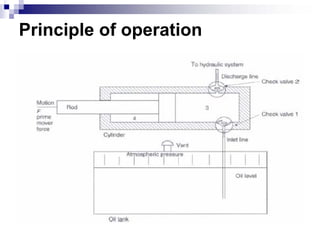
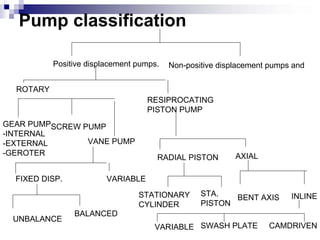
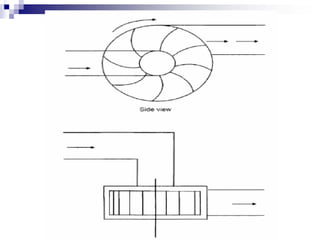
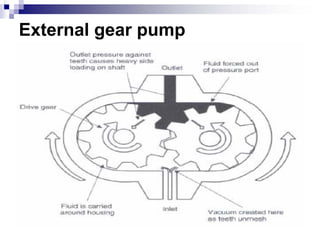
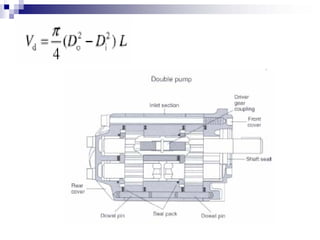
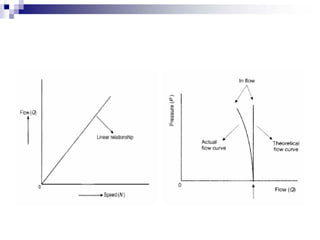
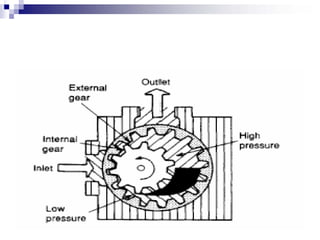
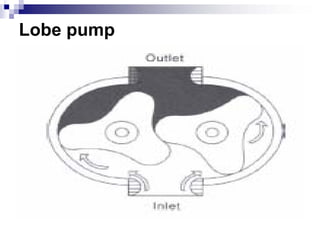
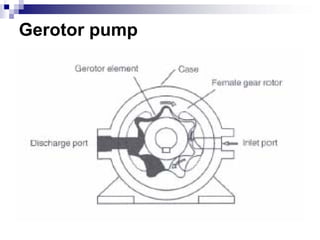
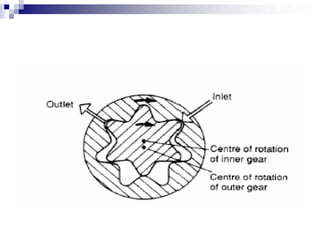
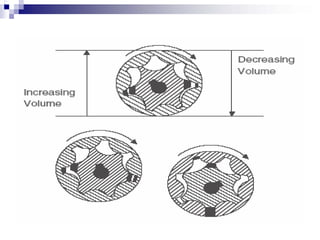
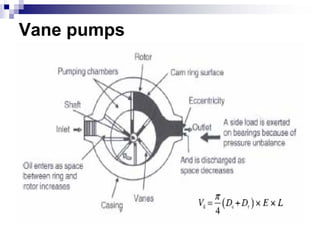
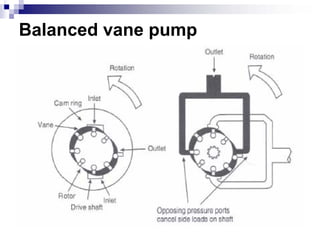
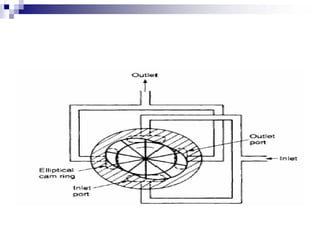
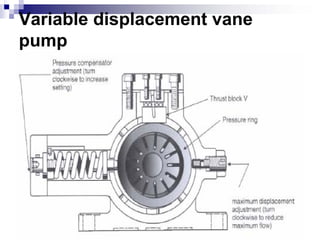
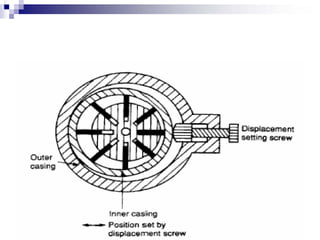
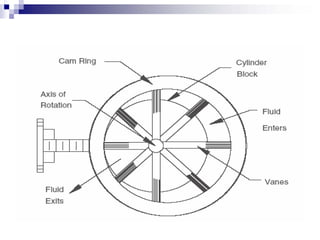
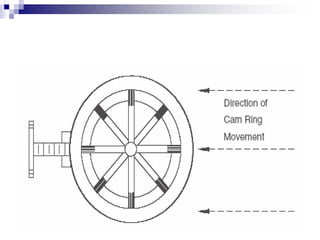
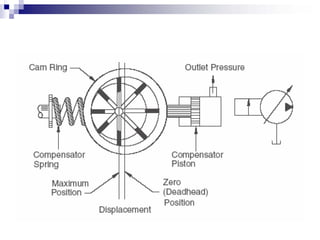
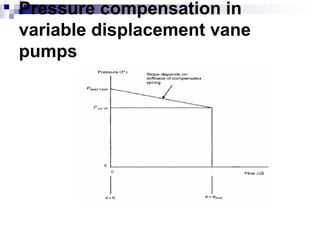
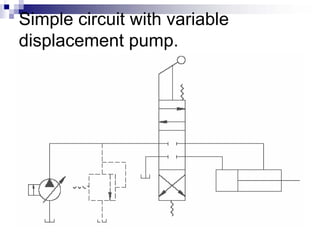
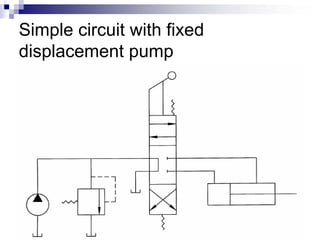
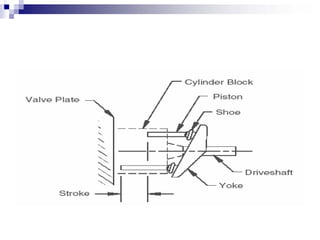
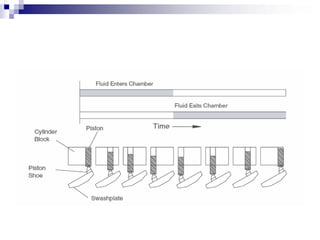
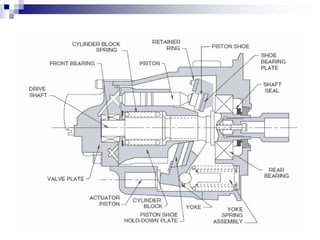
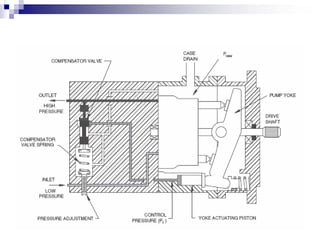
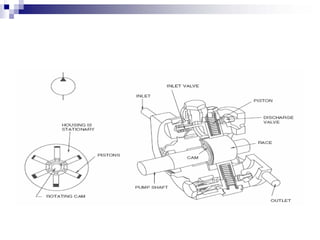
The document discusses different types of pumps used in fluid flow creation and hydraulics applications. It distinguishes between positive displacement pumps, which displace a fixed volume of fluid per revolution, and non-positive displacement pumps, which use fluid inertia to displace fluid. The document goes on to describe various positive displacement pump types including gear pumps, vane pumps, piston pumps, and how their principles of operation differ. It also covers classifications such as fixed vs variable displacement and pressure compensation in pumps.