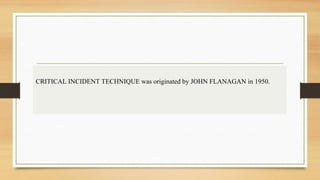
The Critical Incident Technique (CIT) is a method for analyzing specific events to identify effective or ineffective behaviors in human-system interactions, particularly in nursing performance. It involves steps such as determining incidents, fact-finding, identifying issues, and resolving them, while emphasizing the observation of actual behaviors. Although it offers flexibility and rich information, CIT has limitations, including reliance on memory and potential underreporting of incidents.