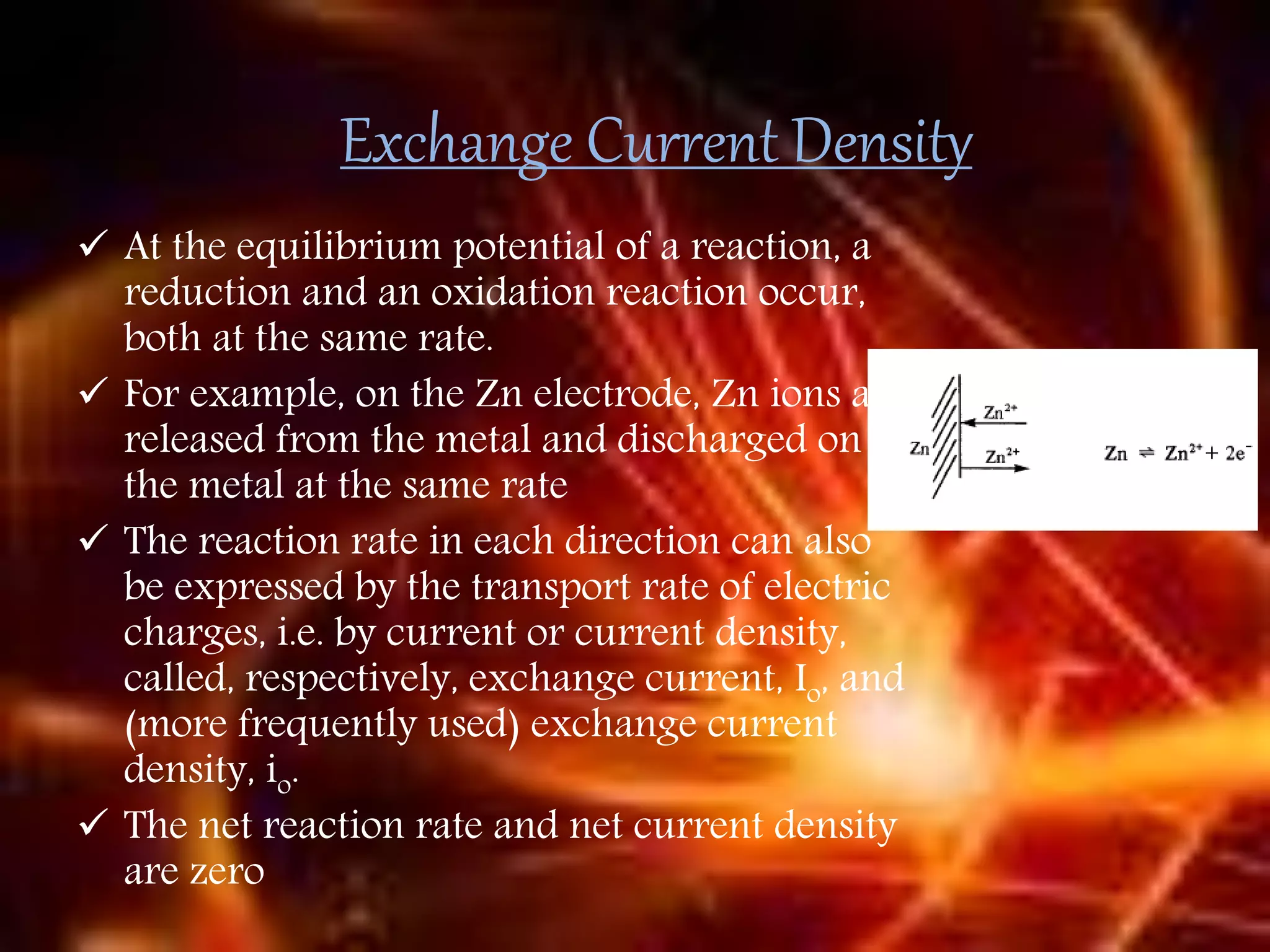
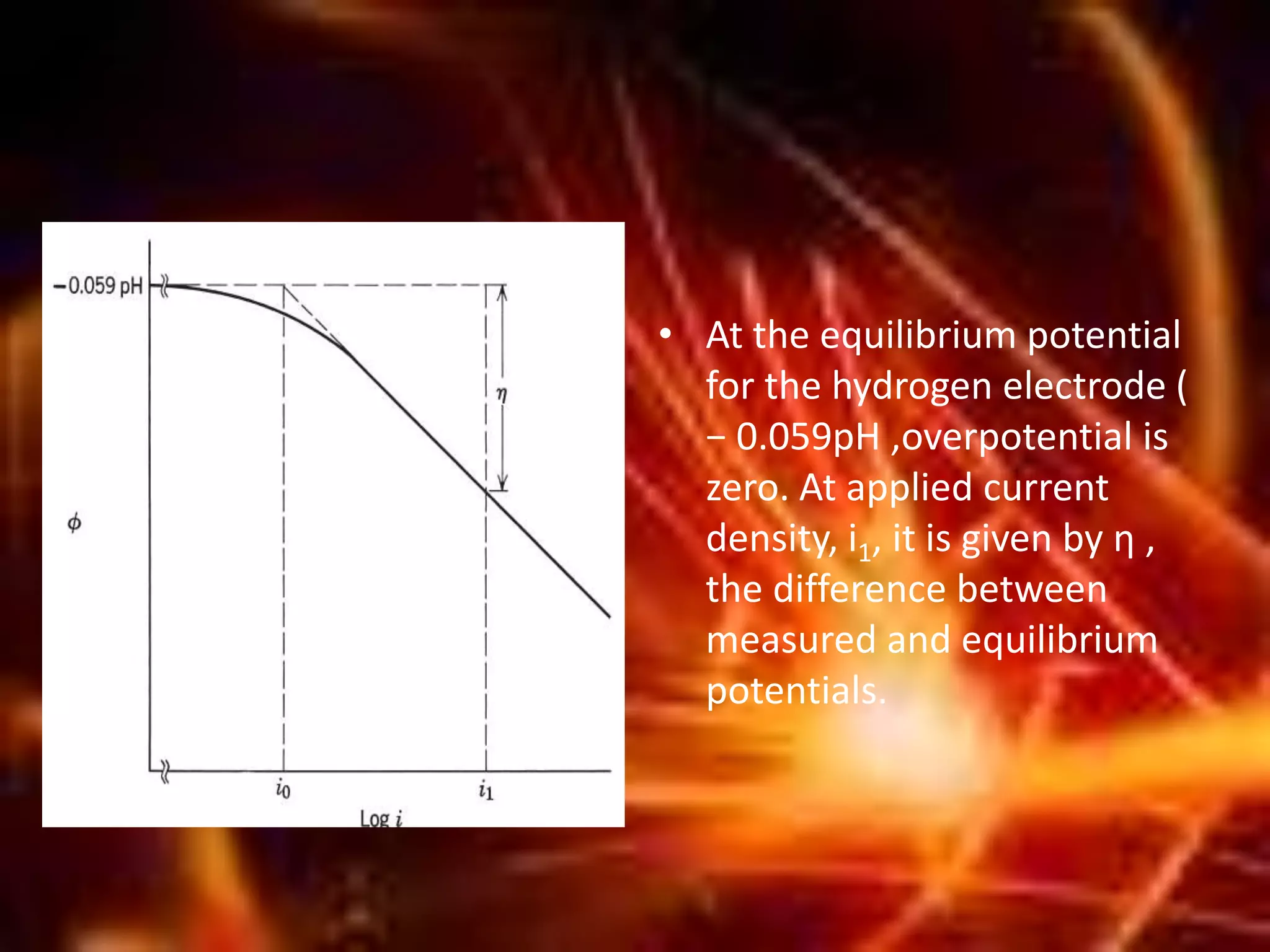
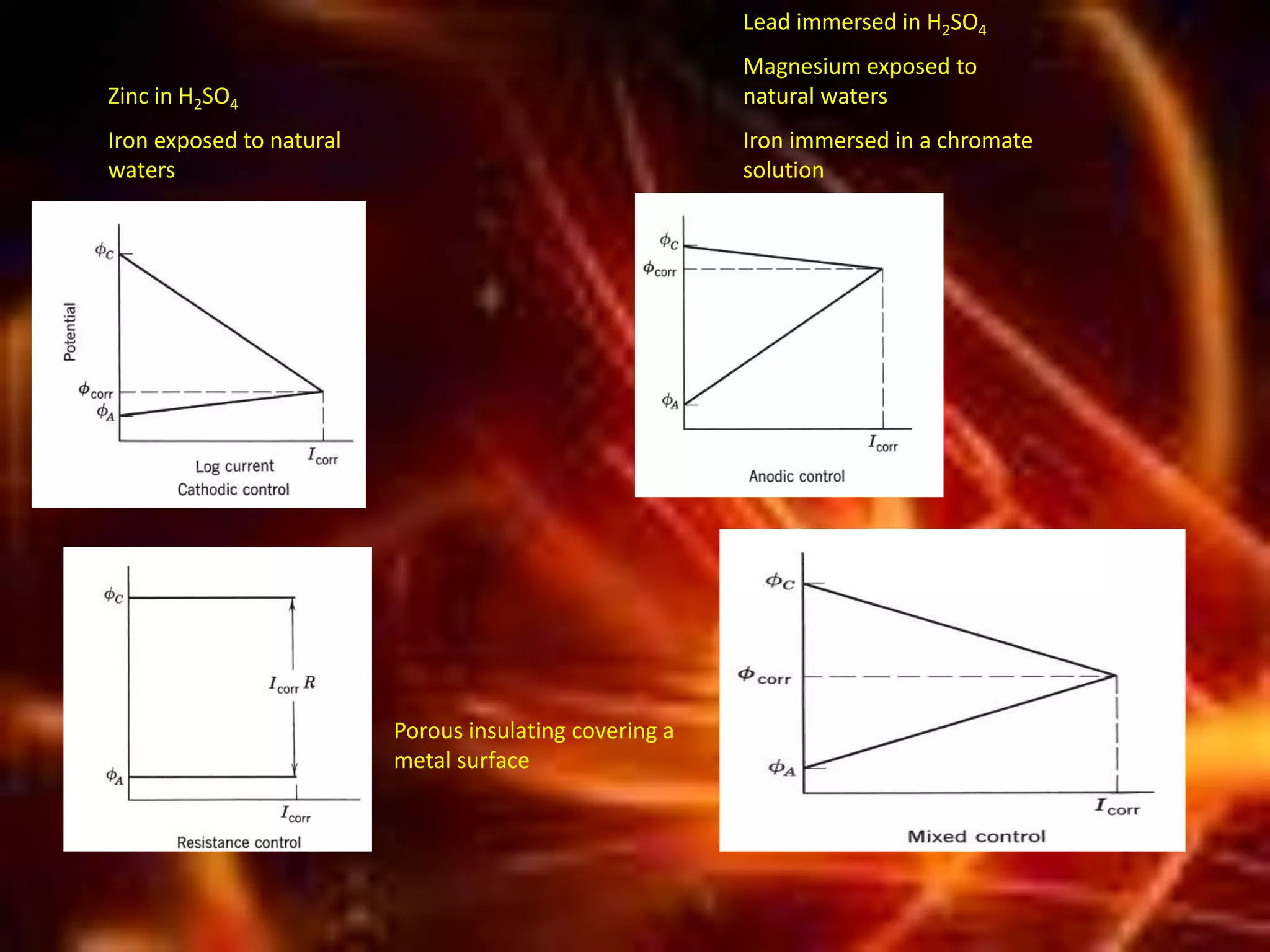
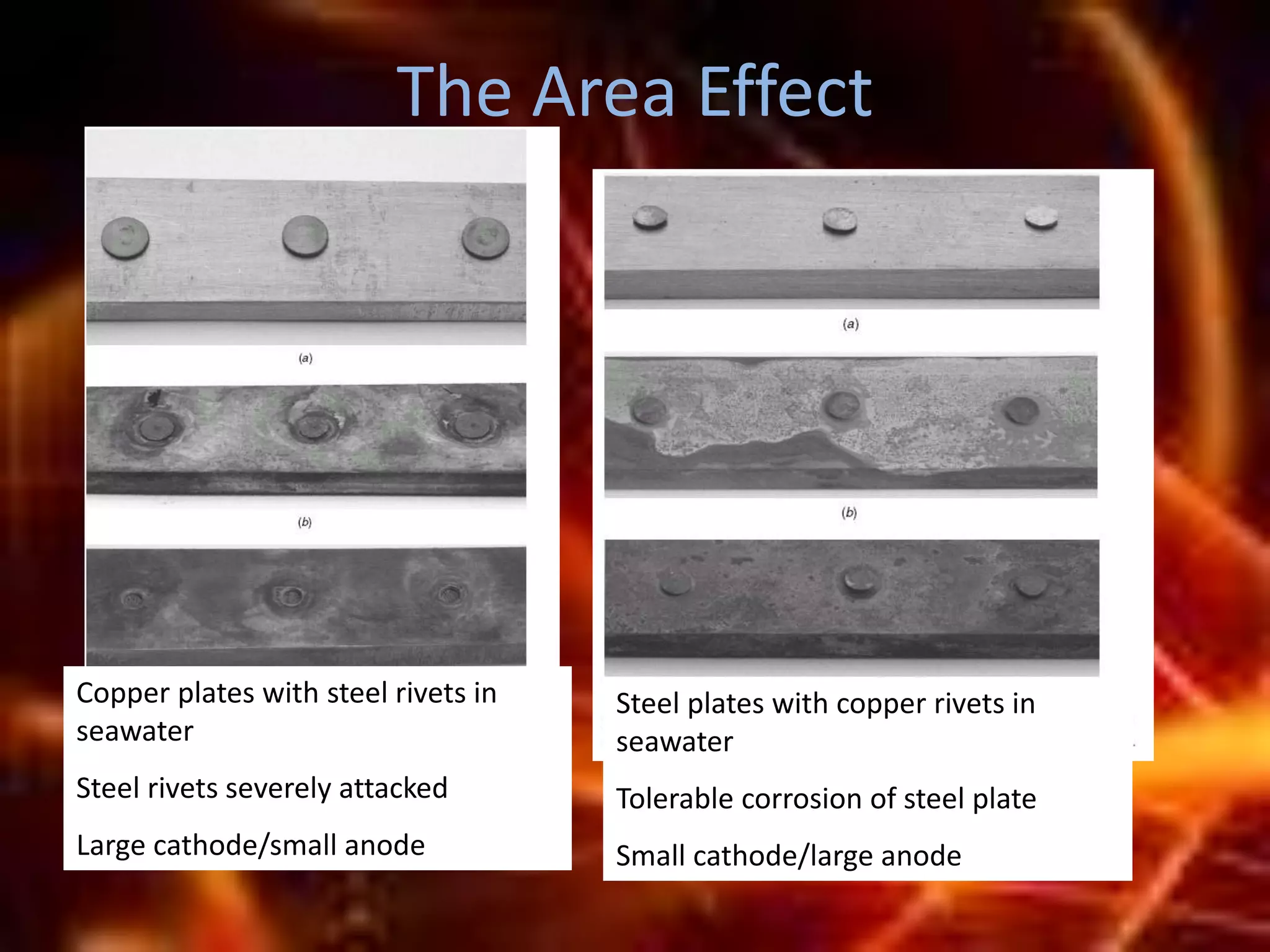
Corrosion is the destructive attack of a metal by chemical or electrochemical reaction with its environment. There are three main types of polarization that influence the corrosion rate - concentration polarization, activation polarization, and IR drop. Concentration polarization occurs when the rate of the electrochemical reaction is controlled by the mass transport of reactants or products. Activation polarization is caused by an energy barrier that must be overcome for the electrochemical reaction to proceed. IR drop is the potential drop across the electrolyte due to its resistance. The total polarization is the sum of the individual polarization contributions. Cathodic polarization generally decreases the corrosion rate while anodic polarization can either increase or decrease the corrosion rate depending on whether the metal is in an active or passive state.