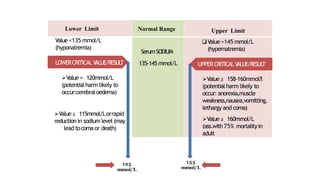
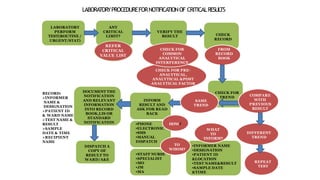
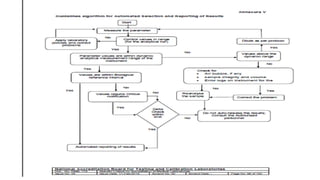
This document discusses critical laboratory values and the importance of communicating them to clinicians in a timely manner. It defines critical values as test results that are outside the normal range and may pose an immediate health risk or require prompt physician action. The document provides examples of critical values for various tests and outlines procedures for laboratories and wards to follow when critical values are identified, including verifying the result, informing the appropriate clinician immediately via phone, and documenting the communication. It emphasizes that properly defining, identifying and reporting critical values is important for patient safety and quality standards.