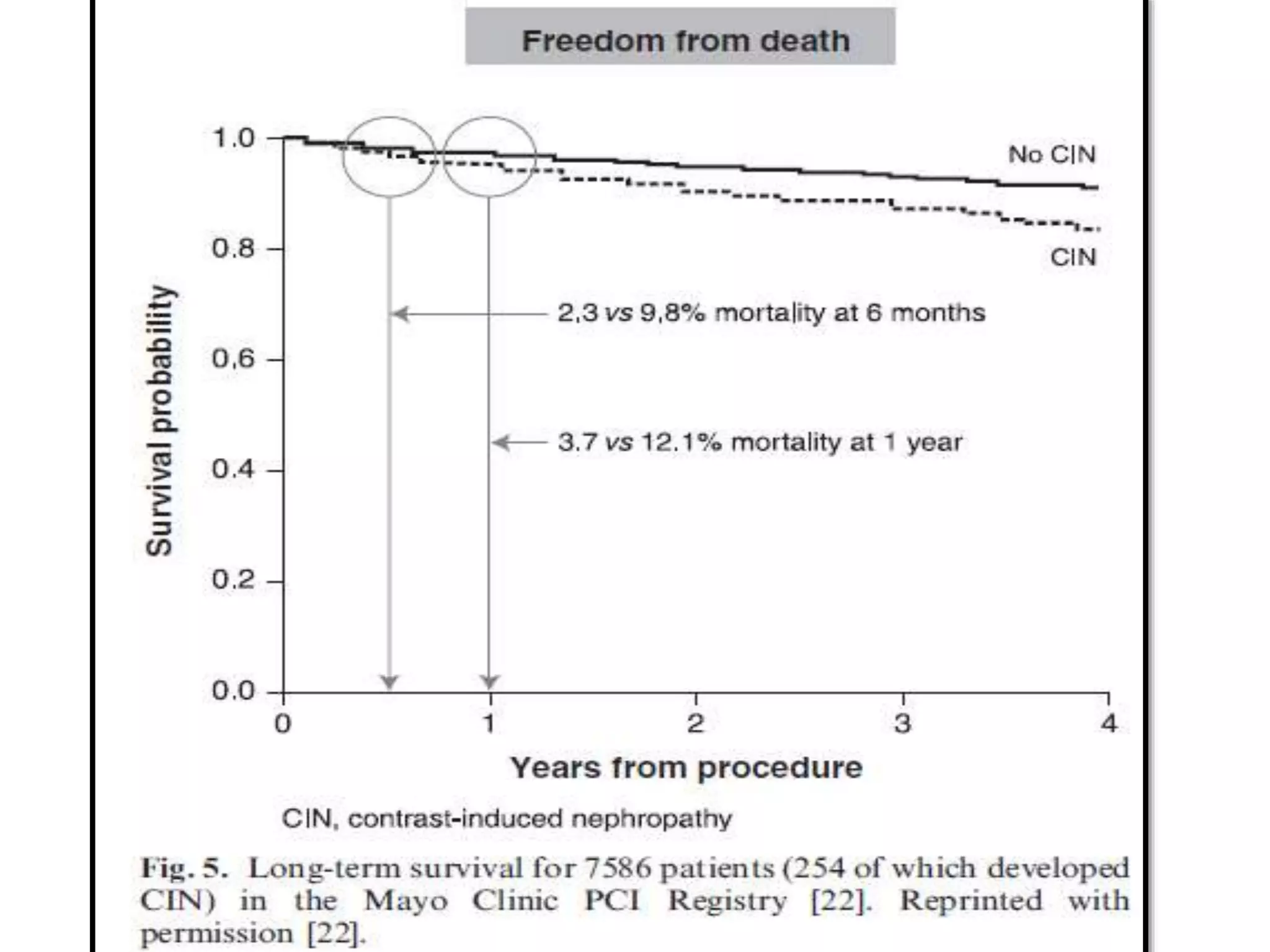
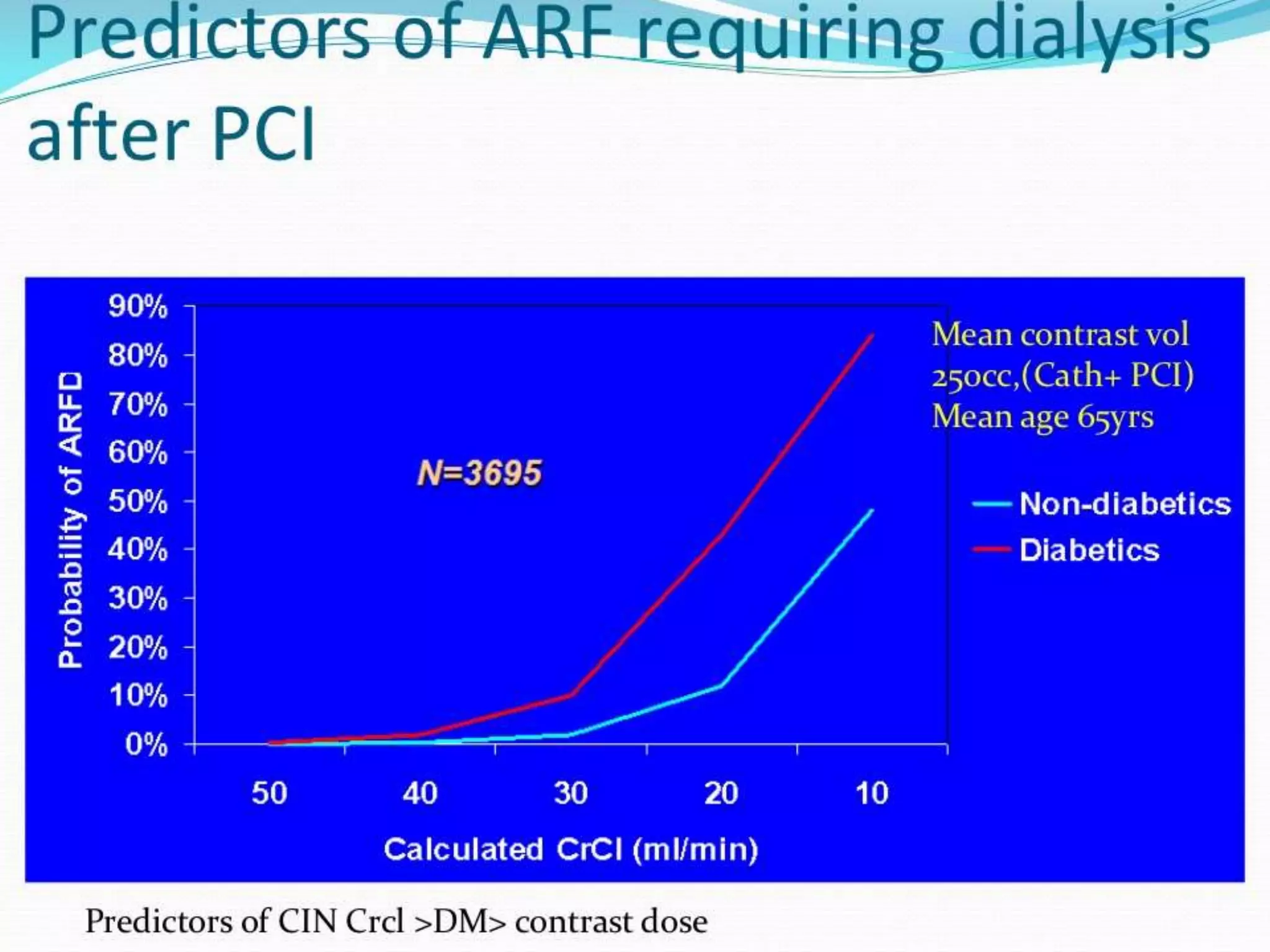
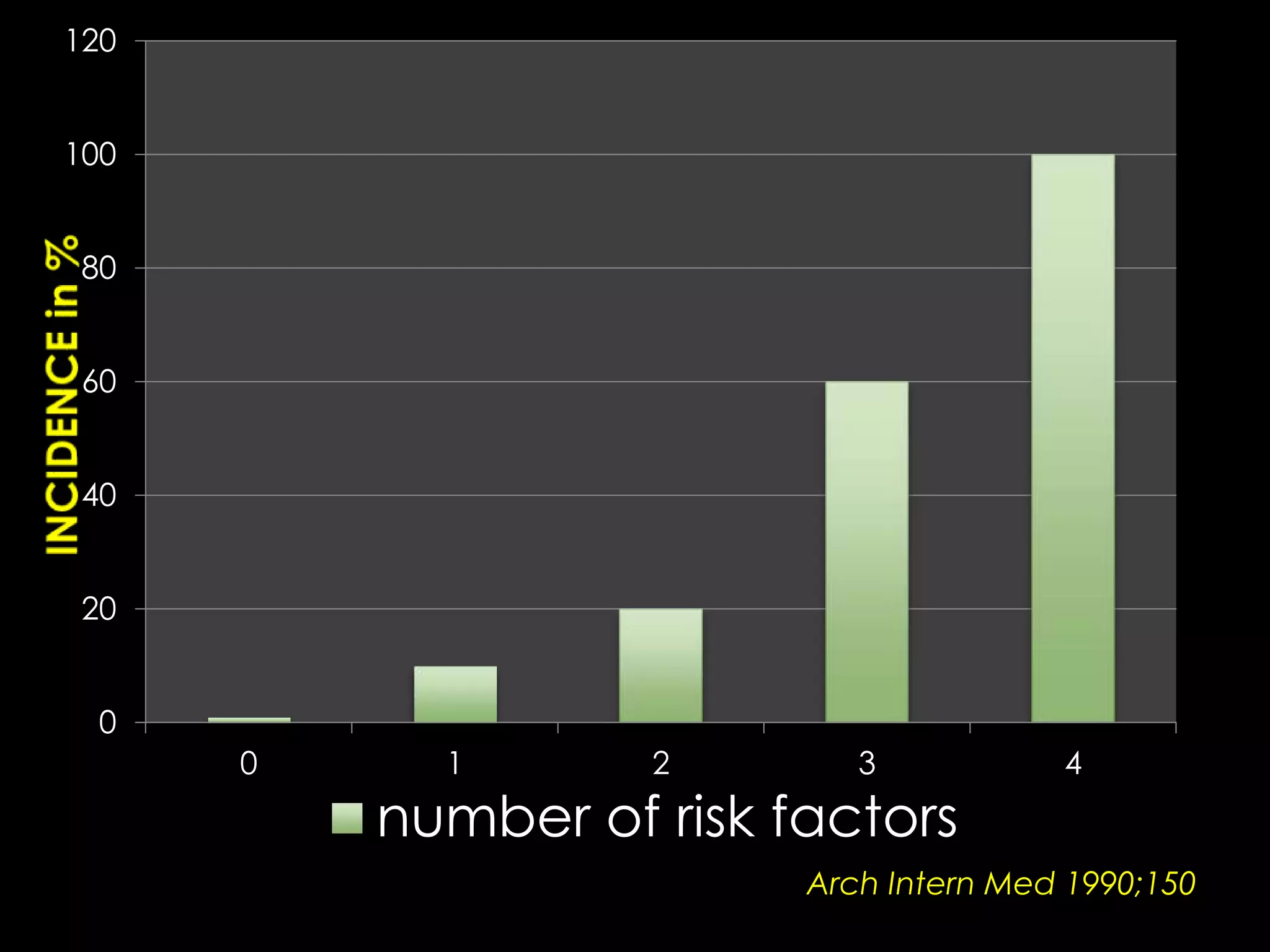
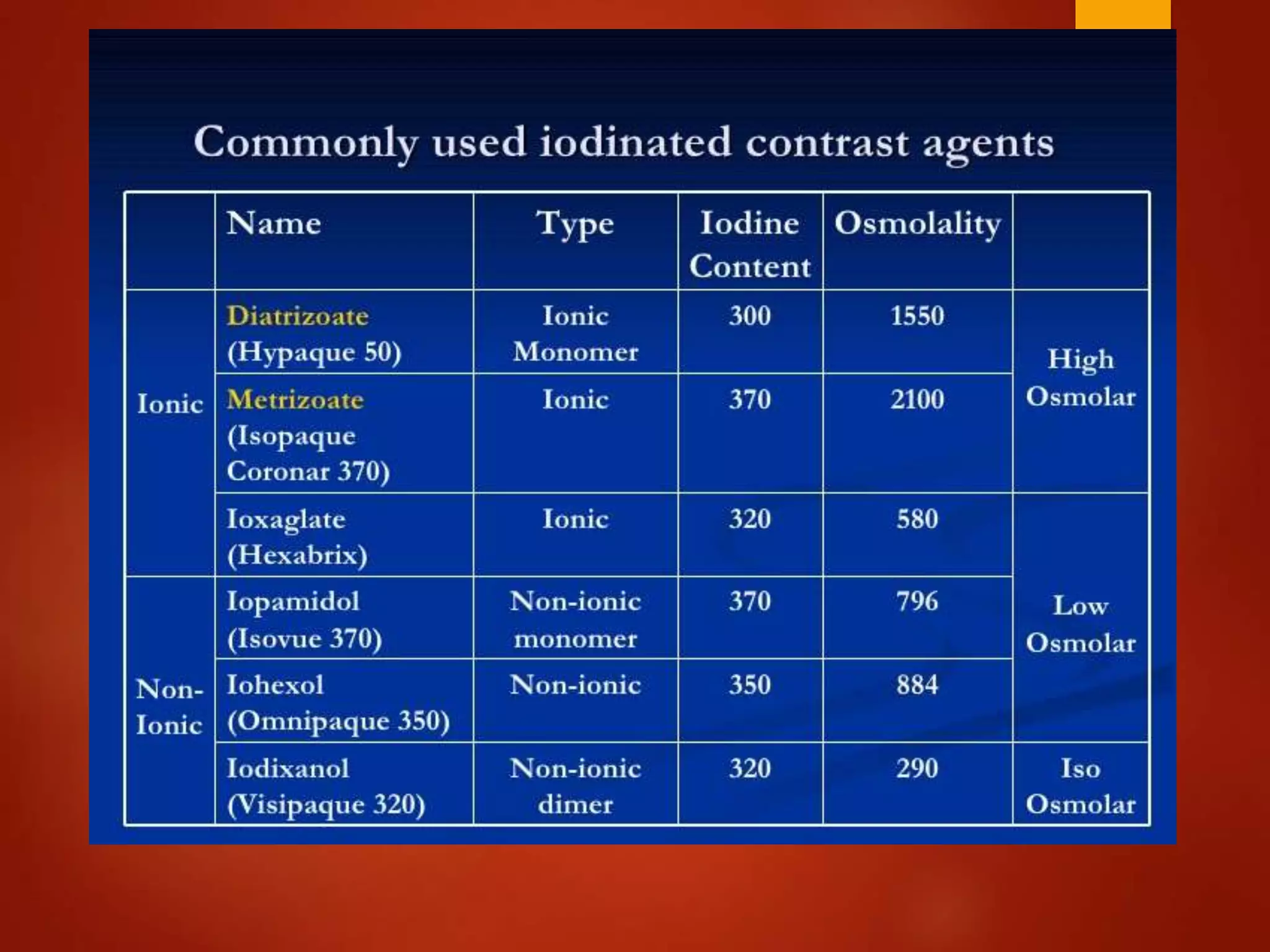
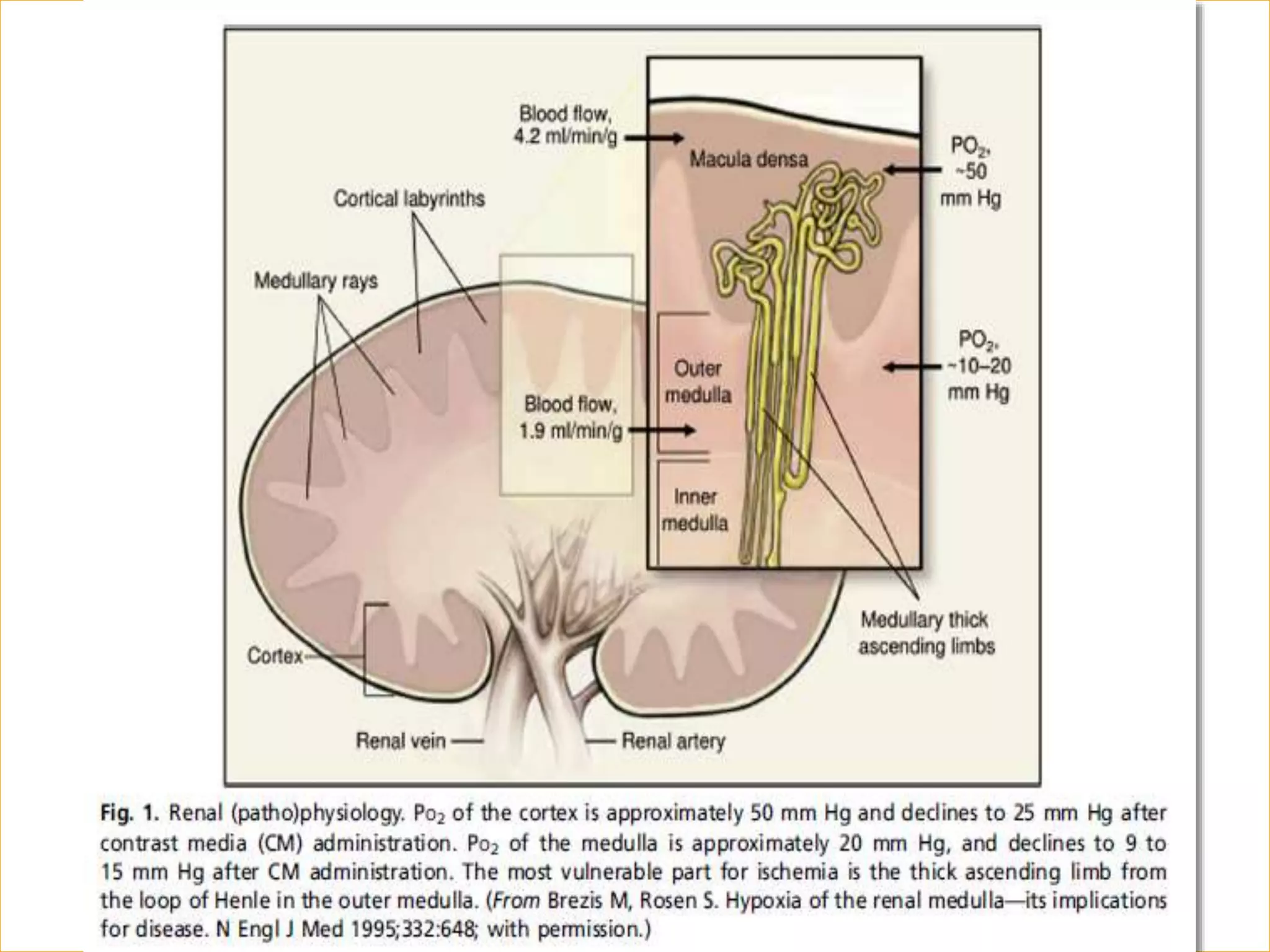
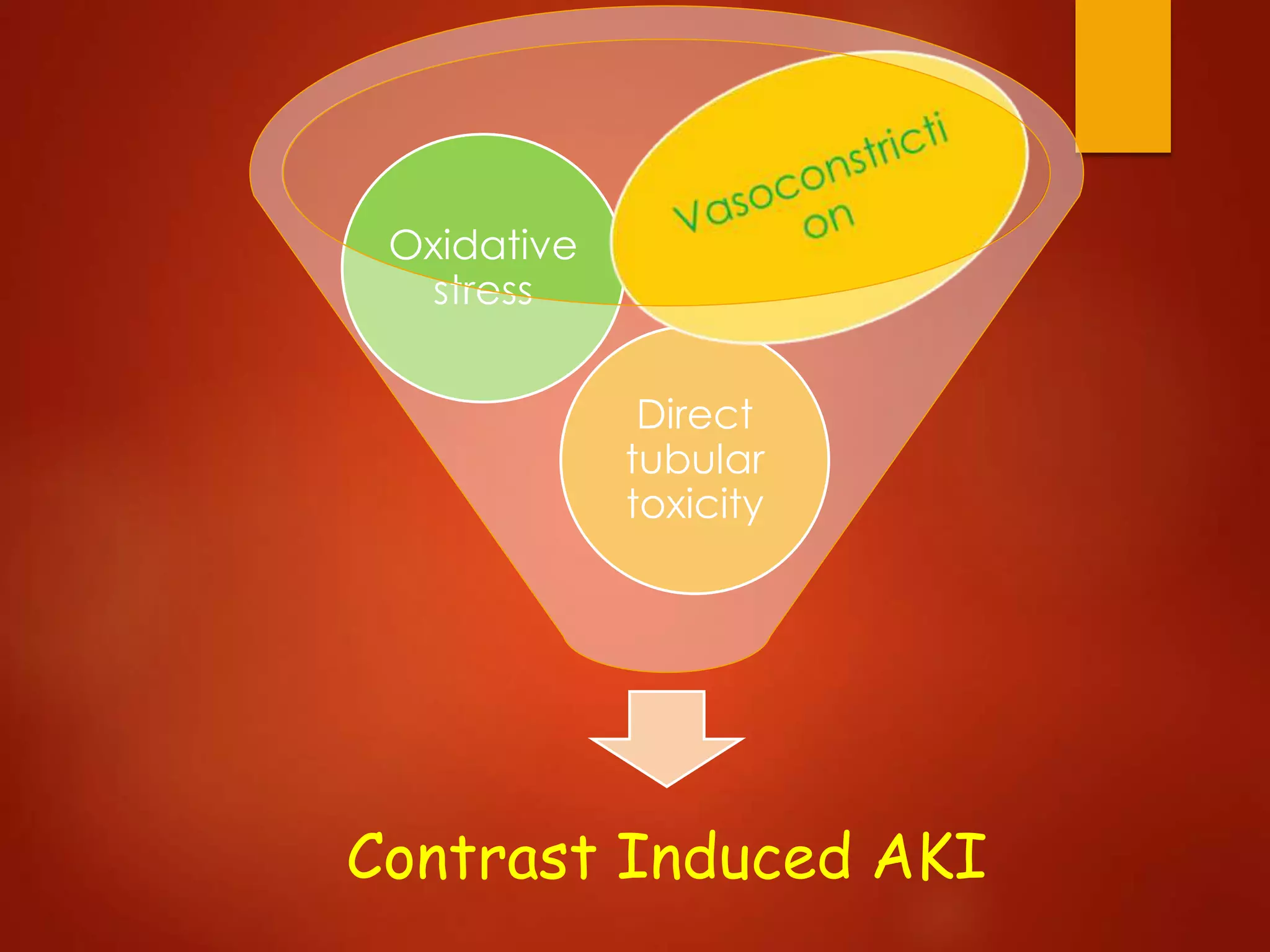
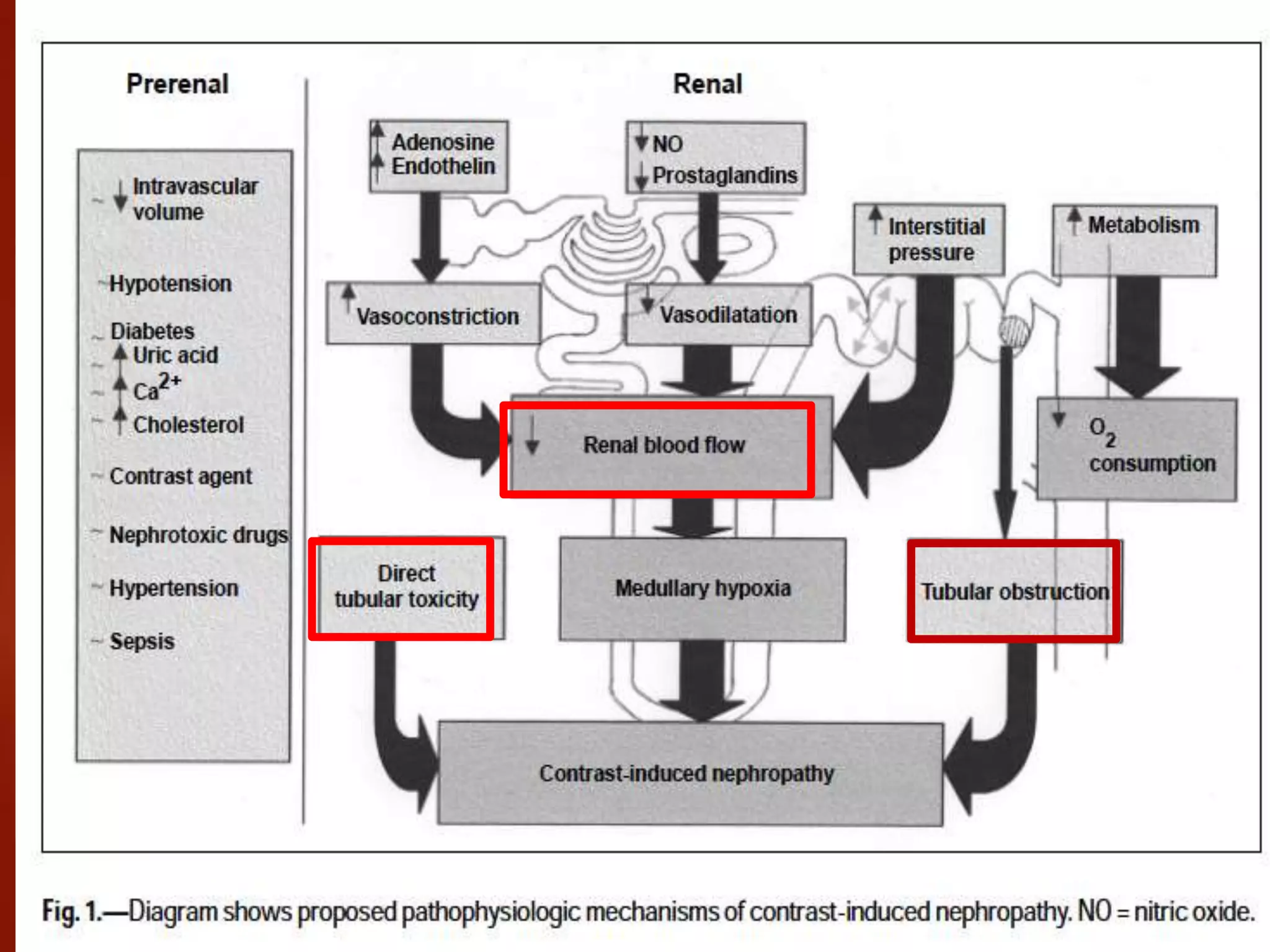
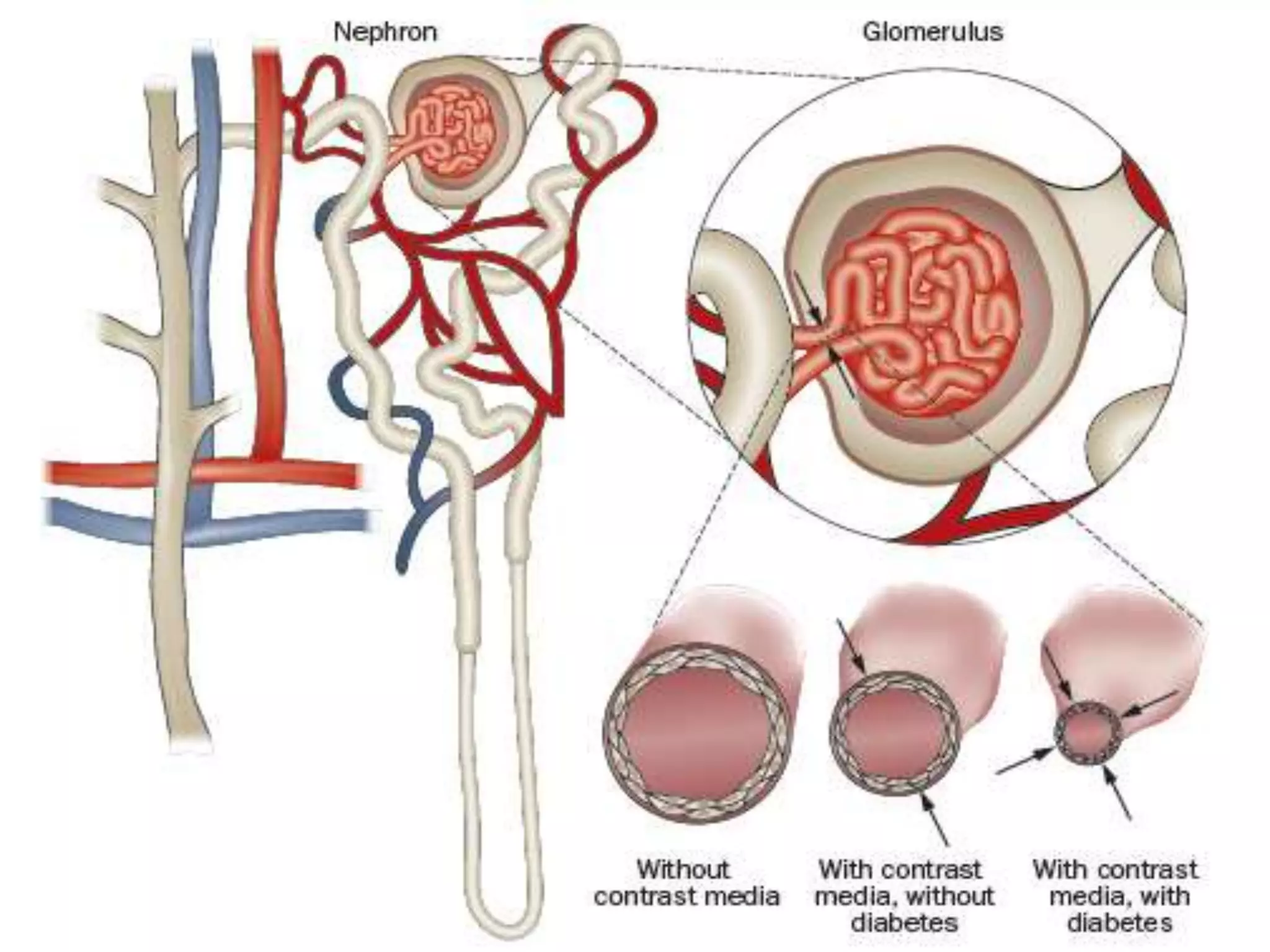
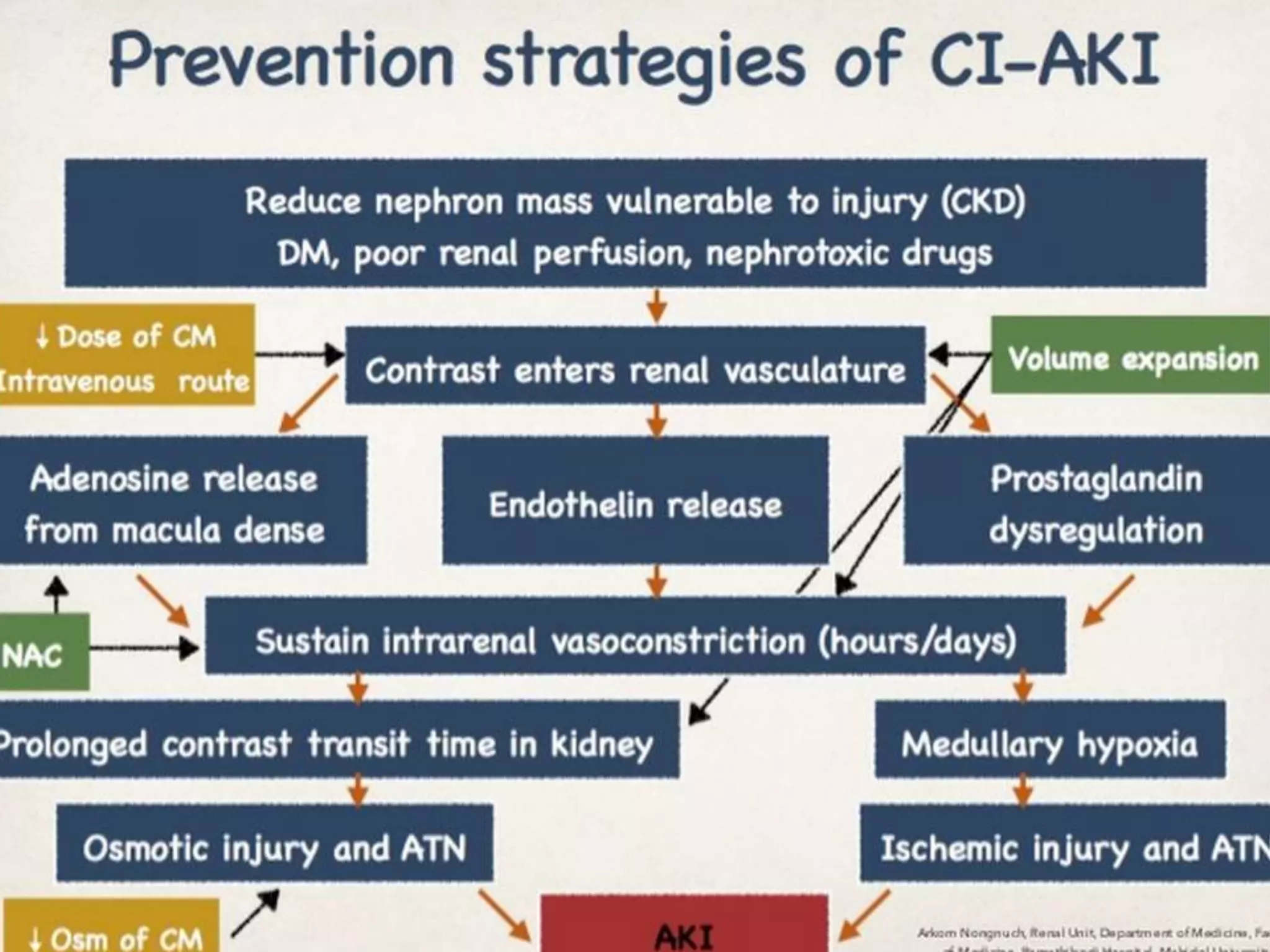
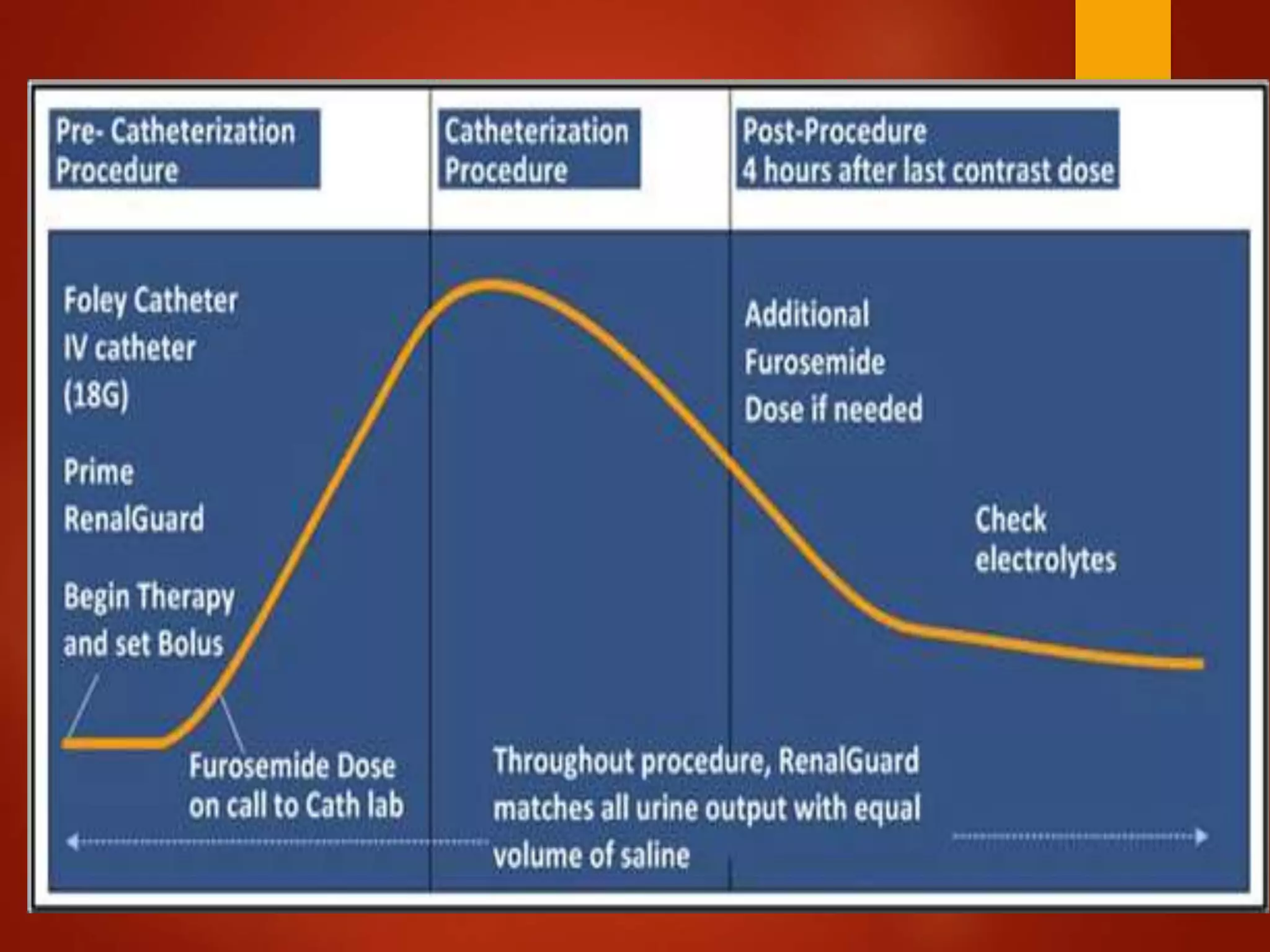
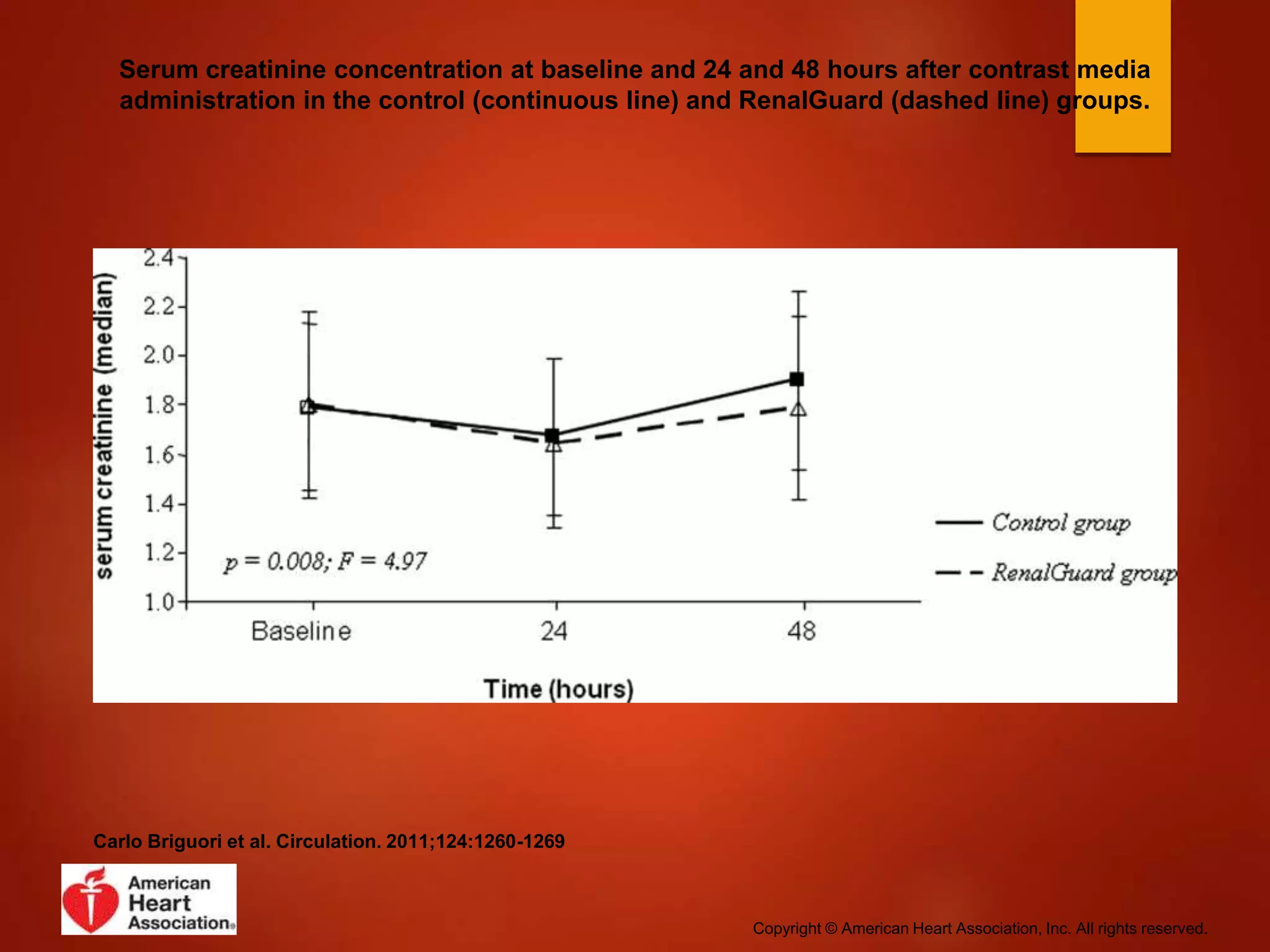
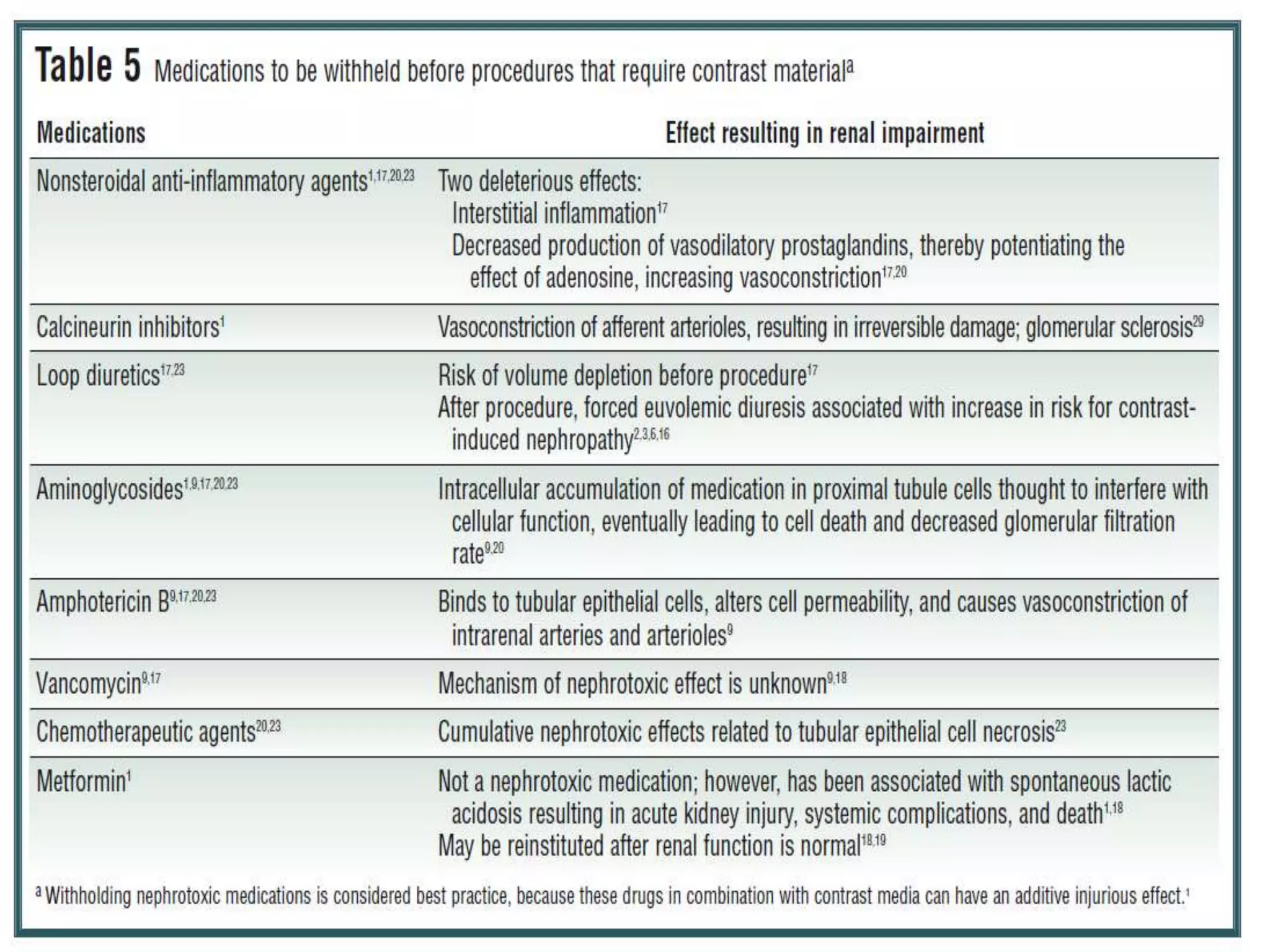
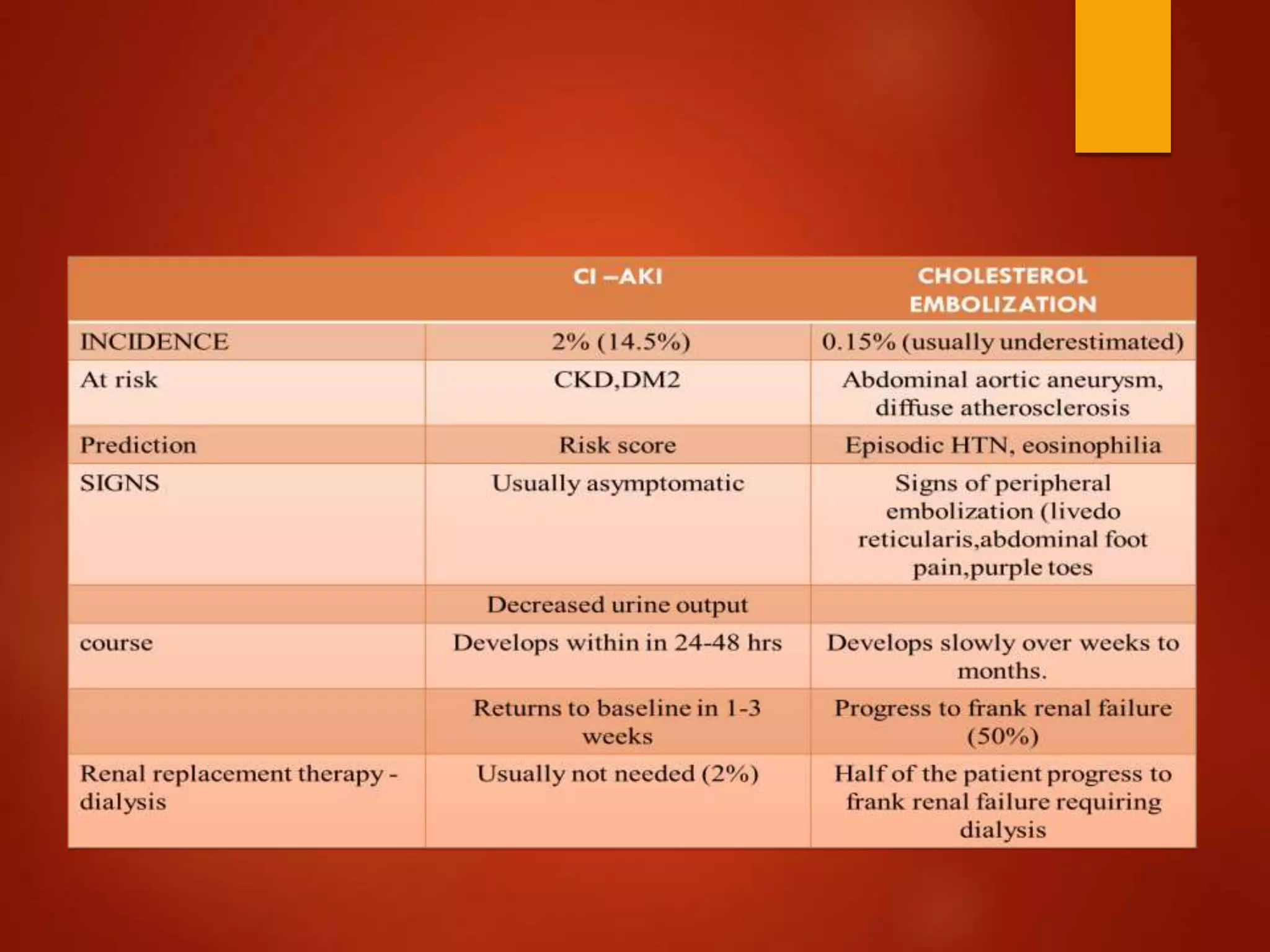
1. Contrast induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) is a common cause of hospital-acquired acute kidney injury that can increase both short and long term morbidity and mortality.
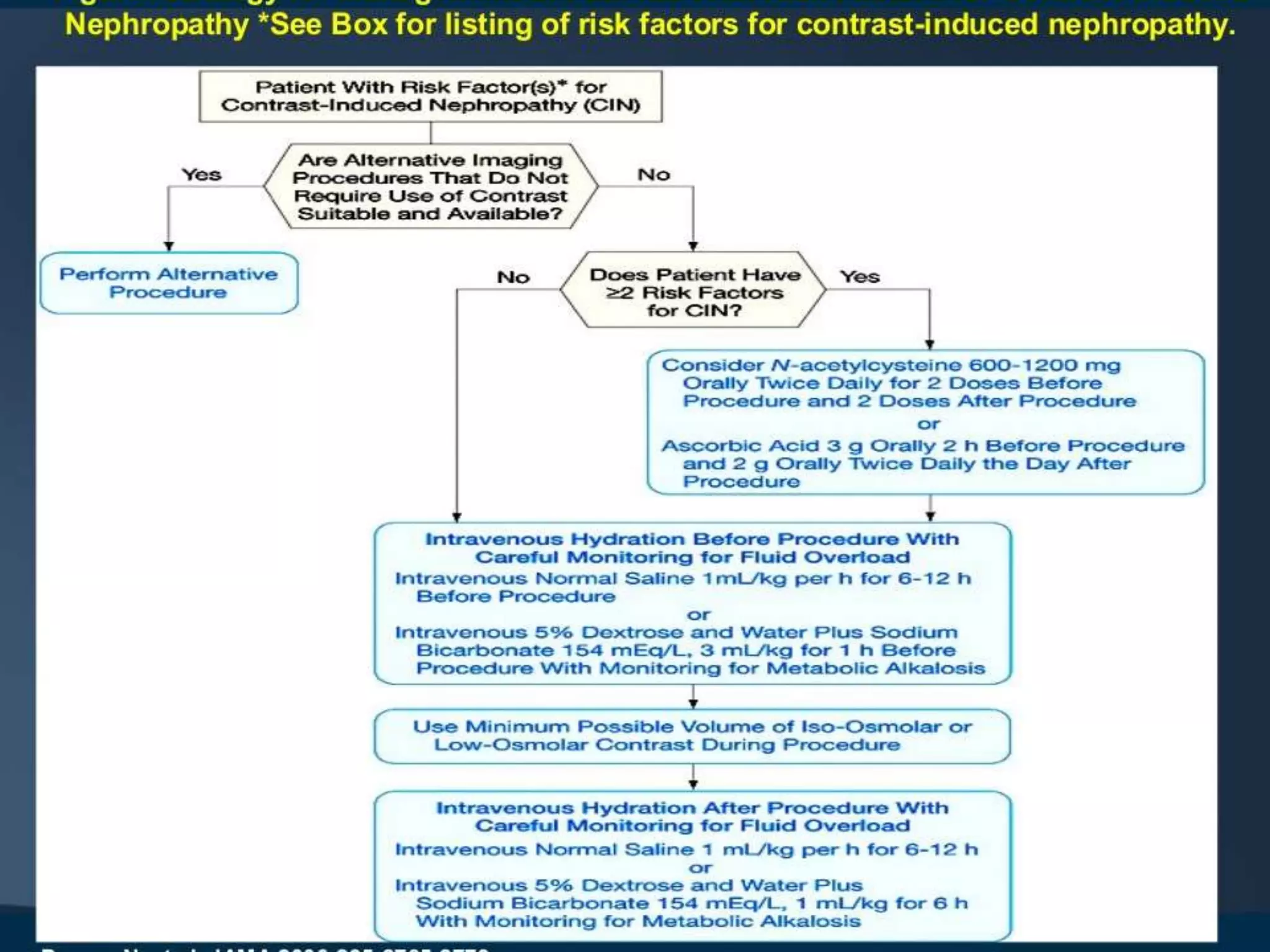
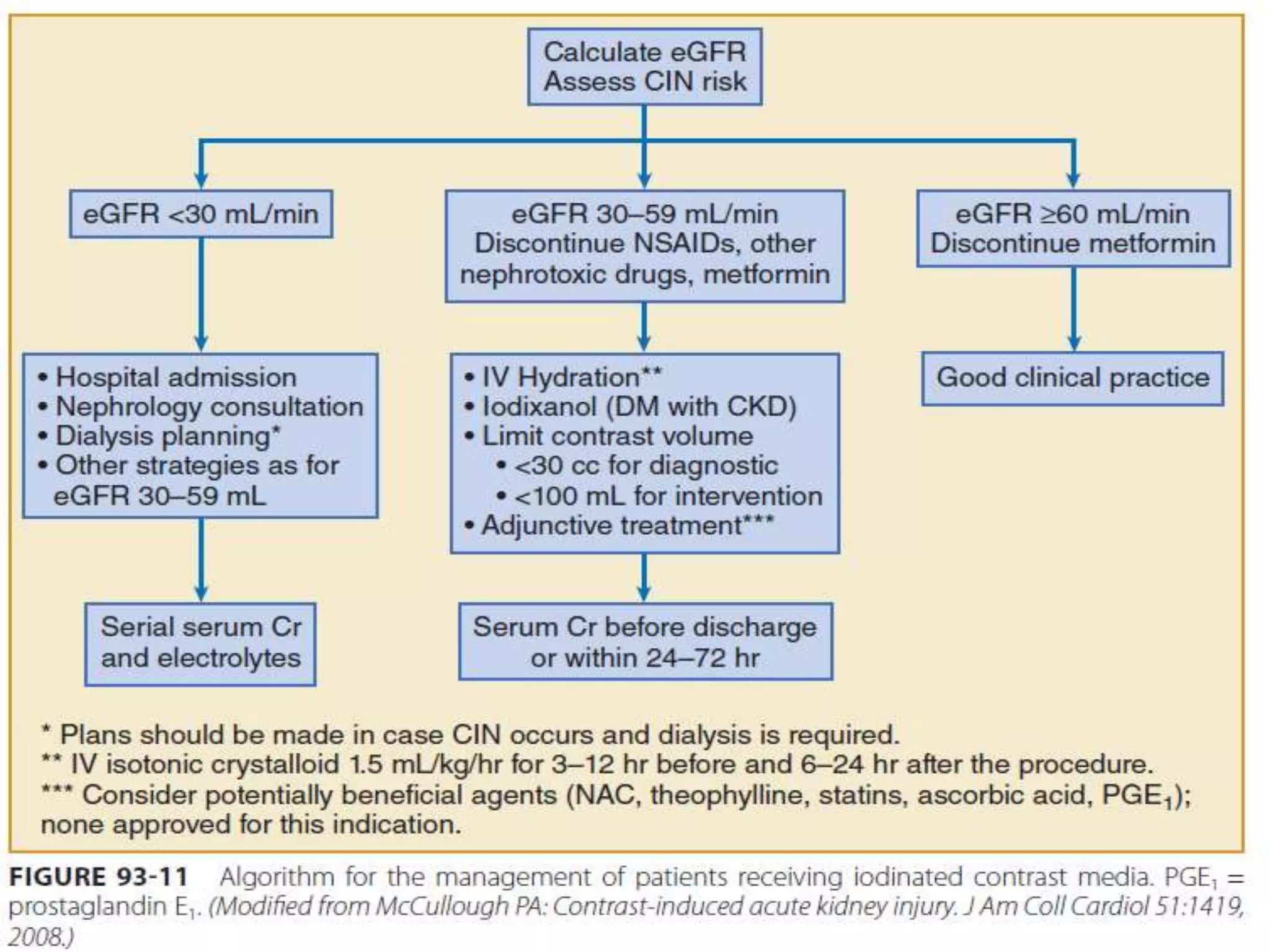
2. Prevention strategies aim to reduce the nephrotoxic effects of iodinated contrast media and are important since treatment options for CI-AKI are limited to supportive measures.
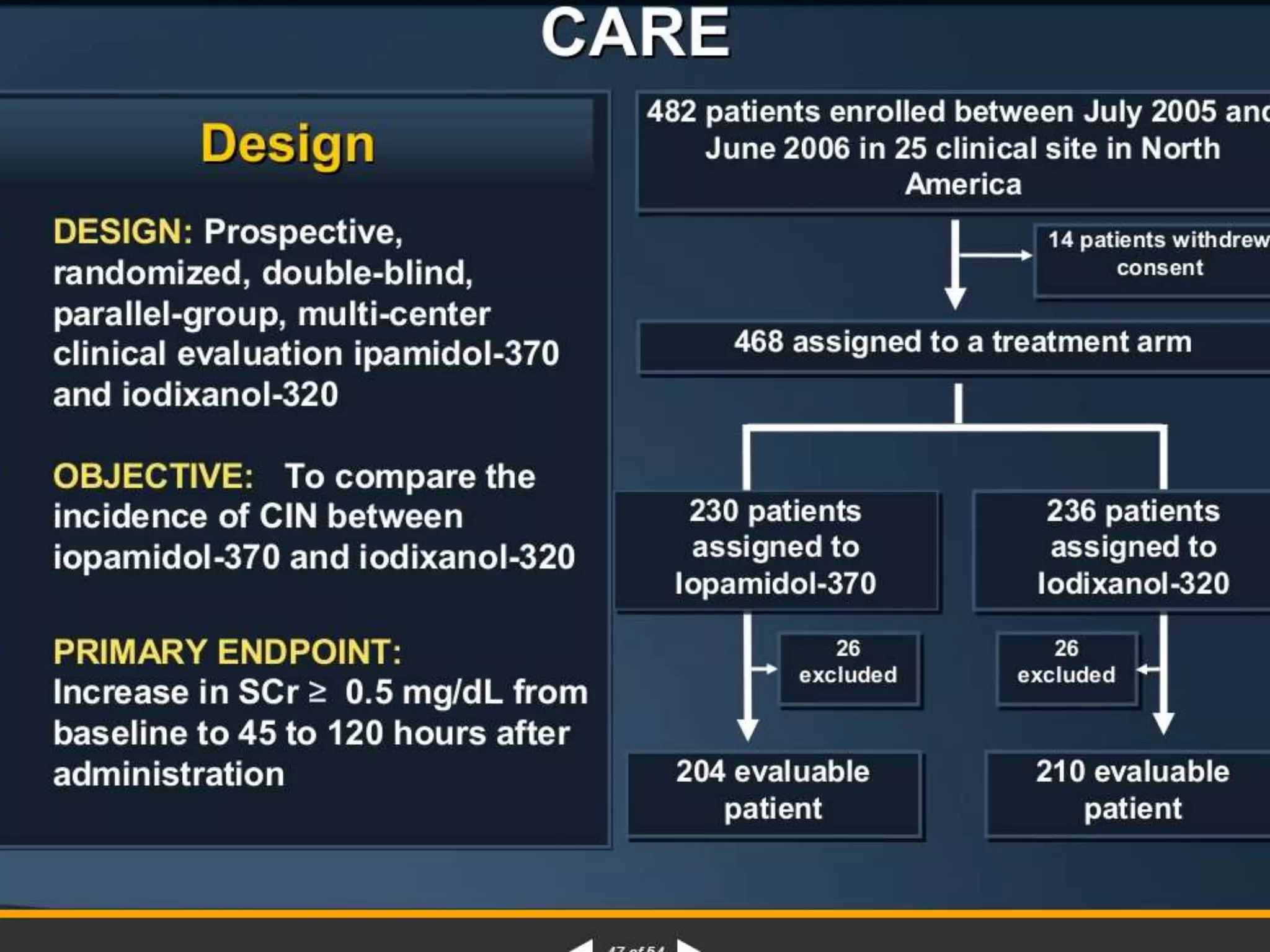
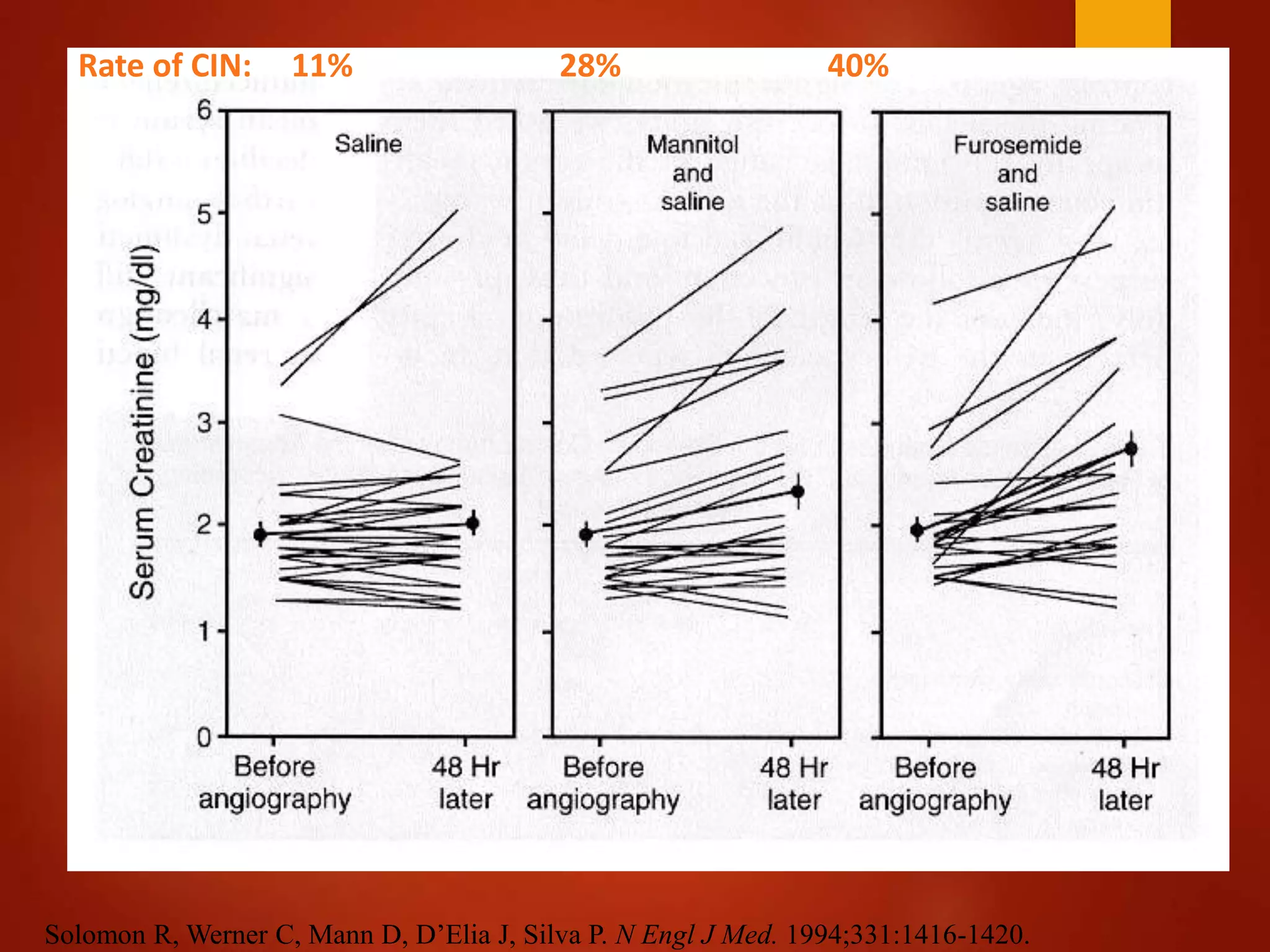
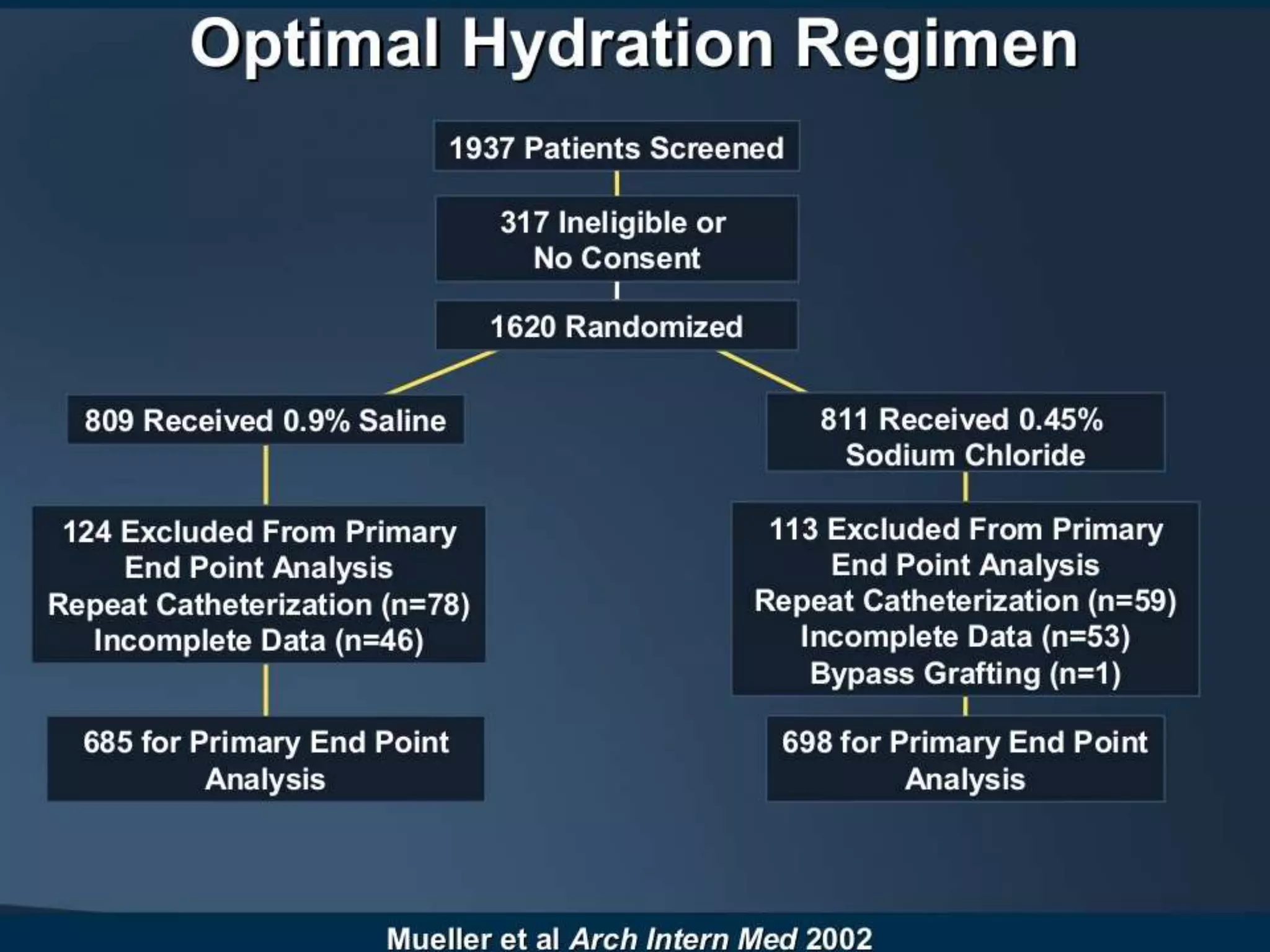
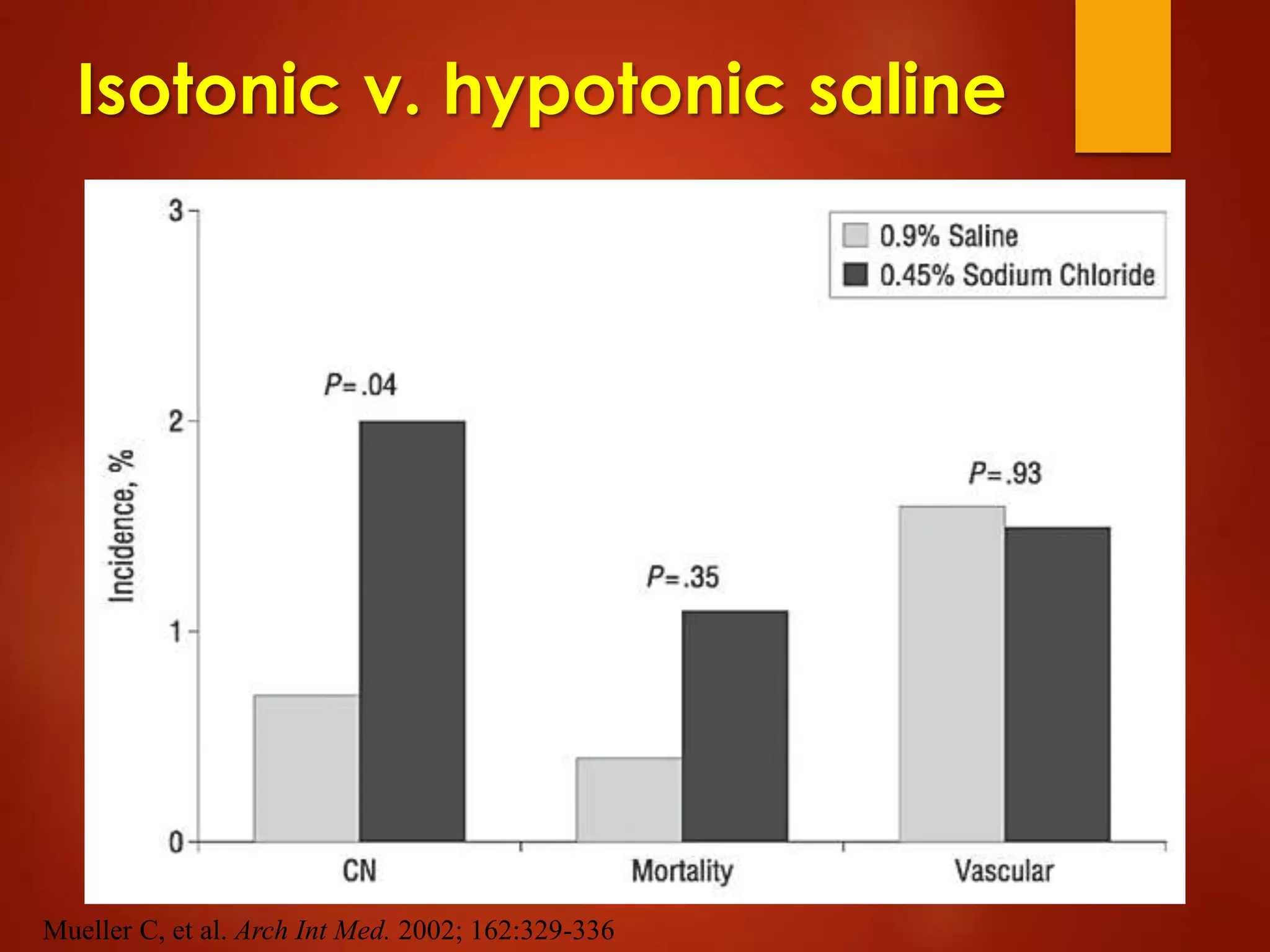
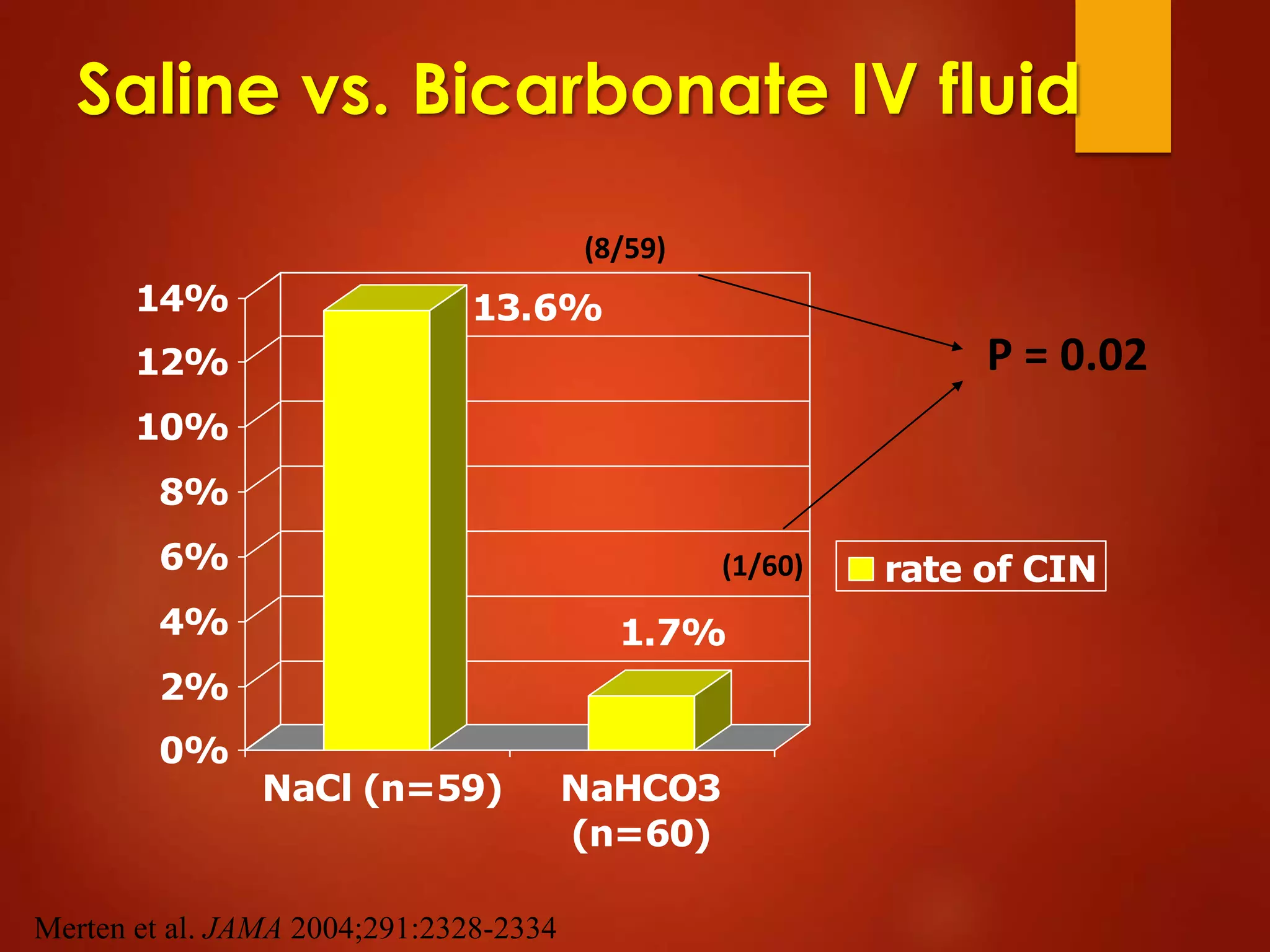
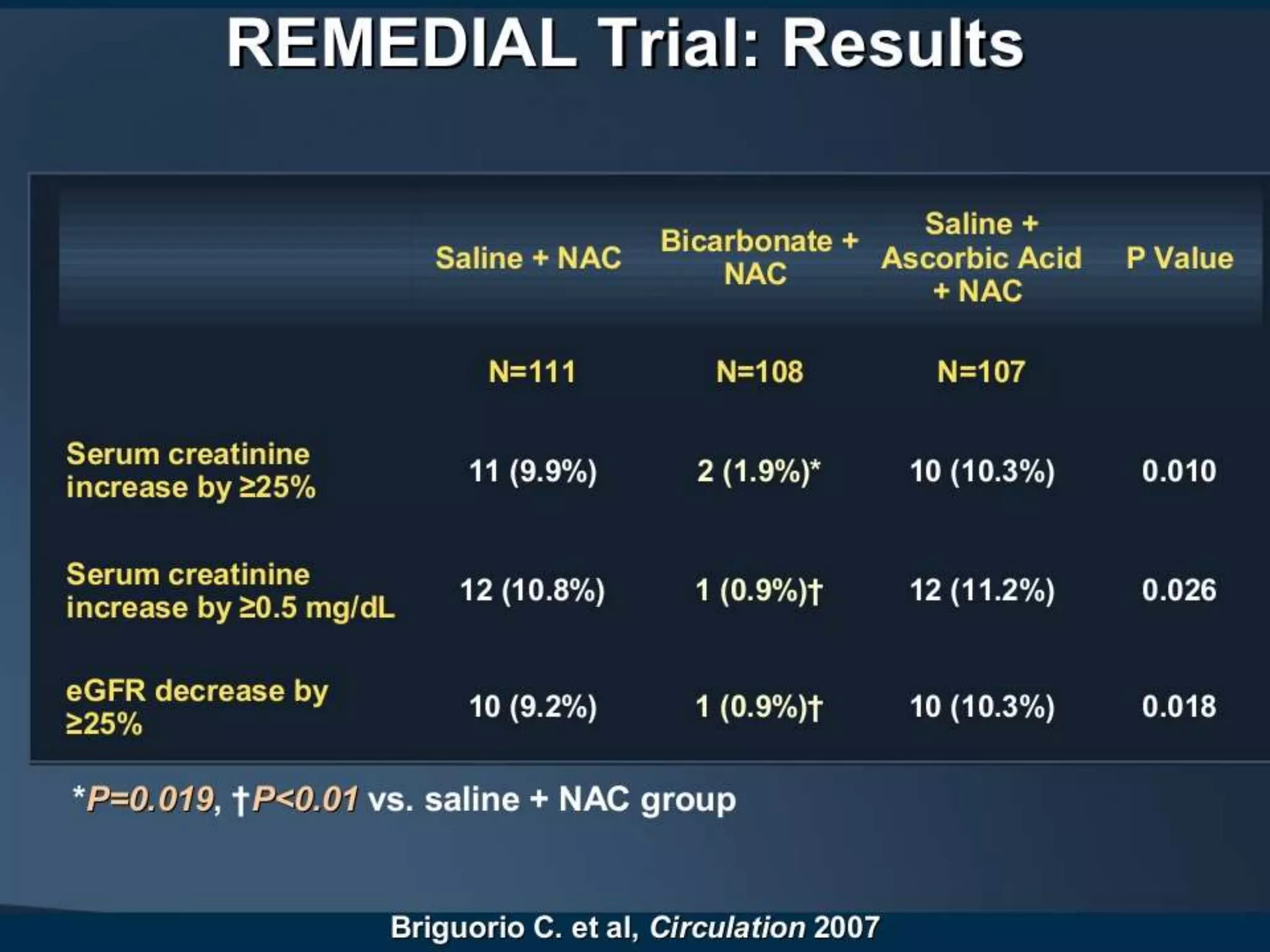
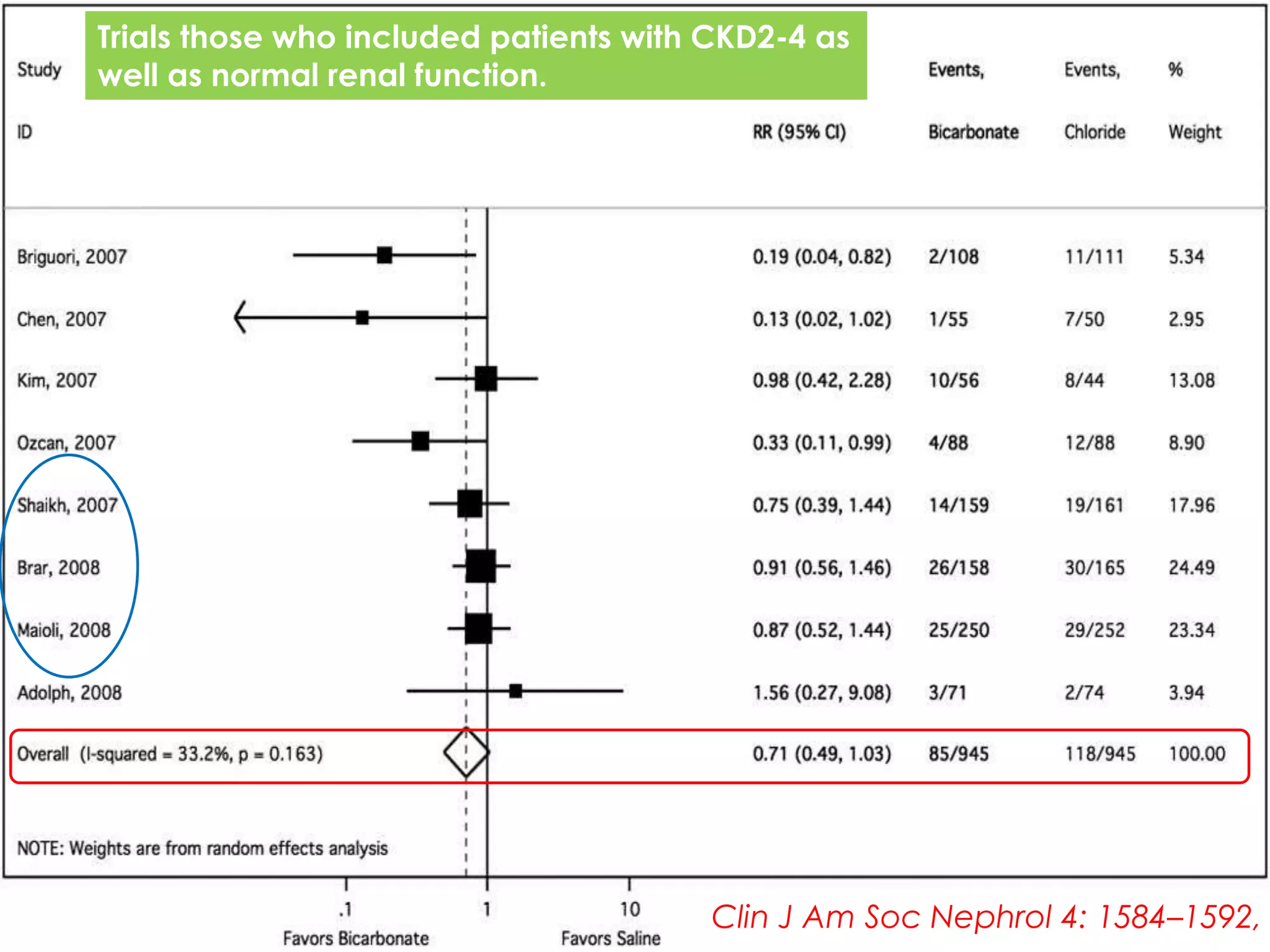
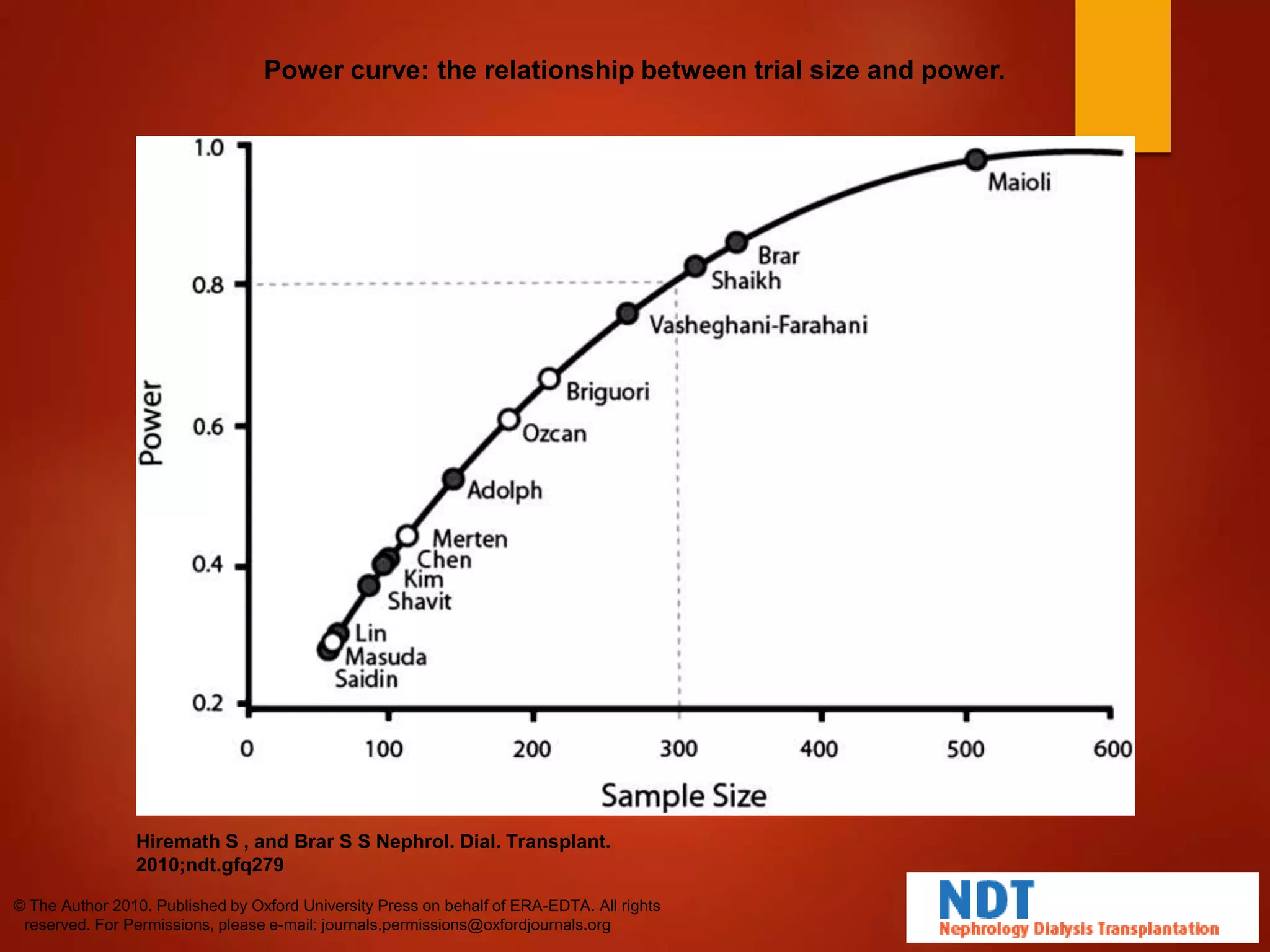
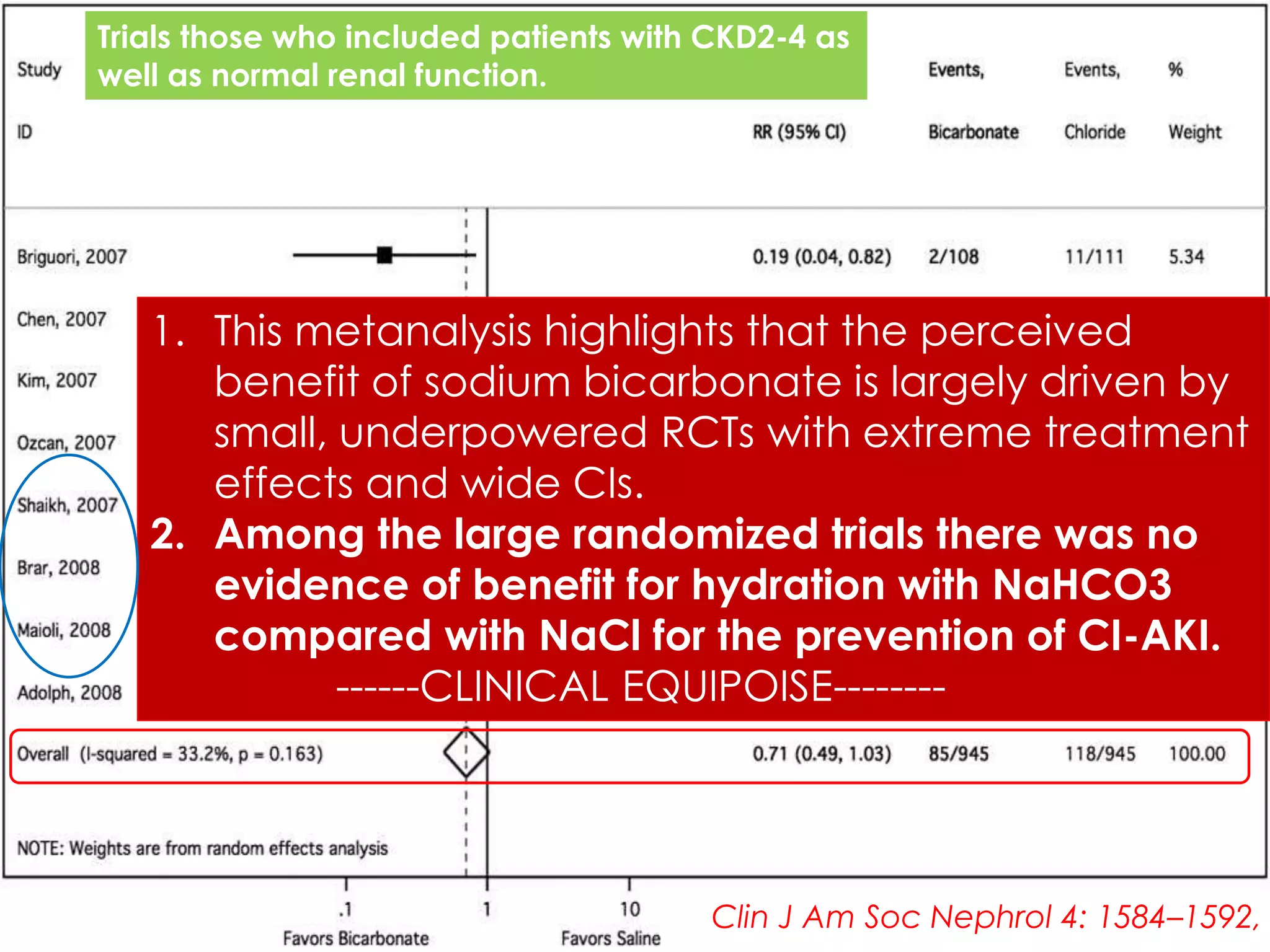
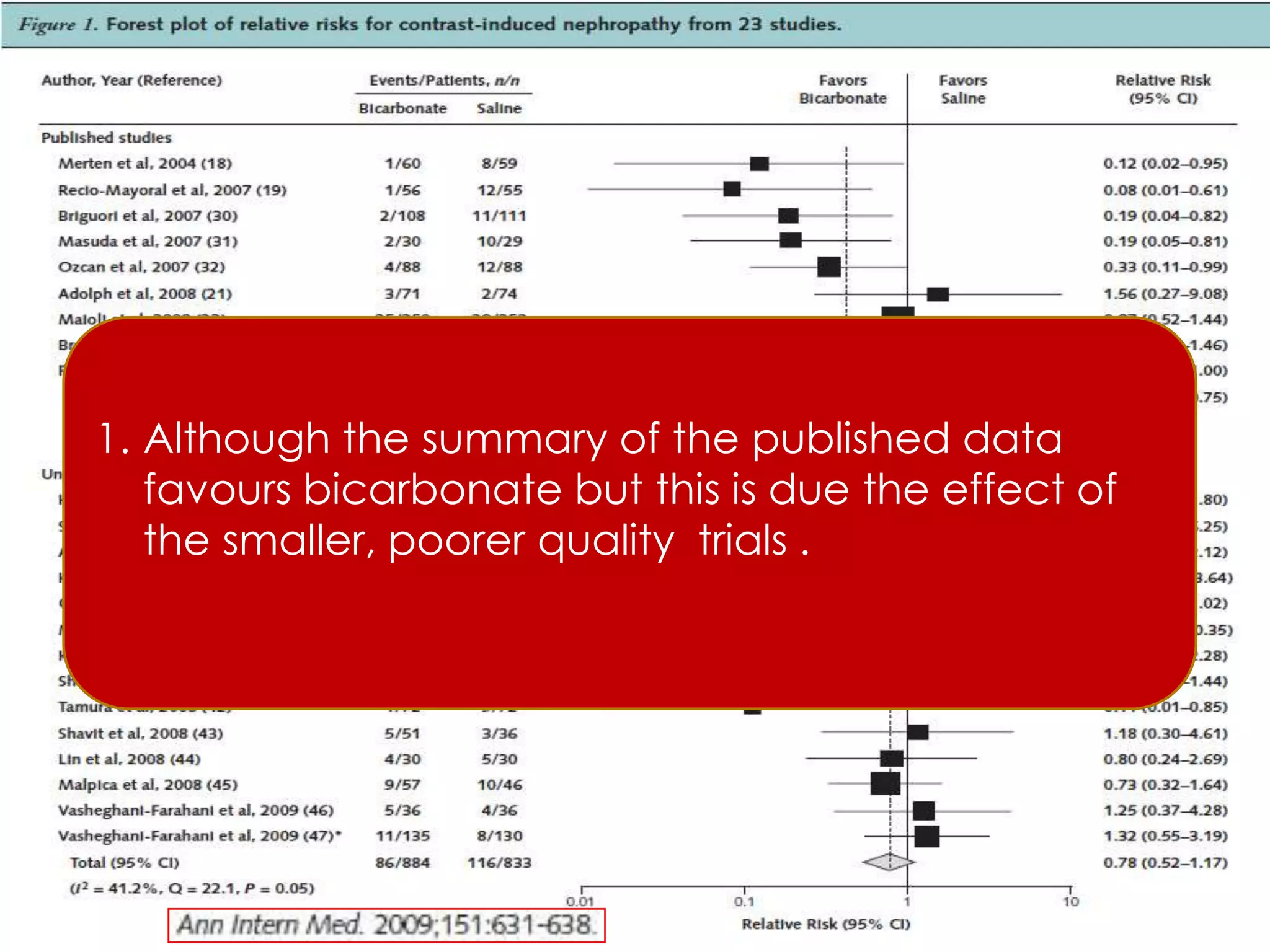
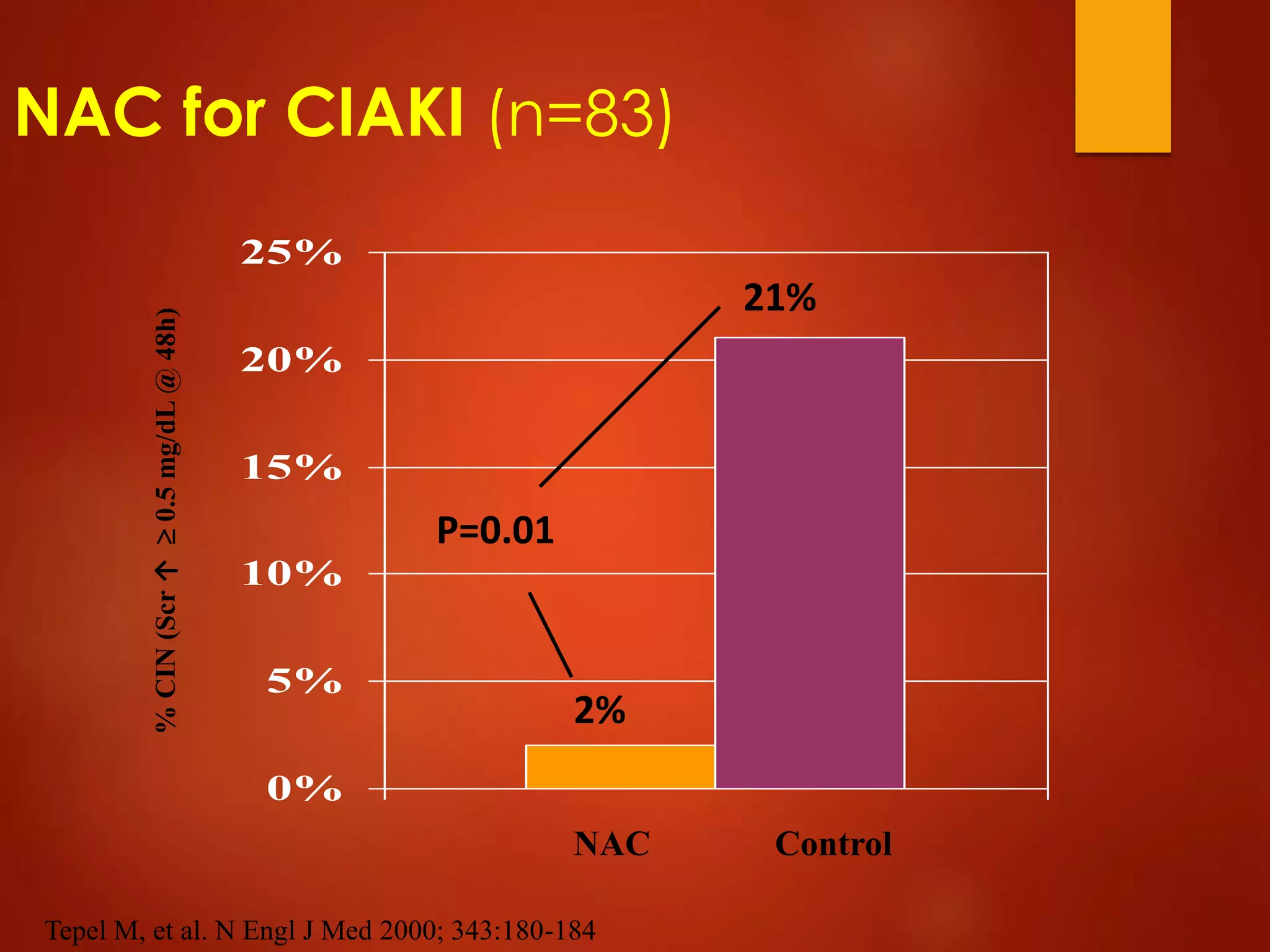
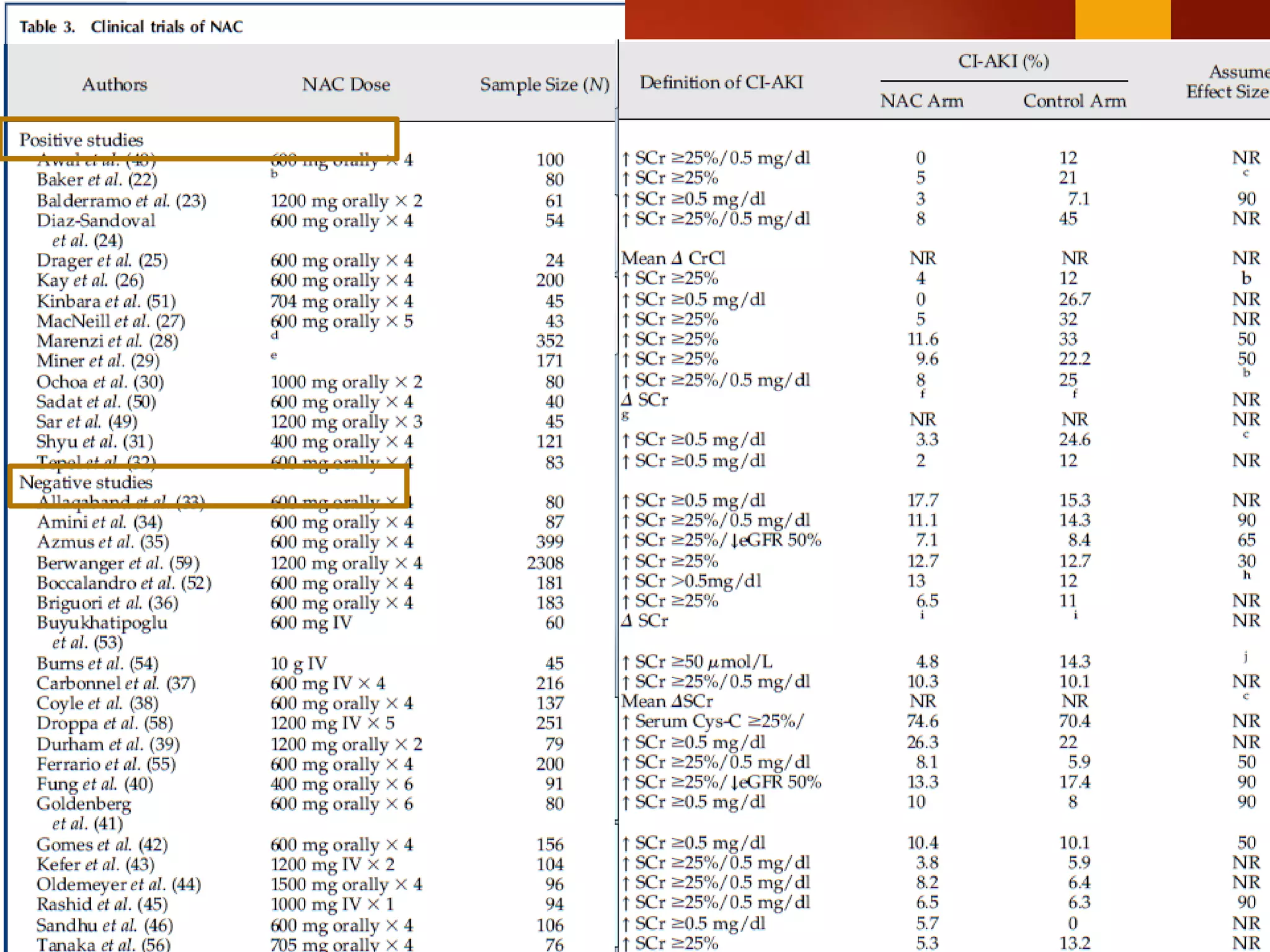
3. While hydration with intravenous fluids is the standard prevention method, evidence for the benefits of specific fluids or adjunctive therapies like N-acetylcysteine is unclear from randomized controlled trials. Larger and higher quality studies are still needed to determine the most effective prevention strategies.