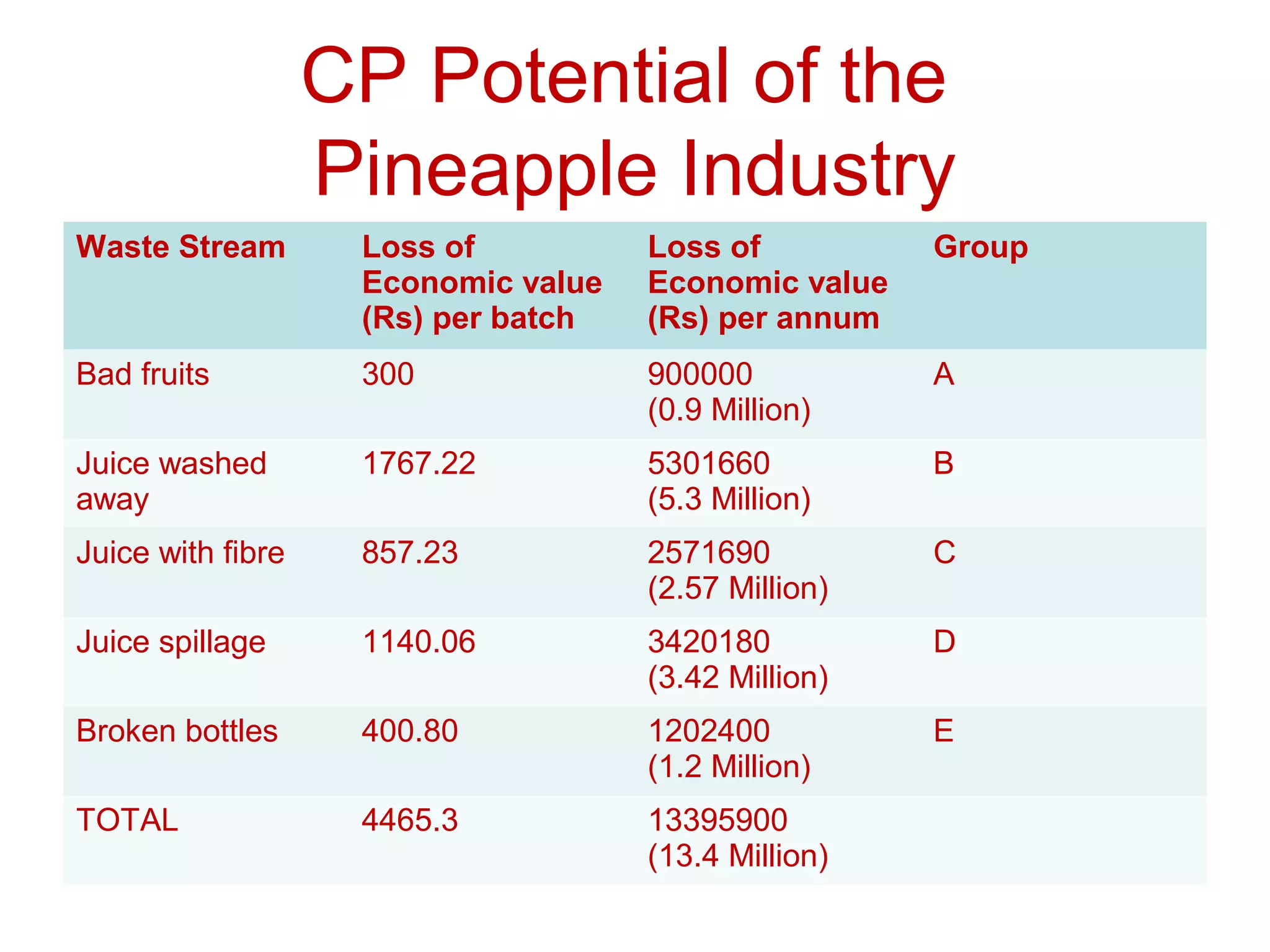
This document provides guidance on using brainstorming to generate cleaner production options. It explains that brainstorming is a technique where a group generates as many ideas as possible in a short period without criticism. Anyone can participate, and combining different perspectives leads to more innovative ideas. Brainstorming can help identify problems, solutions, plans, and ideas for change. The document outlines best practices for conducting a brainstorming session, such as explaining the objective, encouraging free flowing ideas without judgment, accumulating all ideas, and later clarifying and combining similar concepts. It also discusses barriers to creativity and provides an example of brainstorming to generate cleaner production options for reducing waste in the pineapple industry.