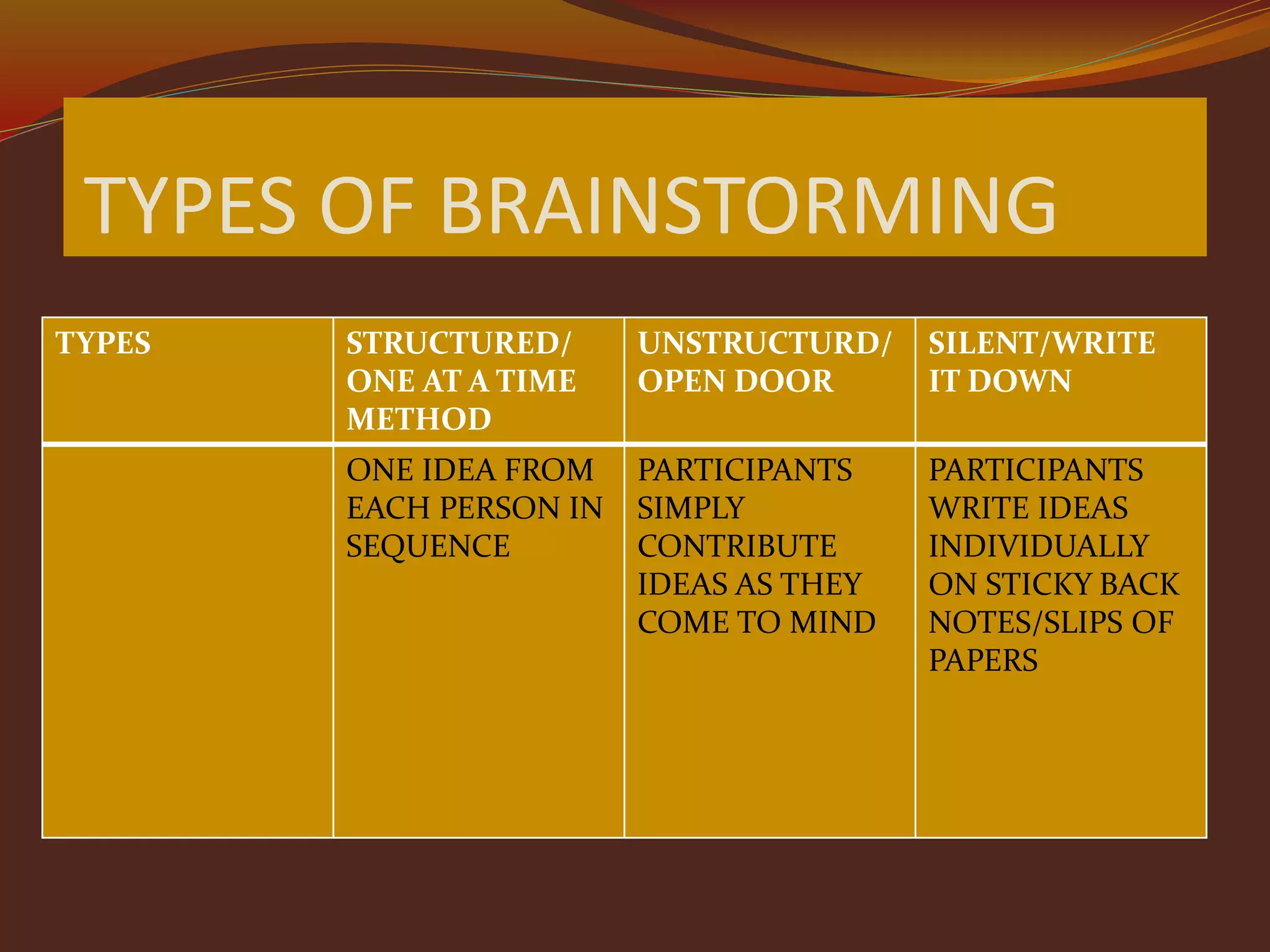
This document discusses the importance of brainstorming and provides guidance on effective brainstorming techniques. It begins by outlining the objectives of a brainstorming session which are to describe the importance, analyze forms, and use brainstorming effectively. Various brainstorming methods like structured, unstructured, and silent are described. Guidelines are provided such as focusing on quality ideas, withholding criticism, welcoming unusual ideas, and combining ideas. The document emphasizes that brainstorming allows for involvement and understanding through collaboration. Effective brainstorming requires focusing on a goal, sharing all ideas openly without judgement, building on others' contributions, and making the session relaxed and time-bound. Evaluation of the session and its impact is also recommended.