The document discusses the dual functions of probation - investigation and supervision. It covers topics such as:
- The presentence investigation report and its important role in sentencing offenders
- Evidence-based supervision practices focusing on high-risk offenders and specialized programs
- Ensuring probation is effective in reducing recidivism through risk assessment, treatment referrals, and performance measures
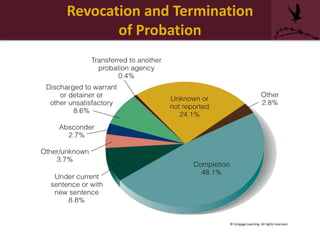
- The revocation process when offenders violate their probation conditions