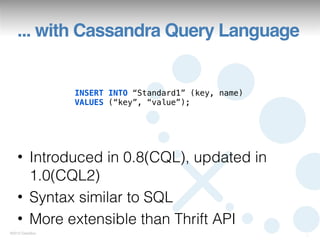
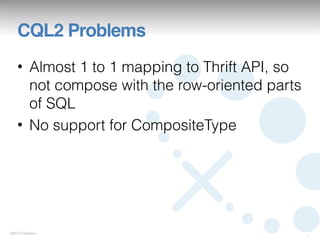
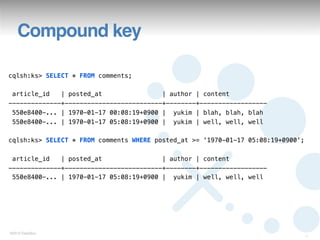
This document summarizes a presentation on Cassandra Query Language version 3 (CQL3). It outlines the motivations for CQL3, provides examples of defining schemas and querying data with CQL3, and notes new features like collection support. The document also reviews changes from earlier versions like improved definition of static and dynamic column families using composite keys.



![Cassandra Storage
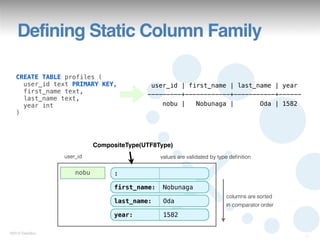
create column family profiles
with key_validation_class = UTF8Type
and comparator = UTF8Type
and column_metadata = [
{column_name: first_name, validation_class: UTF8Type},
{column_name: last_name, validation_class: UTF8Type},
{column_name: year, validation_class: IntegerType}
];
row key columns values are validated by validation_class
nobu first_name Nobunaga
columns are sorted
last_name Oda
in comparator order
year 1582
©2012 DataStax
4](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cct2012-121129201336-phpapp01/85/CQL3-in-depth-4-320.jpg)


















![Collection support
INSERT INTO example (id, tags, points, attributes)
VALUES (
‘62c36092-82a1-3a00-93d1-46196ee77204’,
{‘foo’, ‘bar’, ‘baz’}, // set
[100, 20, 93], // list
{‘abc’: ‘def’} // map
);
©2012 DataStax
27](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cct2012-121129201336-phpapp01/85/CQL3-in-depth-27-320.jpg)
![Collection support
• Set
UPDATE example SET tags = tags + {‘qux’} WHERE ...
UPDATE example SET tags = tags - {‘foo’} WHERE ...
• List
UPDATE example SET points = points + [20, 30] WHERE ...
UPDATE example SET points = points - [100] WHERE ...
• Map
UPDATE example SET attributes[‘ghi’] = ‘jkl’ WHERE ...
DELETE attributes[‘abc’] FROM example WHERE ...
©2012 DataStax
28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cct2012-121129201336-phpapp01/85/CQL3-in-depth-28-320.jpg)
![Collection support
SELECT tags, points, attributes FROM example;
tags | points | attributes
-----------------+---------------+--------------
{baz, foo, bar} | [100, 20, 93] | {abc: def}
• You cannot retrieve item in collection
individually
©2012 DataStax
29](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cct2012-121129201336-phpapp01/85/CQL3-in-depth-29-320.jpg)



